Guide to Triac Dimmers
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for triac dimmers
- Understanding triac dimmers Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of triac dimmers
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for triac dimmers
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for triac dimmers
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for triac dimmers Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential triac dimmers Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for triac dimmers
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the triac dimmers Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of triac dimmers
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for triac dimmers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for triac dimmers
In today’s rapidly evolving energy landscape, triac dimmers stand out as pivotal components in optimizing lighting systems across diverse industries. Their ability to precisely control electrical power not only enhances user comfort but significantly drives energy efficiency — a priority for businesses aiming to reduce operational costs and environmental impact. For B2B buyers operating in dynamic markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of triac dimmer technology is essential to secure competitive advantages and fulfill regional compliance requirements.
This comprehensive guide delves deeply into the multifaceted world of triac dimmers, covering critical areas including types and variations, material composition, manufacturing and quality control standards, and thorough supplier evaluations. Buyers will uncover key insights into global pricing trends and performance metrics, enabling them to tailor procurement strategies that align with both budget constraints and technical specifications.
Additionally, the guide addresses common challenges and frequently asked questions, equipping buyers with clarity to avoid costly mistakes and ensure compatibility with existing lighting infrastructures. Whether sourcing for hospitality projects in Saudi Arabia, industrial applications in Argentina, or smart commercial developments in Europe, this resource empowers decision-makers to identify reliable suppliers and foster strategic partnerships.
By leveraging this expert knowledge, international B2B buyers can confidently navigate the global triac dimmer market, securing high-quality products that meet evolving energy standards and market demands — ultimately driving sustainable growth and operational excellence.
Understanding triac dimmers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leading Edge Dimmer | Controls the leading edge of the AC waveform | Residential and commercial lighting | Pros: Cost-effective, compatible with incandescent/halogen bulbs. Cons: May cause flickering with some LED lights. |
| Trailing Edge Dimmer | Controls the trailing edge of the AC waveform | High-end residential, hospitality | Pros: Smooth dimming, ideal for LEDs and low-voltage lighting. Cons: Higher cost, more complex circuitry. |
| Universal Dimmer | Supports both leading and trailing edge control | Versatile across various lighting types | Pros: Flexible compatibility. Cons: Installation complexity can increase labor costs. |
| Smart Dimmer Switch | Integrates with smart home/automation systems | Modern commercial and residential | Pros: Remote control, energy monitoring. Cons: Requires Wi-Fi, higher initial investment. |
| Rheostat Dimmer | Uses variable resistors to adjust brightness | Specialty/theatre lighting | Pros: Precise control, simple design. Cons: Inefficient, generates heat, limited modern application. |
Leading Edge Dimmer
Leading edge dimmers operate by cutting the front portion of the AC sine wave, making them compatible primarily with incandescent and halogen lamps. Their affordability and widespread availability make them attractive for large-scale residential and commercial projects, especially in regions with established traditional lighting infrastructure. However, buyers targeting LED integration should proceed cautiously, as these dimmers can cause flickering or noise with certain LED drivers. For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East, where cost-efficiency and compatibility with existing lighting are priorities, leading edge dimmers remain a practical choice.
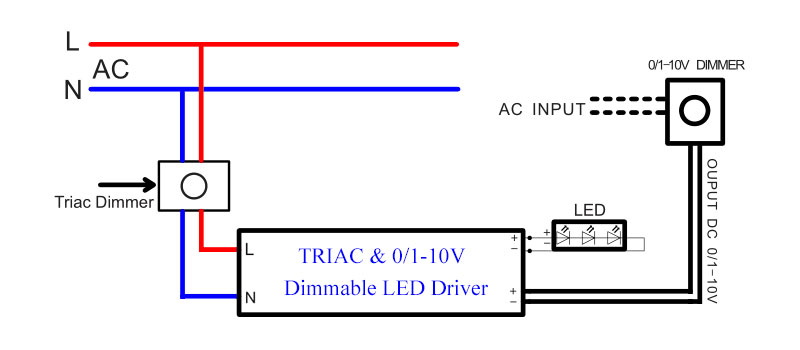
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Trailing Edge Dimmer
Trailing edge dimmers regulate the latter part of the AC waveform, offering smoother dimming and better compatibility with LED and low-voltage lighting systems. This makes them highly suitable for premium hospitality venues, upscale residential developments, and energy-conscious commercial environments in Europe and the Middle East. While trailing edge dimmers come at a higher cost, their ability to reduce flicker and extend LED lifespan provides long-term value. Buyers should consider the total cost of ownership and ensure supplier quality certifications to avoid substandard units that could compromise performance.
Universal Dimmer
Universal dimmers combine the capabilities of leading and trailing edge control, enabling compatibility with a broad spectrum of lighting technologies. This versatility is ideal for distributors and integrators serving mixed lighting portfolios or evolving markets where lighting upgrades are incremental. However, the increased complexity of universal dimmers can lead to more challenging installations and higher labor expenses. B2B buyers should evaluate supplier support services and technical documentation carefully to ensure smooth deployment, especially in regions with limited technical expertise.
Smart Dimmer Switch
Smart dimmers represent the forefront of lighting control, integrating with IoT and building management systems to enable remote operation, scheduling, and energy monitoring. These features are increasingly demanded in modern commercial buildings and luxury residential projects across Europe and the Middle East. Despite their higher upfront cost and reliance on stable internet connectivity, smart dimmers offer significant operational efficiencies and data insights that support sustainability goals. Buyers should prioritize suppliers offering robust cybersecurity measures and compatibility with popular smart home platforms.
Rheostat Dimmer
Rheostat dimmers use a simple resistor-based mechanism to control brightness, favored in niche applications such as theatre and specialty lighting where precise manual control is essential. Although their design simplicity facilitates maintenance and customization, they are inefficient and generate excessive heat, making them unsuitable for mainstream commercial or residential use. For B2B buyers in specialized markets, rheostat dimmers remain relevant but should be sourced with attention to heat dissipation and safety standards to ensure compliance with local regulations.
Related Video: Large Language Models (LLMs) – Everything You NEED To Know
Key Industrial Applications of triac dimmers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of triac dimmers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hospitality | Adjustable lighting control in hotels and restaurants | Enhanced guest experience, energy savings, ambiance control | Compatibility with existing lighting, dimming smoothness, reliability under frequent use |
| Commercial Offices | Dynamic lighting systems for workspaces | Improved employee productivity, energy efficiency | Integration with smart building systems, flicker-free dimming, compliance with regional standards |
| Manufacturing | Machine area and assembly line lighting control | Precise lighting adjustment, reduced energy costs | Robustness in harsh environments, compatibility with LED and halogen lamps, surge protection |
| Retail | Showcase and display lighting | Enhanced product presentation, flexible lighting moods | Wide dimming range, minimal heat generation, ease of installation and maintenance |
| Residential Developments | Smart dimming for home lighting systems | Energy efficiency, user comfort, smart home integration | Support for smart controls, compatibility with diverse bulb types, adherence to local electrical codes |
Hospitality Industry
In hotels and restaurants, triac dimmers enable precise adjustment of lighting levels to create the desired ambiance, which significantly enhances the guest experience. These dimmers help reduce energy consumption by allowing lighting to be lowered during off-peak hours without compromising comfort. For international buyers, especially in regions like the Middle East and Europe, sourcing triac dimmers that seamlessly integrate with prevalent lighting technologies (e.g., halogen and dimmable LEDs) and withstand frequent switching cycles is critical. Ensuring compatibility with existing electrical infrastructure and securing devices with smooth dimming capabilities can prevent flickering and improve overall reliability.
Commercial Offices
Modern commercial office environments increasingly rely on dynamic lighting solutions to boost employee productivity and reduce operational costs. Triac dimmers facilitate smooth, flicker-free dimming that adapts to natural light availability and occupancy patterns. For B2B buyers in Africa and South America, where energy efficiency is a growing priority, selecting dimmers that support integration with smart building management systems is essential. Additionally, compliance with regional electrical safety standards and the ability to handle mixed lighting loads (LEDs and traditional bulbs) are important factors to ensure long-term performance and user satisfaction.
Manufacturing Sector
In manufacturing plants and assembly lines, triac dimmers are used to control task-specific lighting, enhancing visibility and precision while reducing energy consumption during non-peak production times. Buyers from industrial hubs in Europe and the Middle East should prioritize dimmers that offer robustness against electrical noise, surges, and harsh environmental conditions typical of factories. Compatibility with various lamp types, including LED and halogen, and features like surge protection are crucial to avoid downtime and costly maintenance. Selecting dimmers designed for industrial applications ensures durability and consistent performance under demanding conditions.
Retail Industry
Retail environments benefit from triac dimmers by enabling adjustable showcase and display lighting that highlights products effectively while creating inviting shopping atmospheres. International buyers, particularly from South America and Europe, should focus on dimmers with a wide dimming range and minimal heat generation to protect sensitive merchandise and maintain customer comfort. Ease of installation and maintenance is also a key consideration, as retail spaces often require frequent lighting adjustments for seasonal displays. Sourcing dimmers that support smooth transitions without flicker enhances the visual appeal and operational flexibility.
Residential Developments
In residential construction and smart home projects, triac dimmers provide users with intuitive control over lighting intensity, contributing to energy savings and personalized comfort. For B2B buyers in Africa and the Middle East, where smart home adoption is accelerating, selecting dimmers compatible with a variety of bulb types and smart control systems is vital. Ensuring compliance with local electrical codes and offering products that support remote control and automation features can differentiate suppliers in these markets. Buyers should also evaluate the ease of installation and user-friendly interfaces to meet the expectations of modern homeowners.
Related Video: Lamp Dimmer using DIAC & TRIAC
Strategic Material Selection Guide for triac dimmers
When selecting materials for triac dimmers, B2B buyers must consider the performance requirements, environmental conditions, and manufacturing constraints that influence product reliability and cost-effectiveness. The choice of materials impacts the dimmer’s thermal management, electrical insulation, mechanical durability, and compliance with international standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in triac dimmer components, focusing on their properties, advantages, limitations, and regional considerations relevant to buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Thermoplastic Polymers (e.g., Polycarbonate, ABS)
Key Properties:
Thermoplastics like polycarbonate and ABS offer excellent electrical insulation, good mechanical strength, and resistance to moderate heat (typically up to 120°C). They are lightweight and exhibit good impact resistance, making them suitable for dimmer housings and switch covers.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Cost-effective, easy to mold into complex shapes, good electrical insulation, and available in flame-retardant grades.
– Cons: Limited temperature resistance compared to some engineered plastics; prolonged exposure to UV or harsh chemicals can degrade material properties.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for residential and commercial triac dimmers where moderate heat dissipation is sufficient. Not recommended for high-power dimmers exposed to elevated temperatures or harsh industrial environments.
Regional Considerations:
Buyers from regions with hot climates (e.g., Saudi Arabia, parts of Africa) should verify UV resistance and flame retardancy certifications (UL94 V-0 or equivalent). Compliance with European RoHS and REACH standards is crucial for buyers in Europe, while ASTM D635 and ISO 1210 standards are relevant for South American markets like Argentina.
2. Ceramic Substrates
Key Properties:
Ceramics provide excellent thermal stability, electrical insulation, and resistance to high temperatures (often exceeding 300°C). They are chemically inert and highly resistant to corrosion and wear.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Superior heat dissipation, stable dielectric properties, and long service life under demanding conditions.
– Cons: Brittle and prone to cracking under mechanical stress; higher manufacturing complexity and cost.
Impact on Application:
Ceramic substrates are preferred in high-end triac dimmers used in industrial or hospitality sectors where reliability under thermal stress is critical. They ensure stable operation with LED and low-voltage lighting loads that generate heat.
Regional Considerations:
European buyers often require compliance with DIN EN standards for ceramics, while Middle Eastern buyers prioritize materials that withstand high ambient temperatures and dust exposure. South American importers should check for compliance with ABNT NBR standards.
3. Metals (e.g., Aluminum Alloys)
Key Properties:
Aluminum alloys are lightweight metals with excellent thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. They provide mechanical strength and aid in heat dissipation from triac dimmer circuits.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Efficient heat dissipation, durable, corrosion-resistant especially when anodized, and recyclable.
– Cons: Higher cost than plastics; requires precise machining or casting; electrical insulation must be ensured via coatings or barriers.
Impact on Application:
Used primarily for heat sinks and structural components in triac dimmers designed for commercial and industrial applications. Aluminum helps maintain device longevity in environments with fluctuating temperatures.
Regional Considerations:
Buyers in coastal or humid regions (e.g., parts of South America and Africa) should specify corrosion-resistant aluminum grades and surface treatments. Compliance with ASTM B209 and EN 573 standards is common in Europe and Middle East markets.
4. Silicone Rubber
Key Properties:
Silicone rubber offers excellent thermal stability (operating temperatures from -60°C to 250°C), flexibility, and electrical insulation. It is also resistant to moisture, UV radiation, and many chemicals.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Ideal for sealing, gaskets, and flexible insulation components; maintains elasticity over wide temperature ranges.
– Cons: Higher material cost; less mechanically robust compared to harder plastics; requires specialized molding processes.
Impact on Application:
Silicone rubber is frequently used in triac dimmers for sealing and protecting sensitive electronics from dust and moisture, especially in outdoor or harsh environments.
Regional Considerations:
Buyers in regions with high humidity or dust (e.g., Middle East deserts, tropical Africa) benefit from silicone’s protective properties. Compliance with IEC 60243 and ASTM D2240 standards ensures quality. European buyers may also require REACH compliance for silicone materials.
Summary Table of Materials for Triac Dimmers
| Material | Typical Use Case for triac dimmers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermoplastic Polymers (Polycarbonate, ABS) | Housing, switch covers, insulation components | Cost-effective, good electrical insulation, easy to manufacture | Limited heat resistance, UV degradation risk | Low |
| Ceramic Substrates | High-temperature insulation, substrate for circuits | Excellent thermal stability and dielectric properties | Brittle, higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum Alloys | Heat sinks, structural components | Superior heat dissipation, corrosion resistant | Requires insulation, higher cost than plastics | Medium |
| Silicone Rubber | Sealing, flexible insulation, protective gaskets | Wide temperature range, moisture and UV resistant | Higher cost, less mechanical strength | Medium |
This material selection guide equips international B2B buyers with the insights needed to align triac dimmer sourcing with application requirements and regional standards. Prioritizing materials that balance performance, cost, and compliance will enhance product reliability and market acceptance across diverse global markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for triac dimmers
Manufacturing Processes for TRIAC Dimmers: Key Stages and Techniques
The production of TRIAC dimmers involves a series of meticulously controlled stages designed to ensure performance, reliability, and safety. For international B2B buyers from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these manufacturing steps is essential to evaluate suppliers and make informed procurement decisions.
1. Material Preparation
Material selection forms the foundation of quality TRIAC dimmers. Key components include:
- Semiconductor TRIAC chips: Typically made from silicon, these are the core switching elements.
- PCB (Printed Circuit Board): High-quality FR4 or equivalent substrates are used for stability and durability.
- Passive components: Resistors, capacitors, and inductors sourced from reputable vendors.
- Housing materials: Flame-retardant plastics or metal casings for heat dissipation and safety.
Suppliers should source components that comply with international material standards to ensure longevity and compliance with environmental regulations (e.g., RoHS).
2. Forming and Component Fabrication
This stage involves preparing individual parts before assembly:
- PCB fabrication: Multilayer PCB manufacturing with precise etching and solder mask application.
- Component stamping and molding: For metal parts and plastic housings, injection molding and stamping ensure consistent shapes and mechanical properties.
- Surface treatment: Anti-corrosion coatings or plating for metallic parts to enhance durability.
Advanced techniques like automated pick-and-place machines ensure accurate component placement on PCBs, critical for functional TRIAC dimmers.
3. Assembly Process
Assembly is often semi-automated, combining machine precision with manual quality oversight:
- Soldering: Reflow soldering for surface-mount components and wave soldering for through-hole parts.
- Integration of TRIAC and associated circuitry: Careful handling of semiconductors to avoid electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage.
- Mechanical assembly: Housing assembly, button integration, and wiring connections.
- Calibration and adjustment: Some dimmers require tuning to match specific voltage and load characteristics.
Assembly lines that incorporate real-time monitoring systems help minimize defects and maintain process consistency.
4. Finishing and Packaging
Final steps prepare the TRIAC dimmers for shipment and use:
- Functional coating: Application of conformal coatings to protect PCBs from moisture and dust.
- Labeling and marking: Including compliance marks (CE, RoHS) and batch information for traceability.
- Packaging: Anti-static and shock-resistant packaging tailored for international shipping.
Packaging is especially important for buyers in regions with challenging logistics, ensuring products arrive undamaged.
Quality Assurance and Control: Ensuring Reliable TRIAC Dimmer Performance
Quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC) are critical to guaranteeing that TRIAC dimmers meet stringent international standards and function reliably in diverse environments. B2B buyers must assess suppliers’ QC frameworks carefully, especially when sourcing across continents with varying regulatory demands.
Key International and Industry Standards
- ISO 9001: The backbone of quality management systems, ensuring consistent manufacturing processes and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking (Europe): Indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental requirements.
- RoHS Compliance: Restricts hazardous substances, critical for environmentally conscious markets.
- API and IEC Standards: Specific electrical and electronic standards related to product safety and electromagnetic compatibility.
- UL Certification (United States): Sometimes requested for products entering global markets, ensuring fire and electrical safety.
Buyers should verify that suppliers hold valid certifications relevant to their target markets.
Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
– Inspection and testing of raw materials and components for compliance with specifications.
– Verification of semiconductor chips, PCBs, and housing materials to avoid downstream failures. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
– Monitoring assembly processes, solder joints, and component placement accuracy.
– Use of automated optical inspection (AOI) and manual spot checks during production. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
– Comprehensive testing of finished TRIAC dimmers before shipment.
– Functional tests include voltage/load response, dimming smoothness, thermal performance, and safety checks.
Common Testing Methods
- Electrical Testing: Verifying switching thresholds, current handling, and dimming range under simulated load conditions.
- Thermal Testing: Assessing heat dissipation and stability during continuous operation.
- EMC Testing: Ensuring electromagnetic interference is within permissible limits.
- Mechanical Durability: Evaluating resistance to vibration, shock, and wear of mechanical components.
- Safety Testing: Insulation resistance, dielectric strength, and fire retardancy compliance.
How B2B Buyers Can Verify Supplier Quality Control
For international buyers, especially those operating in markets like Argentina, Saudi Arabia, or broader African and South American regions, supplier QC verification is crucial to mitigate risks associated with substandard products.
Recommended Verification Practices
-
Factory Audits: Conduct on-site or third-party audits to assess manufacturing capability, QC infrastructure, and staff expertise. This is particularly important for buyers unfamiliar with supplier regions or when importing large volumes.
-
Quality Documentation Review: Request and analyze QC reports, certificates of conformity, test records, and batch traceability documents before contract finalization.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent inspection agencies to perform random sampling and testing of shipments, providing unbiased quality validation.
-
Sample Testing: Procure pre-production samples or pilot batches for in-house or local lab testing to verify compliance with performance and safety requirements.
-
Compliance with Local Regulations: Ensure that products meet regional electrical standards and certifications, which may differ significantly. For example, the Middle East often requires G-Mark certification, while European buyers prioritize CE and RoHS.
Quality Control Nuances for Diverse International Markets
-
Africa and South America:
Buyers should focus on suppliers with robust supply chain transparency and certifications that guarantee durability under varied climate conditions, such as high humidity or dust exposure common in these regions. Consider suppliers who offer extended warranties and after-sales support. -
Middle East:
Given the region’s emphasis on energy efficiency and safety, prioritize dimmers compliant with stringent IEC and G-Mark standards. Suppliers familiar with harsh environmental conditions and capable of providing heat-resistant and dust-proof designs add value. -
Europe:
Compliance with CE marking and RoHS is mandatory. European buyers should demand thorough EMC testing and insist on traceability documentation aligned with EU regulations. Sustainable sourcing and eco-friendly packaging also carry significant weight.
Summary for B2B Buyers
- Understand the manufacturing stages to anticipate potential quality risks and assess supplier capabilities.
- Demand adherence to international standards (ISO 9001, CE, RoHS) and region-specific certifications.
- Implement multi-level QC verification, including audits, documentation review, and third-party inspections.
- Tailor QC expectations to your regional requirements, recognizing environmental and regulatory differences.
- Establish ongoing communication with suppliers to ensure continuous quality improvements and compliance.
By integrating these manufacturing and quality assurance insights into their procurement strategy, B2B buyers can secure reliable, efficient, and compliant TRIAC dimmers, optimizing operational outcomes across varied international markets.
Related Video: China’s Top 5 Manufacturing and Mass Production Videos | by @miracleprocess
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for triac dimmers Sourcing
Understanding the cost and pricing dynamics of triac dimmers is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize procurement strategies and ensure long-term value. This analysis breaks down the key cost components, identifies pricing influencers, and offers actionable tips tailored for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Key Cost Components in Triac Dimmer Production
-
Materials
The primary raw materials include semiconductor components (TRIAC chips, diodes), capacitors, resistors, printed circuit boards (PCBs), and housing materials such as plastics or metals. Material quality directly affects durability and performance, with higher-grade components commanding premium prices. For example, dimmers designed for LED compatibility require more advanced semiconductors, increasing material costs. -
Labor
Labor costs vary significantly by manufacturing location. Regions with lower wage rates can offer more competitive pricing, but buyers must balance cost savings with quality assurance. Skilled labor is particularly important for assembly and calibration to ensure device reliability and compliance with standards. -
Manufacturing Overhead
This includes factory utilities, equipment depreciation, and indirect labor. Efficient production lines and automation can reduce overhead per unit, benefiting buyers through lower prices at higher volumes. -
Tooling and Setup
Initial tooling for injection molding of casings and PCB assembly can be costly, especially for customized designs. These upfront costs are amortized over production runs, so higher order quantities typically reduce per-unit tooling expenses. -
Quality Control (QC)
Rigorous QC processes including electrical testing, safety certification compliance (e.g., CE, UL, RoHS), and durability checks add to costs but are critical for reducing returns and ensuring regulatory acceptance in target markets. -
Logistics and Shipping
International shipping costs depend on the product’s volume, weight, and shipping method (air, sea, or land). Customs duties, taxes, and handling fees in destination countries like Argentina or Saudi Arabia also influence landed cost. -
Supplier Margin
Suppliers price their products to cover costs and generate profit. Margins fluctuate based on market demand, supplier reputation, and exclusivity of product features.
Influential Factors Affecting Pricing
-
Order Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)
Larger orders benefit from economies of scale, reducing unit prices. Buyers should negotiate MOQ terms carefully to balance inventory risks against cost savings. -
Product Specifications and Customization
Custom features such as smart dimming capabilities, specific dimming curves (leading vs. trailing edge), or enhanced durability increase costs. Off-the-shelf standard models are typically more affordable. -
Material Quality and Certifications
Triac dimmers with compliance to international certifications and usage of premium materials command higher prices but reduce long-term risks related to failures and non-compliance penalties. -
Supplier Reliability and Location
Established suppliers with proven track records may price higher but offer better consistency and after-sales support. Proximity to buyers can reduce logistics costs and lead times. -
Incoterms and Payment Terms
The choice of Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP) impacts pricing and risk allocation. Buyers in Africa and South America should factor in customs clearance complexities and associated costs.
Practical Buyer Tips for Cost-Effective Sourcing
-
Negotiate Volume Discounts and Flexible MOQs
Engage suppliers early to explore tiered pricing and MOQ flexibility, enabling gradual scale-up without excessive inventory investment. -
Prioritize Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Evaluate beyond unit price by considering installation ease, energy efficiency, warranty terms, and potential maintenance costs—critical for markets with variable power quality. -
Leverage Supplier Audits and Quality Certifications
Verify supplier credentials and product certifications to avoid hidden costs from defective or non-compliant units, which can be costly in regions with stringent import regulations. -
Optimize Logistics Strategy
Consolidate shipments where possible and consider regional distribution hubs to mitigate high freight costs and customs delays, especially relevant for buyers in remote or landlocked areas. -
Understand Pricing Nuances by Region
Be aware of local taxes, tariffs, and import restrictions that can significantly affect landed cost. For example, Saudi Arabia’s import procedures differ from those in Argentina, impacting final procurement budgets. -
Consider Long-Term Supplier Partnerships
Building relationships with reliable suppliers can unlock better pricing, priority production slots, and tailored services that reduce overall procurement risks.
Indicative Pricing Disclaimer
Pricing for triac dimmers varies widely depending on specification, order volume, and supplier. As a rough benchmark, standard leading edge dimmers may start from USD 3–5 per unit at scale, while smart or trailing edge variants can range from USD 8–15 or more. These figures are indicative and should be validated through direct supplier quotations.
By carefully analyzing cost structures and leveraging strategic sourcing practices, international B2B buyers can secure competitive pricing for triac dimmers while ensuring product quality and supply chain resilience. This approach is particularly crucial for markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where logistical and regulatory complexities demand informed decision-making.
Spotlight on Potential triac dimmers Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section offers a look at a few manufacturers active in the ‘triac dimmers’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct their own extensive due diligence before any engagement. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for triac dimmers
Critical Technical Properties of TRIAC Dimmers
Understanding the technical specifications of TRIAC dimmers is essential for international B2B buyers to ensure product compatibility, performance, and reliability across diverse applications. Here are the most important properties to consider:
-
Voltage Rating (AC Voltage Compatibility)
This defines the maximum alternating current voltage the dimmer can safely handle, commonly 110V, 220V, or 240V depending on the market. Buyers from regions such as Europe and the Middle East must verify that the dimmer supports their local mains voltage to avoid product failure or safety hazards. -
Load Type and Load Capacity (Wattage Rating)
TRIAC dimmers are designed for specific load types—incandescent, halogen, or dimmable LED lights. Load capacity indicates the maximum wattage the dimmer can control. Overspecifying load capacity prevents overheating and extends product life, which is crucial for commercial buyers managing large lighting installations. -
Material Grade and Heat Dissipation
High-quality TRIAC dimmers use materials with excellent thermal conductivity and insulation properties to manage heat generated during operation. This reduces failure rates, especially in hot climates common in Africa and the Middle East, ensuring long-term durability. -
Dimming Range and Smoothness
The effective dimming range (e.g., 5% to 100%) and the smoothness of brightness transitions directly impact user experience. For hospitality or retail clients, smooth dimming without flicker is vital to create ambiance and reduce complaints. -
Tolerance and Electrical Noise Immunity
Tolerance refers to the precision of the dimmer’s control circuitry, affecting how accurately it adjusts light levels. Electrical noise immunity indicates resistance to interference, which is important in industrial or urban environments to maintain stable lighting. -
Compliance with International Standards
Certifications such as CE, RoHS, and UL indicate adherence to safety, environmental, and quality standards. Buyers should require these certificates to meet regulatory requirements in target markets and minimize import risks.
Key Industry and Trade Terminology for TRIAC Dimmers
Navigating international procurement requires familiarity with common trade terms and industry jargon. Here are essential terms every B2B buyer should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to a manufacturer who produces TRIAC dimmers that other brands sell under their own labels. Partnering with OEMs can enable buyers to customize products and reduce costs through bulk manufacturing agreements. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. Understanding MOQ helps buyers balance inventory investment with supplier requirements, especially critical for emerging markets or smaller distributors. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal inquiry sent to suppliers to obtain pricing, lead times, and terms for TRIAC dimmers. Well-crafted RFQs enable buyers to compare competitive offers and negotiate favorable contracts. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized terms (e.g., FOB, CIF, EXW) that define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs clearance. Clarity on Incoterms avoids costly misunderstandings in delivery and import logistics. -
Dimming Curve
The relationship between the dimmer control input and the actual light output. Different dimming curves (logarithmic, linear) affect how light intensity changes, influencing user satisfaction in various lighting environments. -
Surge Protection
A feature or specification indicating the dimmer’s ability to withstand voltage spikes. Surge protection is crucial for regions with unstable power grids, such as parts of Africa and South America, to prevent device damage.
By prioritizing these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing TRIAC dimmers, ensuring product suitability, regulatory compliance, and supply chain efficiency across diverse global markets.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the triac dimmers Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global triac dimmers market is experiencing robust growth, driven by the escalating demand for energy-efficient lighting solutions across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—regions characterized by diverse infrastructure needs and growing urbanization—triac dimmers represent a critical component in modern lighting systems, enabling enhanced energy management and user comfort.
Key market drivers include rising adoption of LED lighting technologies, increasing regulatory emphasis on energy conservation, and the integration of smart home and building automation systems. In regions like Saudi Arabia and Argentina, government incentives for sustainable energy use and urban development projects are accelerating the uptake of dimmable lighting controls. Additionally, the expansion of hospitality, retail, and commercial real estate sectors across these geographies is fueling demand for advanced dimming solutions that balance ambiance with operational efficiency.
From a sourcing perspective, international buyers are gravitating toward suppliers offering universal and smart dimmer models, as these provide flexibility to accommodate both legacy and modern lighting fixtures. The trend toward smart dimmers equipped with IoT connectivity is particularly pronounced in Europe and the Middle East, where demand for remote management and energy monitoring is high. Conversely, in emerging markets within Africa and South America, cost-effectiveness and compatibility with local electrical standards remain paramount.
Supply chain dynamics are also evolving, with buyers prioritizing manufacturers that demonstrate strong quality control, compliance with international certifications (such as CE, RoHS), and the ability to customize products to regional voltage and load requirements. The growing complexity of triac dimmer technology has increased the importance of supplier technical support and after-sales service, influencing procurement decisions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a decisive factor in the procurement of triac dimmers as businesses worldwide strive to reduce their carbon footprint and adhere to environmental regulations. Triac dimmers contribute to energy savings by enabling precise control of lighting intensity, thereby reducing electricity consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions. This aligns with the sustainability goals of many companies and governments, especially in Europe and the Middle East, where regulatory frameworks push for greener building practices.
For B2B buyers, ethical sourcing of triac dimmers involves partnering with suppliers committed to environmentally responsible manufacturing processes. This includes minimizing hazardous substances, reducing waste during production, and employing recyclable or bio-based materials in product components. Certifications such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) compliance serve as critical benchmarks for evaluating supplier sustainability credentials.
Moreover, transparency in the supply chain is vital. Buyers increasingly demand traceability and social responsibility assurances, ensuring that products are not only environmentally sound but also manufactured under fair labor conditions. Suppliers who integrate sustainability into their business models often provide lifecycle assessments and environmental impact reports, empowering buyers to make informed decisions.
Investing in sustainable triac dimmers also offers long-term cost benefits through enhanced energy efficiency and reduced maintenance needs, reinforcing the business case for green procurement in diverse markets from South America to Africa.
Evolution and Historical Context
The triac dimmer technology has its roots in the mid-20th century with the development of silicon-controlled rectifiers (SCRs) and triacs that enabled electronic control of AC power. Initially designed for incandescent lighting, triac dimmers replaced mechanical rheostats and provided more efficient, quieter, and more reliable dimming solutions.
Over time, triac dimmers evolved to support newer lighting technologies, particularly LEDs, which posed compatibility challenges due to their low power consumption and electronic drivers. This evolution spurred the development of trailing edge and universal dimmers, capable of handling diverse load types and minimizing flicker and noise.
In recent years, the integration of smart technology into triac dimmers has marked a significant shift, allowing remote control, scheduling, and energy monitoring via wireless networks. This progression reflects broader trends in building automation and smart infrastructure, making triac dimmers a strategic component in modern energy management systems worldwide. For international B2B buyers, understanding this technological evolution is crucial for sourcing dimmers that meet both current and future lighting demands.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of triac dimmers
-
How can I effectively vet triac dimmer suppliers from different regions like Africa, South America, or the Middle East?
To vet suppliers internationally, start with verifying their certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and compliance with regional electrical standards (e.g., CE for Europe, SASO for Saudi Arabia). Request product samples and conduct performance testing, especially for compatibility with local lighting systems. Check references from existing international clients and review their production capacity and lead times. Utilize third-party inspection services for factory audits and quality checks to mitigate risks associated with long-distance sourcing. -
Is customization of triac dimmers feasible when sourcing from international manufacturers, and what should I consider?
Many manufacturers offer customization in terms of dimming types (leading/trailing edge), voltage compatibility, and smart features. Clearly communicate your technical specifications, including the types of lighting loads and control systems used locally. Be aware that customization can increase lead times and costs, so negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) and confirm prototype approval processes upfront. Also, assess if the supplier can support after-sales technical assistance for customized products. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs), lead times, and payment terms for triac dimmer orders in international B2B trade?
MOQs vary widely but typically range from 500 to 2,000 units depending on the complexity and customization. Lead times can span 4 to 12 weeks, factoring in manufacturing, quality checks, and shipping. Payment terms often require a 30% deposit upfront with the balance paid before shipment or against documents via letter of credit. Negotiate terms that balance your cash flow needs with supplier confidence, and consider trade assurance or escrow services to secure transactions.
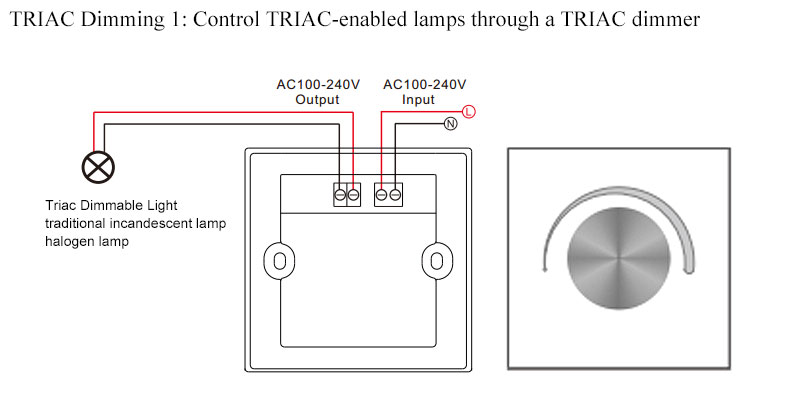
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Which quality assurance certifications and standards should B2B buyers prioritize when sourcing triac dimmers globally?
Prioritize suppliers with ISO 9001 certification to ensure consistent manufacturing quality. Electrical safety certifications like CE (Europe), UL (North America), or SASO (Saudi Arabia) are critical for regulatory compliance. For energy efficiency, look for compliance with IEC standards or local energy certifications. Request detailed quality control reports, including component traceability and final product testing results. These certifications reduce risks of product failure and regulatory hurdles in your target markets. -
What logistics challenges should international buyers anticipate when importing triac dimmers, and how can they be mitigated?
Common challenges include customs clearance delays, import duties, and transportation damage. Work with experienced freight forwarders familiar with your destination’s import regulations and classify products correctly to optimize tariffs. Use sturdy packaging designed to protect sensitive electronic components during transit. Consider shipping insurance and track shipments closely. Establish clear Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) in contracts to clarify responsibilities and reduce disputes. -
How should B2B buyers handle disputes or quality issues with triac dimmer suppliers abroad?
Establish clear contractual terms covering quality standards, inspection procedures, and dispute resolution mechanisms. In case of quality issues, document defects with photos and test reports immediately. Engage suppliers proactively to negotiate replacements or refunds. For unresolved disputes, leverage mediation or arbitration clauses in contracts, preferably under internationally recognized rules (e.g., ICC). Maintaining good communication and having legal recourse plans is essential for protecting your investment. -
Are there specific compatibility concerns B2B buyers should address when purchasing triac dimmers for different regional markets?
Yes, regional differences in voltage (e.g., 110V vs. 220-240V), frequency (50Hz vs. 60Hz), and lighting types (incandescent, LED, halogen) impact dimmer performance. Confirm that dimmers are designed for your local electrical standards and compatible with the intended load. Some dimmers may cause flickering or noise if mismatched. Request technical datasheets and, if possible, test samples under local conditions to ensure seamless integration and customer satisfaction. -
What trends in smart triac dimmers should international B2B buyers consider to stay competitive?
Smart triac dimmers with features like remote control, energy monitoring, and integration with IoT platforms are gaining traction globally, especially in Europe and the Middle East. Buyers should assess supplier capabilities in firmware updates, cybersecurity, and compatibility with popular smart home ecosystems. While initial costs are higher, these products offer value through energy savings and enhanced user experience. Prioritize suppliers who provide comprehensive technical support and scalable solutions for future upgrades.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for triac dimmers
Strategic sourcing of triac dimmers offers international B2B buyers a critical opportunity to enhance energy efficiency, operational flexibility, and lighting quality across diverse applications. Understanding the distinctions between leading edge, trailing edge, universal, smart, and rheostat dimmers enables buyers to align product selection precisely with their technical requirements and end-use environments. For markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this nuanced approach supports cost-effective procurement while ensuring compatibility with regional electrical standards and lighting infrastructures.
Key sourcing insights include:
- Prioritizing suppliers with robust quality control and certifications to guarantee product reliability.
- Evaluating dimmer types based on compatibility with LED and traditional lighting to minimize installation complexities and future maintenance costs.
- Leveraging smart dimmer technology to meet growing demands for automation and energy management, especially in commercial and hospitality sectors.
- Considering total cost of ownership, including installation expertise and energy savings, rather than focusing solely on upfront price.
Looking ahead, the triac dimmer market is poised for continued innovation, driven by sustainability trends and smart building integrations. International buyers are encouraged to cultivate strategic partnerships with manufacturers that demonstrate technological agility and regional market understanding. By doing so, businesses in Argentina, Saudi Arabia, and beyond can confidently navigate evolving lighting demands and secure competitive advantages through optimized energy control solutions. Act now to align your sourcing strategy with these emerging opportunities and future-proof your lighting infrastructure.
