Guide to Led Strips Wireless
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for led strips wireless
- Understanding led strips wireless Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of led strips wireless
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for led strips wireless
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for led strips wireless
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for led strips wireless Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential led strips wireless Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for led strips wireless
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the led strips wireless Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of led strips wireless
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for led strips wireless
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for led strips wireless
Wireless LED strips have rapidly become a cornerstone technology in modern lighting solutions, offering unmatched flexibility, energy efficiency, and aesthetic appeal. For international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in dynamic markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of wireless LED strip sourcing is critical to maintaining a competitive edge. These products are not only transforming commercial and residential lighting but also enabling smarter, more adaptable environments through wireless control and integration.
This comprehensive guide delves deeply into the wireless LED strip market, providing actionable insights tailored to global buyers. It covers the diverse types of wireless LED strips available—from RGB to tunable white—and explores the materials and components that affect durability and performance. Readers will gain clarity on manufacturing standards and quality control processes essential for securing reliable, high-quality products.
Moreover, this guide examines the global supplier landscape, highlighting key sourcing regions and strategies to optimize cost without compromising quality. It addresses crucial considerations such as supply chain management, shipping logistics, and warranty terms to mitigate risks associated with international procurement. The market analysis section equips buyers with knowledge of current trends and emerging technologies, empowering them to anticipate future demands.
By integrating detailed FAQs and expert recommendations, this resource ensures B2B buyers from Nigeria to the UK can make informed, strategic decisions—streamlining procurement processes and unlocking value in their lighting projects. Ultimately, this guide serves as a vital tool for businesses seeking to harness the full potential of wireless LED strips in a fast-evolving global marketplace.
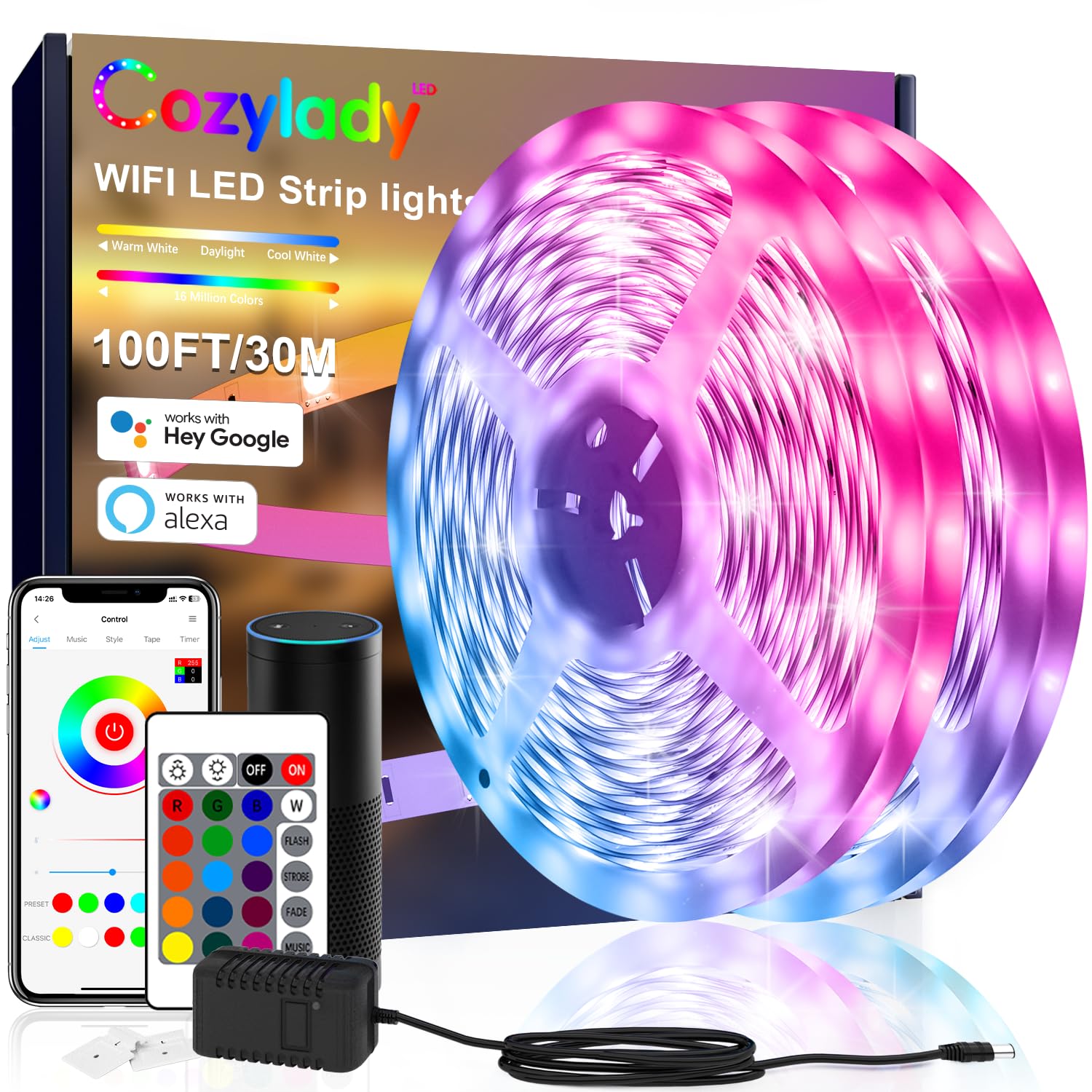
Understanding led strips wireless Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi Controlled LED Strips | Connects via Wi-Fi networks; controlled through apps or hubs | Smart buildings, retail displays, hospitality | + Easy integration with smart systems; – Dependent on network stability |
| Bluetooth LED Strips | Short-range wireless control via Bluetooth-enabled devices | Small commercial setups, event lighting | + Low latency control; – Limited range, less suitable for large areas |
| RF (Radio Frequency) LED Strips | Uses RF remote controls; does not require line-of-sight | Industrial lighting, outdoor signage | + Reliable over obstacles; – Limited customization without complex remotes |
| Zigbee/Z-Wave LED Strips | Mesh network protocols for smart home/building automation | Office spaces, smart homes, large venues | + Scalable and energy-efficient; – Requires compatible hubs, higher initial cost |
| Battery-Powered Wireless LED Strips | Portable, self-contained units without external power source | Temporary installations, exhibitions, outdoor events | + Highly flexible placement; – Limited runtime, higher cost per unit |
Wi-Fi Controlled LED Strips
Wi-Fi controlled LED strips leverage existing wireless networks to enable remote control via smartphones or centralized building management systems. This type is ideal for B2B buyers in smart office buildings, retail environments, and hospitality sectors seeking seamless integration with IoT platforms. When purchasing, businesses should evaluate network compatibility, security features, and supplier support for firmware updates. The reliance on stable Wi-Fi infrastructure means buyers must also plan for network redundancy to avoid disruptions.
Bluetooth LED Strips
Bluetooth LED strips offer straightforward wireless control with low latency, making them suitable for smaller commercial spaces or event venues where quick setup and immediate responsiveness are needed. Their limited range, typically under 10 meters, restricts use to confined areas. Buyers should consider the compatibility of control devices and whether multiple units can be synchronized efficiently. Bluetooth strips are cost-effective but may require additional repeaters for larger spaces.
RF (Radio Frequency) LED Strips
RF LED strips use radio frequency remote controls that do not require line-of-sight, providing robust wireless control even through walls or obstacles. This makes them highly suitable for industrial lighting and outdoor signage where physical obstructions are common. For B2B buyers, the simplicity of RF controls reduces complexity but limits advanced customization unless paired with specialized remotes. Ensuring supplier availability of replacement remotes and compatibility with existing systems is important.
Zigbee/Z-Wave LED Strips
Zigbee and Z-Wave LED strips operate on mesh network protocols designed for smart building automation, allowing scalable and energy-efficient lighting solutions. These types are favored by offices, smart homes, and large venues requiring centralized control and automation. Buyers must invest in compatible hubs and understand integration capabilities with other smart devices. Though initial costs are higher, the long-term benefits include reliable network coverage and reduced energy consumption.
Battery-Powered Wireless LED Strips
Battery-powered wireless LED strips offer maximum installation flexibility without the need for wired power sources, perfect for temporary setups such as exhibitions, outdoor events, or remote signage. Their portability comes with trade-offs in runtime and unit cost, making them more suitable for short-term or mobile applications. B2B buyers should assess battery life, recharge options, and whether bulk purchasing discounts apply given the higher per-unit price. This type facilitates quick deployment but requires careful inventory management for replacement batteries.
Related Video: Govee LED Light Strips for Your Smart Home
Key Industrial Applications of led strips wireless
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of led strips wireless | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail & Commercial | Dynamic in-store lighting and product display illumination | Enhances customer engagement and increases sales | Customizable color options, durability for high-traffic areas |
| Hospitality & Events | Ambient and accent lighting for hotels, restaurants, and event venues | Creates immersive atmospheres, flexible control | Wireless range, ease of integration with existing systems |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Assembly line task lighting and quality inspection illumination | Improves precision and reduces errors | High brightness, robust wireless connectivity in industrial environments |
| Warehousing & Logistics | Flexible aisle and safety lighting with wireless control | Enhances worker safety and operational efficiency | Long battery life, rugged design, compatibility with automation systems |
| Smart Building & Office | Energy-efficient wireless lighting for office spaces and conference rooms | Reduces energy costs, enables centralized control | Compatibility with building management systems, scalability |
Retail & Commercial:
Wireless LED strips are extensively used in retail environments to create dynamic, eye-catching displays and accentuate product features without the constraints of wired installations. For B2B buyers in regions like Europe and South America, wireless LED strips offer flexibility in store layout adjustments and promotional setups. These strips solve problems related to frequent remodeling and seasonal decoration changes by enabling quick reconfiguration. Buyers should prioritize suppliers offering customizable colors, brightness levels, and durable strips that withstand continuous use in high-traffic commercial spaces.
Hospitality & Events:
In the hospitality sector, wireless LED strips are ideal for creating ambient lighting in hotels, restaurants, and event venues. They allow for seamless control of lighting moods and themes without extensive wiring, which is especially beneficial in historic buildings or temporary event spaces common in the Middle East and Africa. These strips help businesses enhance guest experiences and adapt quickly to different event requirements. Key sourcing factors include ensuring strong wireless range, compatibility with smart control apps, and easy integration with existing lighting infrastructure.
Automotive Manufacturing:
Wireless LED strips provide focused illumination for assembly lines and quality inspection stations in automotive plants. Their wireless nature reduces clutter and hazards from cables, improving workplace safety and flexibility in dynamic production environments. For manufacturers in regions such as the UK and Nigeria, these strips facilitate precise lighting adjustments critical for defect detection and process optimization. Buyers should look for high brightness levels, industrial-grade wireless connectivity, and resistance to dust and vibrations to ensure reliability in factory settings.
Warehousing & Logistics:
In warehousing, wireless LED strips are used to illuminate aisles and enhance safety by clearly marking pathways and hazard zones. Their wireless control enables quick adjustments based on operational needs and shifts. This application is vital for logistics hubs in South America and Africa, where infrastructure upgrades are ongoing and flexible lighting solutions reduce installation downtime. Buyers should focus on long battery life, ruggedized designs to withstand harsh environments, and compatibility with warehouse automation and safety systems.
Smart Building & Office:
Wireless LED strips in smart buildings and modern offices enable energy-efficient lighting that can be centrally controlled and programmed for occupancy or daylight responsiveness. This reduces energy consumption and maintenance costs, an important consideration for businesses in Europe and the Middle East aiming for sustainability certifications. These strips also support scalability for expanding office spaces or retrofitting older buildings. Key considerations include seamless integration with building management systems, ease of installation, and robust wireless protocols to avoid interference.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for led strips wireless
Material Analysis for Wireless LED Strips: Key Considerations for B2B Buyers
When selecting materials for wireless LED strips, B2B buyers must evaluate factors such as durability, thermal management, environmental resistance, and compliance with international standards. The choice of material directly affects product performance, longevity, and suitability for diverse applications across different regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Flexible Printed Circuit Board (FPCB) Base Material – Polyimide (PI)
Key Properties:
Polyimide is renowned for its excellent thermal stability (operating temperatures up to 260°C), chemical resistance, and mechanical flexibility. It supports high-density LED mounting and is resistant to moisture and most solvents.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: High heat resistance ensures stable LED performance and longevity. Its flexibility allows for curved or irregular installations common in architectural lighting. Polyimide also offers excellent electrical insulation.
– Cons: Higher cost compared to standard polyester substrates and more complex manufacturing processes. Handling requires care to avoid damage during assembly.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for premium wireless LED strips requiring compact, flexible form factors with reliable heat dissipation. Suitable for indoor and protected outdoor environments where flexibility and durability are critical.
International Considerations:
Buyers in regions with high ambient temperatures (e.g., Middle East, parts of Africa) benefit from polyimide’s heat tolerance. Compliance with UL94-V0 flame retardancy and RoHS standards is common and often expected in Europe and UK markets. Buyers should verify certifications to ensure compatibility with local electrical safety regulations.
2. Flexible Printed Circuit Board Base Material – Polyester (PET)
Key Properties:
Polyester substrates offer moderate thermal resistance (up to ~130°C) and good dimensional stability. They are less expensive and easier to process than polyimide but have lower chemical and heat resistance.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Cost-effective for large volume production, lightweight, and easy to cut or shape. Suitable for less demanding applications.
– Cons: Lower temperature tolerance limits use in high-heat environments. Less durable under prolonged UV exposure or harsh chemicals.
Impact on Application:
Commonly used for indoor wireless LED strips in residential or commercial settings with controlled environments. Not recommended for outdoor or industrial applications with high heat or chemical exposure.
International Considerations:
PET-based strips are popular in cost-sensitive markets like South America and parts of Africa. Buyers should ensure the supplier provides adequate UV protection if outdoor use is intended. Compliance with ASTM D638 (tensile properties) and relevant IEC standards is beneficial for European buyers.
3. Encapsulation Material – Silicone Rubber
Key Properties:
Silicone offers excellent flexibility, UV resistance, and waterproofing capabilities. It maintains elasticity over a wide temperature range (-50°C to 250°C) and provides strong protection against dust and moisture ingress (IP65 to IP68 ratings).
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Enhances durability for outdoor and industrial wireless LED strips. Provides excellent environmental protection without compromising flexibility.
– Cons: Higher material and processing costs. Silicone encapsulation can complicate recycling and repair efforts.
Impact on Application:
Essential for wireless LED strips deployed in harsh climates such as the Middle East deserts or humid tropical regions in Africa and South America. Extends product lifespan and reduces maintenance costs.
International Considerations:
Buyers should verify compliance with international waterproofing standards (IP ratings) and fire safety certifications (e.g., UL94). Silicone encapsulated strips are highly favored in European markets for outdoor architectural lighting and in Middle Eastern projects requiring robust environmental resistance.
4. Conductive Traces – Copper with Protective Coating
Key Properties:
Copper is the standard conductor material due to its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal performance. Protective coatings (e.g., gold plating or tin) prevent oxidation and improve solderability.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Ensures efficient power delivery and heat dissipation, critical for wireless LED strip reliability. Protective coatings extend lifespan and reduce failure rates.
– Cons: Copper is prone to corrosion if coatings are inadequate, especially in humid or salty environments. Cost varies with plating type.
Impact on Application:
Suitable for all wireless LED strip applications, with plating choice tailored to environmental conditions. Gold plating is preferred for high-end, corrosion-sensitive markets; tin plating is cost-effective for general use.
International Considerations:
Buyers from coastal or high-humidity regions (e.g., Nigeria, Brazil) should prioritize copper with robust corrosion-resistant coatings. Compliance with IEC 60228 (conductors) and ASTM B187 (copper sheet) standards ensures quality and interoperability in Europe and South America.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Wireless LED Strips
| Material | Typical Use Case for led strips wireless | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyimide (PI) FPCB | Flexible, high-temperature resistant strips for indoor/outdoor | High thermal stability and flexibility | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Polyester (PET) FPCB | Cost-sensitive indoor applications with moderate environmental demands | Low cost and easy processing | Limited heat and UV resistance | Low |
| Silicone Rubber Encapsulation | Outdoor and industrial wireless LED strips requiring waterproofing | Excellent environmental protection and flexibility | Increased cost and recycling complexity | Medium |
| Copper Conductive Traces w/ Coating | Electrical pathways in all wireless LED strip types | Superior conductivity and thermal management | Corrosion risk if coating is insufficient | Medium |
This guide equips international B2B buyers with actionable insights for selecting appropriate materials for wireless LED strips, balancing performance, cost, and regional compliance to optimize procurement and application outcomes.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for led strips wireless
Manufacturing Processes for Wireless LED Strips
The production of wireless LED strips involves a sophisticated sequence of stages designed to ensure product reliability, performance, and aesthetic quality. For international B2B buyers, understanding these stages helps in selecting suppliers capable of delivering consistent, high-quality goods that meet global market demands.
1. Material Preparation
Raw materials such as flexible printed circuit boards (FPCBs), LED chips, wireless control modules, resistors, capacitors, and protective coatings are procured. Suppliers often source LED chips from specialized manufacturers known for energy-efficient and durable semiconductors. The FPCBs are prepared by layering copper foil onto a flexible substrate, which is then patterned to create electrical circuits tailored for LED placement and wireless connectivity.
- Key Insight:* Buyers should inquire about the origin and specifications of raw materials, ensuring components meet industry standards to avoid performance degradation, especially in regions with high temperature or humidity like parts of Africa and the Middle East.
2. Forming and Circuit Fabrication
The FPCBs undergo photolithography and etching to create precise circuit patterns. This step defines the electrical pathways and ensures minimal resistance and heat generation. For wireless LED strips, additional integration points for control modules and antennas are designed into the circuit.
- Key Insight:* Advanced manufacturing techniques such as surface mount technology (SMT) are used to place tiny LED chips and wireless components accurately. Buyers can request process details to verify the use of high-precision equipment, which is critical for durability and signal integrity.
3. Assembly and Soldering
LED chips, resistors, wireless control units (e.g., Bluetooth or Wi-Fi modules), and connectors are mounted onto the FPCB. Soldering is primarily done using reflow soldering ovens that provide consistent heat profiles to avoid damage. Automated optical inspection (AOI) systems typically follow to detect soldering defects or component misalignment.
- Key Insight:* Buyers should confirm that manufacturers implement automated and manual inspection at this stage to catch defects early, minimizing downstream failures. For international buyers, especially from Europe and South America where product liability is stringent, this is a crucial quality step.
4. Protective Coating and Finishing
Once assembled, strips are coated with waterproof or dustproof layers such as silicone or epoxy resin, depending on the intended application. This finishing protects against environmental factors, extending product life. Wireless LED strips may also receive a final programming step where firmware for wireless control is uploaded and tested.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Key Insight:* The quality of protective coatings is vital for buyers in humid or outdoor environments (e.g., Nigeria or the Middle East). Certifications on waterproof ratings (IP65, IP67) should be verified during supplier evaluation.
Quality Assurance and Control (QA/QC) in Wireless LED Strip Manufacturing
Effective quality control is non-negotiable for wireless LED strip suppliers serving international markets. B2B buyers must understand the quality assurance frameworks and checkpoints to ensure product compliance and reliability.
International and Industry-Specific Standards
- ISO 9001: This globally recognized standard for quality management systems ensures that manufacturers have structured processes for continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Required for products entering the European market, CE certification confirms compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- RoHS Compliance: Restriction of hazardous substances is critical for electronics sold in Europe and increasingly in South America and Africa.
- FCC / IC Certification: Wireless LED strips using radio frequencies must comply with Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the U.S. and Industry Canada (IC) regulations, ensuring that wireless emissions do not interfere with other devices.
-
API and Regional Certifications: Some Middle Eastern and African markets may require additional local certifications or approvals. Buyers should verify these with suppliers.
-
Key Insight:* Buyers should request copies of all relevant certifications and verify their authenticity with issuing bodies or through third-party services.
QC Checkpoints Throughout Production
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection and testing of raw materials and components to ensure they meet specifications before production begins. This minimizes the risk of defective inputs.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring during assembly, soldering, and coating stages. Checks include solder joint integrity, component placement accuracy, and wireless module functionality.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of finished products, including brightness uniformity, wireless connectivity range and response, waterproof testing, and overall visual inspection.
-
Key Insight:* Request detailed QC protocols from suppliers. Leading manufacturers provide documented checkpoints and test reports, which help buyers assess the rigor of the supplier’s QA system.
Common Testing Methods
- Electrical Testing: Verifies voltage, current, and power consumption conform to design specifications.
- Optical Testing: Measures color temperature, brightness (lumens), and color rendering index (CRI).
- Wireless Signal Testing: Assesses communication reliability, latency, and compatibility with control devices.
- Environmental Stress Testing: Includes thermal cycling, moisture resistance (IP rating tests), and vibration testing to simulate real-world conditions.
- Durability Testing: Evaluates lifespan under continuous operation and resistance to mechanical stress.
How B2B Buyers Can Verify Supplier Quality Control
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, ensuring supplier QC requires proactive measures:
- Factory Audits: On-site inspections by your procurement or third-party quality teams can verify manufacturing capabilities, process adherence, and working conditions.
- Review of QC Documentation: Request and analyze inspection reports, test certificates, and quality management system certifications.
- Third-Party Inspections: Employ independent inspection agencies to perform random batch testing, pre-shipment inspections, and compliance verification.
- Sample Testing: Obtain product samples for in-house testing or through accredited labs to verify performance claims and compliance with local regulations.
-
Supplier Performance History: Evaluate past delivery performance, defect rates, and responsiveness to quality issues.
-
Key Insight:* For buyers in regions with emerging regulatory frameworks (e.g., Nigeria, parts of South America), partnering with suppliers who hold internationally recognized certifications (ISO 9001, CE, RoHS) simplifies import clearance and market acceptance.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
- Africa and the Middle East: Customs and import regulations may require additional documentation or local certification. Buyers should confirm that wireless LED strips meet electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards applicable in these regions.
- Europe: The emphasis on environmental and safety standards means buyers must prioritize suppliers with full CE, RoHS, and REACH compliance. Wireless functionality must align with EU radio equipment directives.
- South America: Requirements can vary widely; some countries recognize international certifications, while others require local testing. Buyers should clarify these details early in supplier negotiations.
- Cross-Region Logistics: Ensure packaging and product labeling meet destination country regulations, including language requirements and safety warnings.
Conclusion
For international B2B buyers seeking wireless LED strips, a thorough understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance frameworks is essential. Engaging suppliers with transparent, well-documented production methods and robust QC systems — validated through certifications, audits, and testing — safeguards investment and ensures product reliability in diverse markets. Prioritizing these factors will empower buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to make informed sourcing decisions, reduce risks, and achieve consistent project success.
Related Video: LED Light Making Process | How LED Lights Made Inside Factory | Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for led strips wireless Sourcing
Understanding the cost and pricing dynamics of wireless LED strips is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize procurement strategies and ensure competitive pricing. The cost structure involves multiple components, while pricing is influenced by various factors linked to volume, specifications, and supplier conditions. Here is a detailed breakdown to guide buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Key Cost Components in Wireless LED Strips Sourcing
-
Materials: The primary cost driver, including LED chips, flexible PCB substrates, wireless communication modules (e.g., Bluetooth or Wi-Fi controllers), power supplies, and connectors. High-quality LEDs and certified wireless modules tend to increase costs but enhance reliability and lifespan.
-
Labor: Skilled labor costs vary depending on the manufacturing country. Assembly, testing, and packaging labor contribute significantly, especially for products with advanced features or customizations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: Includes factory utilities, equipment depreciation, quality control processes, and facility maintenance. Efficient factories with automation may have lower overhead per unit.
-
Tooling and Setup: Initial costs for molds, stencils, and programming of wireless modules. These are often amortized over production volumes but can be substantial for small or custom orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes, including functional testing of wireless connectivity and LED performance, add to costs but reduce returns and warranty claims.
-
Logistics and Shipping: Freight charges, customs duties, and insurance, which vary considerably by destination region and shipping method (air vs. sea). Packaging for fragile electronics also impacts shipping costs.
-
Supplier Margin: Markup applied by manufacturers and distributors to cover profit and business sustainability.
Factors Influencing Price Negotiation and Final Cost
-
Order Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger volumes typically yield lower per-unit prices due to economies of scale and better amortization of tooling/setup costs. Buyers should consolidate orders where feasible to leverage this.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized wireless protocols, colors, lengths, or additional features (e.g., dimming, app control) increase complexity and cost. Standardized models are more cost-effective.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Products with certifications such as CE, RoHS, FCC, or UL often command premium pricing but are crucial for compliance in Europe, the Middle East, and other regulated markets.
-
Supplier Reliability and Location: Established suppliers with proven quality and consistent delivery may price higher but reduce risks. Proximity to ports and trade agreements can also affect landed costs.
-
Incoterms and Payment Terms: The agreed Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP) influence who bears shipping and customs costs. Favorable payment terms (e.g., letters of credit, extended credit) can improve cash flow and reduce financing costs.
Practical Tips for B2B Buyers in Diverse Regions
-
Negotiate Based on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond unit price. Factor in warranty support, shipping reliability, customs clearance efficiency, and after-sales service. For buyers in Nigeria or South America, delays or customs complexities can add hidden costs.
-
Request Samples and Pilot Runs: Validate product quality and wireless performance before committing to large orders. This is particularly important when sourcing from new suppliers or unfamiliar regions.
-
Leverage Group Purchasing or Partnerships: Buyers in smaller markets can collaborate with regional partners to meet MOQs and negotiate better pricing.
-
Understand Local Import Regulations and Duties: Knowledge of tariffs and certification requirements can prevent unexpected expenses or shipment rejections, especially in the Middle East and Europe.
-
Use Technology for Price Benchmarking: Platforms offering transparent pricing and supplier reviews can help identify cost-effective sources without compromising quality.
-
Plan for Currency Fluctuations and Payment Risks: Currency volatility impacts landed costs; consider forward contracts or multi-currency accounts when dealing with suppliers abroad.
Indicative Pricing Disclaimer
Prices for wireless LED strips vary widely depending on specifications, order size, and supplier terms. As a general guide, wholesale prices can range from approximately $2 to $10 per meter for standard models, with custom or certified products commanding higher rates. Buyers should conduct due diligence and obtain multiple quotes to establish current market pricing.
By thoroughly understanding these cost drivers and pricing influencers, international B2B buyers can negotiate more effectively, optimize sourcing decisions, and ensure a competitive edge in their respective markets.
Spotlight on Potential led strips wireless Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section offers a look at a few manufacturers active in the ‘led strips wireless’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct their own extensive due diligence before any engagement. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for led strips wireless
Critical Technical Properties of Wireless LED Strips
Understanding the key technical properties of wireless LED strips is essential for B2B buyers to ensure product suitability, quality, and long-term value. Here are the most important specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade and Durability
Wireless LED strips typically use flexible printed circuit boards (FPCBs) made from high-grade copper or polyimide substrates. The material grade affects flexibility, heat dissipation, and lifespan. For buyers in diverse climates—such as humid coastal regions in Africa or colder European markets—choosing strips with high-quality materials ensures reliability and durability under varied environmental conditions. -
Wireless Connectivity Type
Wireless LED strips commonly use technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or proprietary RF (radio frequency) protocols. The choice influences control range, interference susceptibility, and compatibility with smart devices. For B2B buyers deploying in commercial or large-scale projects, understanding connectivity options ensures seamless integration with existing automation systems and mobile apps. -
Power Consumption and Voltage
Typical wireless LED strips operate at low DC voltages (commonly 12V or 24V) with varying power consumption based on LED density and brightness. Knowing the power specs allows buyers to plan appropriate power supply solutions and estimate operational costs, which is critical for large installations across retail or hospitality sectors. -
IP Rating (Ingress Protection)
IP ratings define the strip’s resistance to dust and water. For example, an IP65 rating means the strip is dust-tight and protected against water jets, suitable for outdoor or damp environments. Buyers in regions with high humidity or outdoor exposure, such as the Middle East or South America, must prioritize IP-rated strips to avoid premature failure. -
Color Temperature and Brightness (Lumens)
Wireless LED strips come in various color temperatures (measured in Kelvins) and brightness levels (lumens per meter). This affects ambiance and functional lighting. B2B buyers should select strips that match the intended use—warm white for cozy atmospheres or high-lumen RGB strips for dynamic commercial displays. -
Cuttable and Linkable Lengths
Flexibility in installation is enhanced when strips can be cut to size or connected end-to-end without compromising functionality. This property is vital for customized projects, enabling buyers to optimize material usage and reduce waste.
Common Trade Terminology in Wireless LED Strip Procurement
Navigating the B2B buying process for wireless LED strips requires familiarity with key industry terms. Here are essential trade terms every buyer should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This refers to suppliers who manufacture products that other companies rebrand and sell. OEM partnerships often enable customization and cost savings. Buyers seeking private-label wireless LED strips can negotiate OEM agreements to differentiate their offerings. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity a supplier will accept for an order. Understanding MOQ helps buyers plan inventory and budget effectively, especially in emerging markets where upfront capital may be limited. Negotiating MOQs can also improve accessibility for smaller businesses. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document buyers send to suppliers asking for detailed pricing, lead times, and terms. Using RFQs allows buyers to compare multiple offers transparently and select the best value wireless LED strip supplier for their region. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These standardized trade terms define responsibilities, costs, and risks between buyers and sellers during shipping. Common Incoterms include FOB (Free On Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight). For international buyers, understanding Incoterms ensures clarity on delivery costs and liability. -
Lumen Output
Refers to the total quantity of visible light emitted. Higher lumen output means brighter light. Buyers need this metric to assess whether the strip meets their lighting intensity requirements. -
Color Rendering Index (CRI)
CRI measures how accurately a light source displays colors compared to natural light. A higher CRI (above 80) is preferable for retail or hospitality environments where true color representation is important.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers—from Nigeria to the UK—can make informed decisions that align product capabilities with their project requirements, optimize procurement processes, and build resilient supplier relationships. This foundational knowledge helps reduce risk, control costs, and enhance the success of wireless LED strip lighting initiatives.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the led strips wireless Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for wireless LED strips is expanding rapidly, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient, versatile lighting solutions across commercial, industrial, and residential sectors. Key growth drivers include the rise of smart building technologies, urbanization, and the need for flexible, customizable lighting that integrates seamlessly with IoT ecosystems. For B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial to making informed sourcing decisions.
In Africa and South America, emerging economies are witnessing increased investments in infrastructure and commercial real estate, creating new opportunities for wireless LED strip installations in offices, retail spaces, and hospitality venues. The Middle East’s focus on smart city initiatives and sustainable urban development further fuels demand for advanced lighting solutions that offer remote control, energy monitoring, and adaptive lighting capabilities. Europe, led by regulatory frameworks emphasizing energy efficiency and sustainability, remains a mature market prioritizing innovative features like app-controlled RGB strips, dimmable modules, and integration with building management systems.
From a sourcing perspective, B2B buyers should monitor trends such as the growing preference for wireless LED strips that support Bluetooth Mesh and Zigbee protocols, enabling enhanced scalability and interoperability. Suppliers increasingly offer modular designs and customizable options to cater to diverse applications and regional preferences. Additionally, the rise of online wholesale platforms and direct-from-manufacturer sourcing is streamlining procurement, reducing costs, and improving access to the latest technology.
Market dynamics are also influenced by supply chain resilience concerns. Businesses are advised to diversify supplier bases across multiple geographies, emphasizing manufacturers with proven quality control and certifications. For international buyers, leveraging local distribution hubs can minimize lead times and shipping costs, critical factors in large-scale projects.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a pivotal consideration in the wireless LED strips sector, reflecting broader corporate responsibility trends and regulatory pressures worldwide. The environmental impact of LED lighting is generally positive compared to traditional lighting; however, sourcing practices and product lifecycle management remain areas for improvement.
For B2B buyers, prioritizing suppliers committed to ethical sourcing is essential. This includes verifying that components such as LED chips, circuit boards, and batteries are procured from manufacturers adhering to responsible labor practices and environmental regulations. Certifications like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals), and Energy Star provide assurance of compliance with environmental and safety standards.
Green materials and recyclable packaging are gaining traction, particularly among European buyers, where circular economy principles influence procurement decisions. Wireless LED strips designed for easy disassembly and component recycling support sustainability goals and reduce electronic waste. Additionally, energy-efficient drivers and power supplies that minimize standby power consumption contribute to lower carbon footprints.
Ethical supply chains also mitigate risks related to reputational damage and regulatory non-compliance, which can be costly in international trade. Buyers from emerging markets such as Nigeria or Brazil are increasingly evaluating supplier transparency, seeking partners who provide traceability and audit reports. Engaging with suppliers who invest in sustainability innovations—such as biodegradable components or solar-compatible LED strips—can also provide a competitive edge and align with clients’ environmental commitments.
Brief Evolution and Historical Context
The evolution of wireless LED strips reflects broader advances in LED technology and wireless communication protocols. Initially, LED strips were wired, limiting their flexibility and installation scope. The integration of wireless control technologies, such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, emerged in the early 2010s, driven by the proliferation of smartphones and smart home devices.
This shift enabled remote control, color customization, and synchronization with other smart devices, revolutionizing applications in commercial lighting and interior design. Over time, improvements in LED chip efficiency, miniaturization of wireless modules, and the adoption of standardized communication protocols have enhanced product reliability and interoperability.
For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution highlights the importance of selecting wireless LED strips that are compatible with current smart infrastructure and scalable for future upgrades. This historical perspective underscores the sector’s rapid innovation pace, encouraging buyers to partner with suppliers who invest in ongoing R&D and technology adoption.
Related Video: International Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of led strips wireless
-
How can I effectively vet wireless LED strip suppliers for international B2B purchases?
To vet suppliers, prioritize those with verified business licenses and positive trade history, especially on recognized B2B platforms. Request product certifications such as CE, RoHS, and FCC to ensure compliance with international standards. Verify manufacturing capabilities through factory audits or virtual tours and assess customer reviews and references from similar markets (e.g., Africa, Europe). Confirm their experience handling international shipments and customs. Establish clear communication channels and responsiveness before committing to bulk orders to reduce risks. -
What customization options are typically available for wireless LED strips, and how should I approach them?
Most suppliers offer customization in length, color temperature, brightness, wireless control protocols (e.g., Wi-Fi, Bluetooth), and packaging. For branding or specific project requirements, request OEM/ODM services including private labeling or unique packaging designs. Clearly specify technical needs upfront and discuss minimum order quantities (MOQs) for custom products, as these may be higher. Request samples of customized strips before mass production to verify quality and compatibility with your target market’s standards. -
What are common minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for wireless LED strip wholesale orders?
MOQs vary widely but typically range from 100 to 500 meters per model, depending on customization and supplier scale. Lead times generally span 3 to 8 weeks, influenced by order size, customization complexity, and current supply chain conditions. For international buyers, factor in additional time for shipping and customs clearance. Negotiate MOQs and lead times upfront, especially if you’re entering new markets like Nigeria or the UK, to align with your inventory and sales forecasts. -
Which payment terms and methods are recommended for international B2B buyers of wireless LED strips?
Common payment terms include 30% upfront deposit with balance upon shipment or letter of credit (L/C) for larger orders. Secure methods such as PayPal, escrow services, or bank transfers are preferred. Negotiate terms that balance risk and cash flow, especially if dealing with new suppliers. For buyers in Africa, South America, or the Middle East, consider currency exchange implications and choose payment methods that minimize fees and delays. Always confirm payment terms in the contract to avoid disputes. -
What quality assurance (QA) measures and certifications should I require from wireless LED strip suppliers?
Insist on QA processes including in-line inspections, aging tests, and final product testing to verify brightness, color accuracy, and wireless functionality. Certifications like CE (Europe), RoHS (hazardous substances), FCC (wireless communication), and ISO 9001 (quality management) are critical for regulatory compliance and market acceptance. Request test reports and ensure products meet local electrical safety standards in your target markets. Conduct third-party inspections if necessary to guarantee consistent quality. -
How can I optimize logistics and shipping when importing wireless LED strips internationally?
Work with suppliers who offer consolidated shipping options like FOB or CIF to control costs and simplify customs clearance. Choose reliable freight forwarders experienced in your region (Africa, South America, Middle East, Europe) to navigate local import regulations efficiently. Plan shipments to avoid peak seasons or delays, and use tracking systems for real-time visibility. Consider inventory warehousing near key markets to reduce delivery times and improve responsiveness to customer demand. -
What should I do if I encounter disputes or defects with wireless LED strip shipments?
Establish clear dispute resolution terms in your purchase agreement, including warranty coverage and return policies. Document all issues with photos and detailed descriptions promptly. Engage your supplier immediately to negotiate remedies such as replacements, refunds, or discounts. Use third-party inspection reports or arbitration if disputes escalate. Maintaining strong communication and a collaborative approach often leads to faster resolutions and preserves long-term supplier relationships. -
How can I ensure wireless LED strips comply with import regulations in diverse international markets?
Research each target market’s electrical, safety, and wireless communication regulations thoroughly. Ensure suppliers provide necessary certifications (CE for Europe, SONCAP for Nigeria, INMETRO for Brazil, etc.) and comply with local standards. Collaborate with customs brokers familiar with your markets to pre-validate documentation and labeling requirements. Staying informed about evolving regulations helps avoid customs delays or fines, ensuring smoother market entry and customer trust.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for led strips wireless
Strategic sourcing of wireless LED strips presents a compelling opportunity for international B2B buyers seeking to enhance their product offerings with innovative, energy-efficient lighting solutions. Key takeaways emphasize the importance of partnering with reputable suppliers who provide high-quality components, customizable options, and scalable inventory to meet diverse project needs across commercial, industrial, and residential sectors. Leveraging bulk purchasing not only reduces costs but also ensures consistency and access to the latest technology, crucial for maintaining competitive advantage in dynamic markets.
Effective supply chain management—including diversified sourcing, robust inventory control, and reliable logistics—further strengthens procurement strategies, minimizing risks associated with delays or quality issues. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional supplier capabilities and shipping frameworks is essential to optimize lead times and costs.
Looking ahead, wireless LED strips are set to evolve with smarter integrations and enhanced durability, creating new avenues for value-added applications. B2B buyers are encouraged to proactively engage with innovative suppliers, request samples to validate quality, and adopt technology-driven sourcing tools to future-proof their investments. Embracing strategic sourcing now will position businesses to capitalize on the growing demand for flexible, wireless lighting solutions across global markets.
