Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for led strip with raspberry pi
The integration of LED strips with Raspberry Pi technology represents a transformative opportunity for businesses across industries such as smart lighting, digital signage, and IoT-enabled environments. For international B2B buyers, especially those operating in dynamic markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including the UK and Kenya), understanding the nuances of sourcing and deploying these components is critical to maintaining a competitive edge. The ability to control LED strips programmatically via Raspberry Pi enables highly customizable lighting solutions that enhance energy efficiency, user experience, and operational flexibility.
This guide delivers an authoritative roadmap to mastering the global supply landscape of LED strips compatible with Raspberry Pi controllers. It covers a comprehensive range of topics including the various LED strip types (RGB, single-color, individually addressable Neopixels), quality materials and manufacturing standards, and essential electrical components such as MOSFETs and power supplies. Buyers will gain insight into rigorous quality control practices that ensure product reliability and longevity, as well as strategic sourcing tips to identify reputable suppliers and manufacturers worldwide.
Cost considerations and market trends specific to each region are analyzed to help businesses optimize procurement budgets without compromising quality. Additionally, the guide addresses frequently asked questions related to integration challenges, compatibility, and after-sales support. By equipping buyers with actionable intelligence and practical knowledge, this resource empowers decision-makers to confidently navigate the complexities of the international LED strip with Raspberry Pi market, securing solutions that align with their operational goals and regional market demands.
Understanding led strip with raspberry pi Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analog RGB LED Strip | SMD5050 chips with 3 color LEDs per chip; single color control per strip segment | Basic ambient lighting, signage, decorative lighting | Pros: Cost-effective, simple control Cons: No individual LED control, limited color effects |
| Single-Color LED Strip (SMD3528) | Single-color LEDs per chip; no RGB mixing capability | Industrial status indicators, accent lighting | Pros: Low power consumption, straightforward integration Cons: Limited to one color, less versatile |
| Addressable RGB LED Strip (WS2812B / Neopixel) | Individually controllable LEDs with integrated driver ICs | Dynamic displays, interactive installations, complex lighting effects | Pros: High customization, vibrant effects Cons: Higher cost, more complex programming and power requirements |
| High-Density LED Strip | Increased LED count per meter for brighter, uniform light | Professional-grade displays, retail lighting, architectural lighting | Pros: Superior brightness and uniformity Cons: Higher power demand, increased cost |
| Waterproof LED Strip | Encapsulated with silicone or epoxy for moisture resistance | Outdoor signage, marine applications, industrial environments | Pros: Durability in harsh conditions Cons: Slightly reduced brightness, higher price |
Analog RGB LED Strip
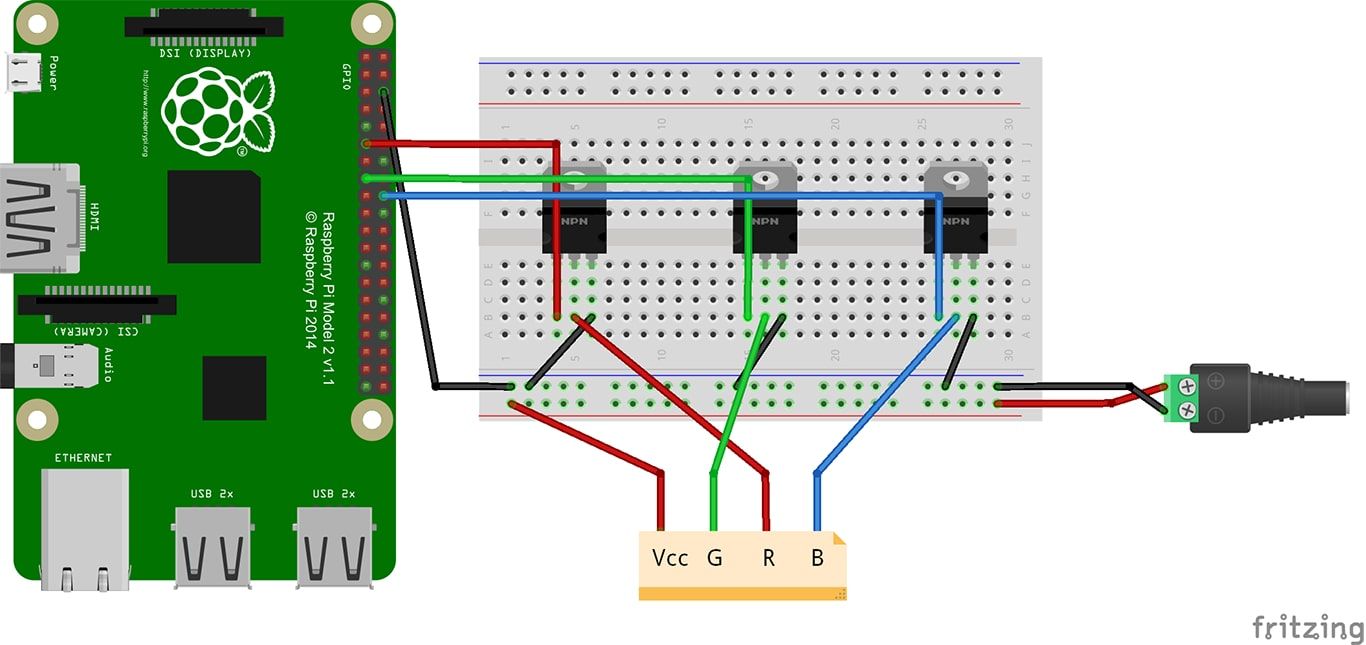
Analog RGB LED strips utilize SMD5050 LEDs that contain red, green, and blue diodes within a single chip. These strips can only display one color at a time across the entire length, controlled via three pins corresponding to the RGB channels. Ideal for B2B buyers needing cost-effective, basic lighting solutions, they are widely used in ambient lighting and simple decorative applications. When purchasing, consider the voltage requirements (commonly 12V) and ensure compatibility with Raspberry Pi GPIO outputs through appropriate MOSFET drivers. Their simplicity makes them suitable for large-scale installations where complex color control is unnecessary.
Single-Color LED Strip (SMD3528)
These strips feature single-color LEDs, often arranged in repeating color patterns, and lack the ability to mix colors. Their low power consumption and straightforward wiring make them attractive for industrial status indicators, accent lighting, or environments where consistent color output is essential. For B2B procurement, buyers should verify the LED chip type and ensure the power supply matches the strip’s voltage and current demands. While less flexible than RGB variants, their durability and simplicity can reduce maintenance costs in operational settings.
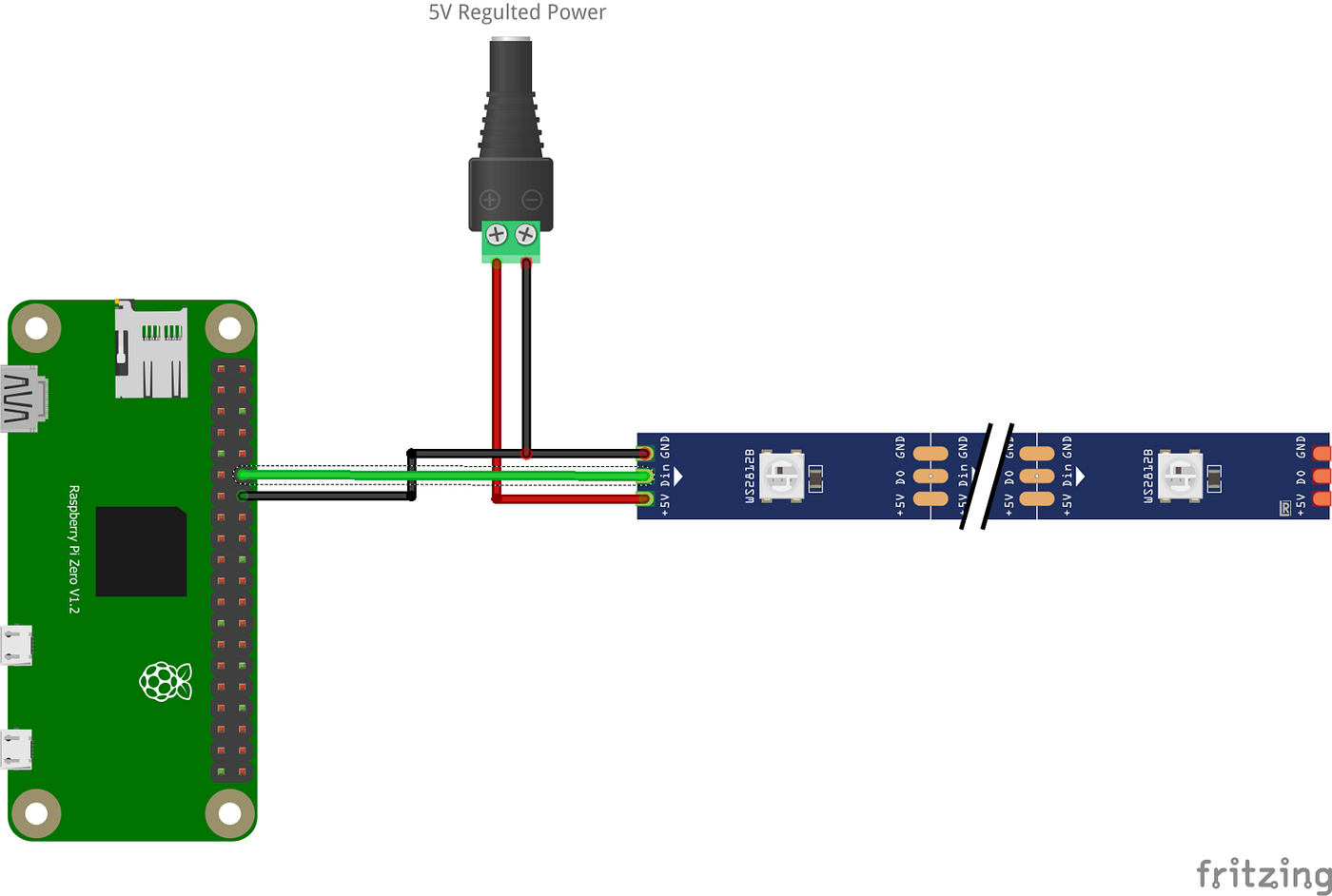
Addressable RGB LED Strip (WS2812B / Neopixel)
Addressable LED strips incorporate driver ICs within each LED chip, enabling individual control of every LED. This feature supports complex lighting patterns, animations, and interactive displays, making them ideal for high-end retail, exhibitions, and architectural projects requiring dynamic visual effects. B2B buyers must evaluate the increased complexity in programming and power supply design, as well as the need for precise timing protocols compatible with Raspberry Pi libraries. Despite higher costs, their versatility offers significant value in differentiated lighting solutions.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
High-Density LED Strip
High-density strips increase the number of LEDs per meter, providing brighter and more uniform illumination. These are preferred in professional-grade applications such as retail displays, architectural lighting, and any scenario demanding high luminosity and smooth color transitions. From a procurement standpoint, buyers should assess power consumption, heat dissipation requirements, and ensure the Raspberry Pi setup can handle the control signals and power demands. Investing in high-density strips can enhance product appeal in premium market segments.
Waterproof LED Strip
Encased in silicone or epoxy, waterproof LED strips offer resilience against moisture, dust, and harsh environmental conditions. These strips are essential for outdoor signage, marine applications, and industrial environments exposed to weather or liquids. B2B buyers should confirm the IP rating (e.g., IP65, IP67) to match the intended use case and consider the slight trade-off in brightness due to encapsulation. The increased durability justifies the higher upfront cost, reducing long-term replacement and maintenance expenses in challenging environments.
Related Video: How To Use Addressable RGB WS2812B LED Strips With a Raspberry Pi Single Board Computer
Key Industrial Applications of led strip with raspberry pi
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of led strip with raspberry pi | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smart Manufacturing | Automated visual status indicators on assembly lines | Enhances real-time monitoring, reduces downtime, and improves quality control | Reliable components with industrial-grade durability; compatibility with existing PLC systems; power supply stability |
| Retail & Hospitality | Dynamic ambient lighting and interactive product displays | Increases customer engagement and sales conversion through personalized lighting | Flexibility in color control; ease of integration with IoT platforms; sourcing from suppliers offering local support |
| Agriculture & Horticulture | Controlled spectrum grow lights for optimized plant growth | Boosts crop yields and energy efficiency by tailoring light conditions | High-efficiency LED strips with adjustable spectra; weather-resistant hardware; compliance with regional electrical standards |
| Transportation & Logistics | Vehicle interior and cargo area lighting with programmable alerts | Improves safety and operational efficiency by signaling status or hazards | Robust, vibration-resistant LED strips; low power consumption; availability of technical support in target markets |
| Smart Building & Infrastructure | Intelligent architectural lighting for energy management and aesthetics | Reduces energy costs and enhances building appeal with programmable lighting schemes | Scalability of LED systems; integration capability with building management systems (BMS); sourcing from certified manufacturers |
In smart manufacturing, LED strips controlled by Raspberry Pi are widely used as visual indicators on assembly lines. By programming different colors and blinking patterns, production managers can instantly identify machine status or faults, thereby minimizing downtime and enhancing quality control. For international buyers, particularly in Africa and South America where infrastructure variability exists, sourcing robust and industrial-grade components that ensure long-term reliability and power supply stability is critical.
Within the retail and hospitality sectors, the combination of LED strips with Raspberry Pi allows businesses to create dynamic and interactive lighting displays that adapt to customer behavior or promotional events. This application drives customer engagement and improves sales conversion rates. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize suppliers offering flexible color control options and seamless IoT integration, along with local support to facilitate installation and maintenance.
In agriculture and horticulture, programmable LED strips provide tailored light spectra to optimize plant growth cycles indoors or in greenhouses. This precise control over light quality boosts crop yields while lowering energy consumption. For B2B buyers in regions like Kenya and Brazil, it is essential to source high-efficiency, weather-resistant LED strips that comply with local electrical safety standards to ensure sustainable operation.
The transportation and logistics industry benefits from LED strips integrated with Raspberry Pi for vehicle interior lighting and cargo area alerts. These programmable lighting systems enhance safety by signaling operational status or hazards during loading and transit. Buyers must focus on sourcing vibration-resistant LED strips with low power requirements and accessible technical support to maintain operational continuity across diverse geographic markets.
Lastly, in smart building and infrastructure, LED strips controlled by Raspberry Pi enable intelligent architectural lighting solutions that combine aesthetics with energy management. Programmable lighting schemes can reduce energy costs and create appealing environments in commercial and residential buildings. International buyers should evaluate the scalability of LED systems, their compatibility with existing building management systems (BMS), and verify certifications from reputable manufacturers to meet regional compliance and performance expectations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for led strip with raspberry pi
When selecting materials for LED strips integrated with Raspberry Pi controllers, B2B buyers must consider performance, durability, cost-efficiency, and regional compliance standards. The choice of materials directly influences the longevity, safety, and adaptability of the final product, especially across diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in LED strip manufacturing and their strategic implications for international buyers.
1. Flexible Printed Circuit Boards (FPC) – Polyimide or PET Base
Key Properties:
FPCs used as the substrate for LED strips are typically made from polyimide or polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyimide offers excellent thermal stability (up to 260°C), high flexibility, and good chemical resistance. PET is less heat resistant (around 120°C) but more cost-effective and environmentally stable under normal operating conditions.
Pros & Cons:
Polyimide-based FPCs provide superior durability and flexibility, ideal for installations requiring bending or shaping around corners. However, they are more expensive and require sophisticated manufacturing processes. PET substrates are cheaper and easier to source but may degrade faster under high temperatures or UV exposure.
Impact on Application:
For outdoor or industrial applications in hot climates (e.g., Middle East, parts of Africa), polyimide substrates ensure longer lifespan and reliability. PET-based strips suit indoor or controlled environments, common in European or South American office and retail settings.
Regional Considerations:
Buyers in Europe and the UK often require compliance with RoHS and REACH regulations, favoring polyimide for its eco-friendly profile. In Africa and South America, cost sensitivity may drive preference toward PET-based FPCs, provided local environmental conditions are moderate. Understanding ASTM D-3359 (adhesion) and IPC standards for FPCs is critical for quality assurance.
2. LED Chip Encapsulation – Epoxy Resin vs. Silicone
Key Properties:
Epoxy resin encapsulation is rigid, with good adhesion and chemical resistance but limited flexibility and UV stability. Silicone encapsulation offers excellent flexibility, high thermal stability (up to 200°C), and superior resistance to UV and weathering.
Pros & Cons:
Epoxy is cost-effective and widely used but prone to yellowing and cracking under prolonged UV exposure. Silicone encapsulation, though more expensive, extends LED lifespan significantly in outdoor or harsh environments.
Impact on Application:
For outdoor installations in regions with intense sunlight (e.g., Middle East, Kenya), silicone encapsulation is preferable to maintain color fidelity and durability. Epoxy encapsulation fits well for indoor applications with controlled lighting and temperature, typical in European commercial spaces.
Regional Considerations:
International buyers should verify compliance with IEC 60529 (Ingress Protection) ratings, as encapsulation affects water and dust resistance. Silicone’s higher IP ratings offer advantages in humid or dusty environments common in South America and Africa.
3. Conductive Traces – Copper with Surface Finish (Tin, Gold, or Silver)
Key Properties:
Copper is the standard conductive material due to its excellent electrical conductivity. Surface finishes like tin, gold, or silver protect copper from oxidation and improve solderability.
Pros & Cons:
Tin finishes are cost-effective but prone to oxidation in high-humidity environments. Gold finishes provide superior corrosion resistance and longevity but at a higher cost. Silver offers excellent conductivity but can tarnish and is less common.
Impact on Application:
In humid or coastal regions (e.g., parts of Africa and South America), gold-plated copper traces ensure reliable connections over time. Tin-plated copper is suitable for dry, indoor environments, prevalent in European and Middle Eastern offices.
Regional Considerations:
Buyers should confirm adherence to IPC-4552 standards for surface finishes and consider local environmental conditions to avoid premature failure. Gold plating is often preferred in high-reliability sectors such as industrial automation in Europe.
4. Protective Coatings – UV-Resistant Polyurethane vs. Acrylic
Key Properties:
Protective coatings shield LED strips from moisture, dust, and mechanical damage. UV-resistant polyurethane coatings offer excellent weatherability and abrasion resistance. Acrylic coatings are easier to apply and cheaper but less durable under UV exposure.
Pros & Cons:
Polyurethane coatings enhance outdoor durability but increase manufacturing complexity and cost. Acrylic coatings are suitable for indoor use with minimal UV exposure but degrade faster outdoors.
Impact on Application:
For outdoor LED strip installations in the Middle East or African markets with high solar exposure, polyurethane coatings significantly improve product lifespan. European buyers installing indoor lighting may opt for acrylic coatings to balance cost and protection.
Regional Considerations:
Compliance with international standards such as ASTM D-4366 (UV resistance) is essential. Buyers should also consider local climatic factors and warranty requirements when selecting protective coatings.
| Material | Typical Use Case for led strip with raspberry pi | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyimide Flexible PCB | Flexible, high-temperature applications, outdoor installations | High thermal stability and durability | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| PET Flexible PCB | Indoor, cost-sensitive applications | Cost-effective and easy to source | Lower heat and UV resistance | Low |
| Silicone LED Chip Encapsulation | Outdoor, high UV exposure environments | Excellent UV and thermal resistance | Higher material cost | High |
| Epoxy LED Chip Encapsulation | Indoor, controlled environments | Cost-effective and good chemical resistance | Prone to yellowing and cracking outdoors | Low |
| Gold-Plated Copper Conductive Traces | High-reliability, humid or corrosive environments | Superior corrosion resistance and longevity | Expensive surface finish | High |
| Tin-Plated Copper Conductive Traces | Indoor, low-humidity environments | Cost-effective and widely available | Susceptible to oxidation in humid conditions | Low |
| UV-Resistant Polyurethane Coating | Outdoor, harsh weather conditions | Excellent abrasion and UV resistance | Increased manufacturing complexity and cost | Medium |
| Acrylic Protective Coating | Indoor, low UV exposure environments | Easy application and lower cost | Less durable under UV exposure | Low |
This material selection guide equips B2B buyers with actionable insights to optimize LED strip products integrated with Raspberry Pi controllers for diverse international markets. By aligning material properties with regional environmental and regulatory requirements, buyers can ensure product performance, compliance, and cost-effectiveness tailored to their target applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for led strip with raspberry pi
The manufacturing of LED strips integrated with Raspberry Pi control modules involves a complex, multi-stage process combining electronics assembly with precision component integration. For international B2B buyers—especially those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—understanding these manufacturing stages and quality assurance protocols is critical to ensuring product reliability, compliance, and optimal performance.
Manufacturing Process Overview
1. Material Preparation
The process begins with sourcing and preparing raw materials. High-quality components such as SMD LEDs (e.g., SMD5050 or WS2812B Neopixels), flexible PCB substrates, MOSFET transistors, resistors, capacitors, and Raspberry Pi microcontroller boards are procured from certified suppliers. Material preparation includes:
- Inspection and verification of component specifications against design requirements.
- Surface treatment of PCBs to ensure solderability and durability.
- Cutting and shaping of flexible PCB strips to required lengths.
Material quality at this stage directly impacts the longevity and functionality of the final product.
2. Forming and PCB Assembly
Next is the formation and assembly of the LED strip circuitry:
- Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is used to place LEDs and electronic components onto the flexible PCB. Automated pick-and-place machines ensure precision placement to support uniform lighting and electrical performance.
- Soldering is typically performed using reflow ovens, which provide consistent heat profiles to ensure robust solder joints without damaging sensitive components.
- For Raspberry Pi integration, connector interfaces (e.g., GPIO headers, jumper wires) are soldered or mechanically assembled to enable seamless communication between the LED strip and the microcontroller.
3. Component and Module Assembly
This stage focuses on integrating the LED strip with control electronics:
- MOSFETs and power management units are installed to regulate current flow, critical for controlling brightness and color mixing.
- The Raspberry Pi module is mounted, often within protective casings, and wired to the LED strip and power supply.
- Additional components such as power jacks, resistors for signal conditioning, and heat sinks may be added depending on design complexity.
Automated and manual assembly lines work in tandem to maintain efficiency while accommodating customization.
4. Finishing and Packaging
Finishing steps ensure durability and ease of installation:
- Protective coatings or laminates are applied to the LED strip for water resistance and mechanical protection, important for outdoor or industrial applications.
- Cutting and connector attachment are finalized, with options for custom lengths or plug-and-play connectors.
- Comprehensive packaging solutions safeguard the product during transit and storage, with clear labeling for compliance and usage instructions.
Quality Assurance and Control (QA/QC) Protocols
Quality assurance is paramount for B2B buyers who demand consistent performance and compliance with international standards. Key QA/QC elements include:
International and Industry Standards
- ISO 9001: The foundational quality management system standard ensuring manufacturers implement structured processes, continual improvement, and customer satisfaction mechanisms.
- CE Marking: Mandatory for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- RoHS Compliance: Restriction of hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, critical for European and global markets.
- UL Certification: Especially important for buyers in markets requiring electrical safety certification.
- API or Industry-Specific Certifications: For buyers integrating LED strips into larger industrial or automotive systems, relevant certifications may apply.
Quality Control Checkpoints
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Verifies the quality of raw materials and components before manufacturing. This includes visual inspections, electrical testing of LEDs, and component traceability checks.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during assembly, IPQC involves monitoring solder joint quality, correct placement of components, and functional testing of circuit segments to detect defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing post-assembly, including full functionality tests, visual inspection for cosmetic defects, and packaging verification.
Common Testing Methods
- Electrical Testing: Verifies voltage, current, and signal integrity to ensure LEDs and control circuits function within specifications.
- Optical Testing: Measures brightness, color accuracy, and uniformity across the LED strip, crucial for lighting applications.
- Environmental Stress Testing: Includes thermal cycling, humidity exposure, and vibration testing to simulate real-world operating conditions.
- Safety Testing: Checks for electrical insulation resistance, grounding effectiveness, and compliance with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards.
Verifying Supplier Quality for International Buyers
B2B buyers should adopt a proactive approach to verify supplier quality, especially when sourcing from emerging markets or unfamiliar regions.
- Factory Audits: On-site inspections or virtual audits assess manufacturing capabilities, equipment condition, workforce skills, and adherence to quality processes such as ISO 9001.
- Review of Quality Documentation: Request and review quality manuals, process flow charts, inspection records, and test reports to understand the supplier’s quality culture.
- Third-Party Inspections: Independent quality inspection agencies can perform sampling inspections, functional testing, and certification verification on behalf of the buyer.
- Sample Testing: Procuring and testing product samples in the buyer’s own labs or through third-party labs ensures product performance aligns with contractual specifications.
QC and Certification Nuances for Regional Buyers
Africa and South America:
Buyers in these regions should emphasize supplier compliance with international standards to avoid customs delays and ensure product safety. Given logistical challenges, partnering with suppliers offering robust packaging and clear documentation is critical. Local regulations may require additional certifications or testing; buyers should liaise with local authorities or consultants.
Middle East:
Products often need to meet GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council) standards alongside CE and RoHS. Buyers should verify that suppliers understand these regional requirements and can provide relevant certificates. Environmental factors such as high temperatures also necessitate rigorous thermal testing.
Europe (e.g., UK):
Post-Brexit, UK buyers should verify both CE and UKCA markings on products. The European market places high value on sustainability and environmental compliance; suppliers with clear RoHS and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) compliance will be preferred.
General Recommendations:
- Insist on traceability for all components and materials.
- Ensure suppliers have a robust corrective action system to handle defects or non-conformities.
- Engage in long-term partnerships with manufacturers committed to continuous quality improvement and transparent communication.
- Leverage digital tools for remote monitoring and quality data exchange, especially when physical audits are challenging.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing stages and embedding rigorous quality assurance protocols, international B2B buyers can secure LED strip with Raspberry Pi solutions that meet performance, safety, and regulatory expectations, thereby reducing risk and enhancing market competitiveness.
Related Video: LED Light Making Process | How LED Lights Made Inside Factory | Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for led strip with raspberry pi Sourcing
Cost Components Breakdown
When sourcing LED strips integrated with Raspberry Pi controllers for B2B applications, understanding the detailed cost structure is essential to optimize procurement strategies and ensure competitive pricing.
-
Materials: The primary cost drivers include the RGB LED strips (typically SMD5050 or WS2812B types), Raspberry Pi boards (various models depending on performance needs), MOSFETs for switching, power supplies (12V DC), wiring, and connectors. Quality of components, such as LED chip brand or Raspberry Pi model (e.g., Pi 4 vs Pi Zero), significantly impacts cost.
-
Labor: Assembly involves soldering, wiring, and testing. Labor costs vary widely by manufacturing location. For buyers in Africa, South America, or the Middle East, sourcing from local or regional manufacturers can reduce labor costs and lead times compared to European suppliers.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: Includes factory utilities, equipment depreciation, and indirect labor. Overhead allocation depends on production scale and facility efficiency. Larger volume orders usually benefit from lower overhead per unit.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling for PCB assembly, custom enclosures, or cable harnesses can add upfront costs. For customized LED strip lengths or Raspberry Pi integration kits, tooling amortization is a factor in pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Testing LED functionality, Raspberry Pi performance, and electrical safety are critical. Certified quality control processes (e.g., ISO 9001) add to cost but ensure reliability, which is crucial for B2B buyers targeting professional applications.
-
Logistics: Freight charges, import duties, and customs clearance costs depend on shipping mode (air vs sea), Incoterms, and destination country. For buyers in Kenya or South America, import tariffs and local taxes can significantly influence landed cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add margins to cover profit and contingencies. Margins vary by supplier type (distributor vs contract manufacturer) and negotiation leverage.
Key Price Influencers for B2B Buyers
-
Order Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders reduce unit cost by spreading fixed costs and enabling bulk discounts. However, some suppliers impose high MOQs that may not align with smaller buyers’ budgets, especially in emerging markets.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized LED strip lengths, specific Raspberry Pi models, or added features (e.g., waterproofing, IP ratings) increase costs. Buyers should clearly define technical requirements to avoid scope creep.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality LEDs with longer lifespans or Raspberry Pi boards with official certifications command premium prices. Certifications like CE, RoHS, or UL ensure compliance with regional regulations, impacting market access in Europe or the Middle East.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier location, reputation, lead times, and after-sales support influence pricing. Established European suppliers may charge more but offer faster shipping and better warranty terms. Conversely, Asian manufacturers often provide cost advantages but require careful vetting.
-
Incoterms and Payment Terms: The choice of Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP) affects who bears shipping and customs costs. Payment terms (advance, letter of credit, net 30/60) also impact cash flow and negotiation flexibility.
Strategic Buyer Tips for International B2B Procurement
-
Negotiate Beyond Unit Price: Discuss tooling amortization, payment terms, warranty, and after-sales service. For buyers in Africa and South America, negotiating local assembly or partial manufacturing can reduce import duties and shipping costs.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Factor in not only purchase price but also logistics, customs, installation, maintenance, and potential downtime. Higher initial costs for certified, reliable components often reduce long-term expenses.
-
Leverage Regional Trade Agreements: For European buyers, sourcing within the EU can eliminate tariffs and simplify compliance. Middle Eastern buyers should explore GCC or other regional agreements for favorable terms.
-
Demand Transparency in Pricing: Request detailed cost breakdowns to identify savings opportunities. Transparent suppliers help buyers understand price drivers and avoid hidden fees.
-
Plan for Lead Times and Buffer Stock: Due to global supply chain variability, especially for Raspberry Pi boards, order with adequate lead times and consider safety stock to avoid production delays.
-
Validate Supplier Credentials: Use certifications, factory audits, and sample orders to ensure quality and reliability, critical for maintaining brand reputation in competitive markets.
Disclaimer: Pricing and cost structures for LED strips with Raspberry Pi integration vary widely based on specifications, order quantities, supplier location, and market conditions. The above analysis provides indicative guidance to assist international B2B buyers in making informed sourcing decisions.
Spotlight on Potential led strip with raspberry pi Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘led strip with raspberry pi’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for led strip with raspberry pi
Critical Technical Properties for LED Strip with Raspberry Pi Integration
When sourcing LED strips designed to interface with Raspberry Pi controllers, understanding key technical specifications is vital for ensuring product quality, compatibility, and performance in your projects or product lines.
-
LED Chip Type (e.g., SMD5050 vs. SMD3528):
LED chips define the color capability and brightness. SMD5050 chips contain three color diodes (red, green, blue) enabling full RGB color mixing, essential for dynamic lighting effects controlled by Raspberry Pi. SMD3528 chips have a single color per diode, limiting color flexibility but often reducing cost. For B2B buyers, selecting the right chip type aligns with end-use requirements and price targets. -
Voltage and Current Ratings (Typically 12V DC, 2A+):
LED strips commonly operate at 12V DC with varying amperage depending on length and LED density. Ensuring the power supply matches these ratings is crucial to avoid underpowering (dim lights) or overloading (potential damage). For buyers, specifying correct voltage/current safeguards operational reliability and reduces warranty claims. -
Control Interface and Pin Configuration:
Standard RGB LED strips used with Raspberry Pi often feature 4-pin connectors (12V, R, G, B) for analog PWM control via MOSFETs. Alternatively, addressable LED strips (e.g., WS2812B/Neopixels) use a single data line for individual LED control. Understanding these interfaces impacts hardware compatibility and software integration, influencing procurement choices. -
Gate Threshold Voltage of MOSFETs (Max 3.3V Logic Level):
The Raspberry Pi GPIO pins output 3.3V signals. MOSFETs used to switch LED channels must fully turn on at this voltage to achieve optimal brightness. Logic-level MOSFETs (e.g., IRLZ34N) ensure efficient switching. Buyers should verify MOSFET specifications to avoid dim or flickering LEDs and ensure energy efficiency. -
LED Density and Length (LEDs per Meter):
LED strip density, often expressed as LEDs per meter (e.g., 30, 60, 144), affects brightness, resolution of lighting effects, and power consumption. Higher densities provide smoother color gradients but increase cost and power needs. Selecting the appropriate density is a balance between application requirements and budget. -
Material and IP Rating (Ingress Protection):
The physical construction, including PCB quality and protective coatings (silicone, epoxy), determines durability and suitability for environments (indoor vs. outdoor). IP ratings (e.g., IP20, IP65) indicate resistance to dust and water. Buyers must align product specs with installation environments to ensure longevity and reduce maintenance costs.
Key Industry and Trade Terms for International B2B Buyers
Familiarity with common terminology in electronics and international trade streamlines communication and negotiation with suppliers and logistics partners.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer):
Refers to companies that produce components or products sold under another brand’s name. Many LED strips and Raspberry Pi accessories are OEM-manufactured, allowing buyers to customize branding or specifications. Understanding OEM relationships aids in sourcing tailored solutions or volume discounts. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity):
The smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. MOQs affect inventory planning and cash flow. For buyers in emerging markets or smaller enterprises, negotiating lower MOQs or consolidating orders can improve accessibility and reduce risk. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation):
A formal inquiry sent to suppliers requesting pricing, lead times, and terms for specified quantities and product configurations. RFQs are critical in the B2B procurement process to compare offers objectively and secure favorable conditions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms):
Standardized trade terms defining responsibilities, risks, and costs between buyers and sellers during shipping (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP). Understanding Incoterms helps buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe evaluate total landed costs and select appropriate logistics arrangements. -
Lead Time:
The duration between placing an order and receiving the goods. Lead time impacts project scheduling and inventory management. Suppliers with shorter, reliable lead times are preferred to reduce downtime and improve market responsiveness. -
BOM (Bill of Materials):
A comprehensive list of components and materials required to assemble a product. For complex integrations like Raspberry Pi-controlled LED strips, a clear BOM facilitates cost estimation, quality control, and supplier coordination.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimize supply chains, and ensure seamless integration of LED strips with Raspberry Pi controllers for their diverse applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the led strip with raspberry pi Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for LED strips integrated with Raspberry Pi controllers is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for customizable lighting solutions in industrial automation, smart buildings, entertainment, and retail sectors. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are capitalizing on the versatility and cost-effectiveness of Raspberry Pi-driven LED strips to develop innovative lighting and display applications.
Key market drivers include:
- Rising adoption of IoT and smart technologies: The Raspberry Pi’s flexibility enables seamless integration with IoT ecosystems, allowing businesses to deploy intelligent lighting systems with remote control, automation, and data analytics capabilities.
- Customization and scalability: LED strips controlled via Raspberry Pi offer granular color control, dynamic effects, and energy-efficient operation, which are highly valued in commercial and industrial projects.
- Cost-sensitive sourcing: Buyers in emerging markets such as Kenya and parts of South America prioritize affordable yet reliable components, often sourcing from Asia-based manufacturers who provide competitive pricing and customizable kits.
- Supply chain diversification: Due to geopolitical tensions and logistics challenges, companies are increasingly seeking alternative suppliers and local distributors in Europe and the Middle East to reduce lead times and mitigate risks.
- Technological advancements: The introduction of new LED chip types (e.g., WS2812B Neopixels) and improved Raspberry Pi models (e.g., Raspberry Pi 5) enhances performance and broadens application possibilities.
B2B buyers should monitor trends like modular LED strip designs that simplify integration, increased demand for embedded software solutions, and emerging standards for interoperability. Leveraging platforms that offer comprehensive Raspberry Pi kits and technical support can also accelerate time-to-market and reduce development costs.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a critical consideration for international B2B buyers in the LED strip with Raspberry Pi sector. The environmental impact of electronic components—including LED strips and Raspberry Pi units—stems largely from raw material extraction, manufacturing processes, and end-of-life disposal.
Key sustainability insights for B2B buyers:
- Material selection: Opt for LED strips manufactured using lead-free solder and halogen-free materials to minimize toxic waste. Suppliers offering chips with reduced energy consumption and longer lifespans contribute to lowering carbon footprints.
- Energy efficiency: Raspberry Pi-controlled LED strips enable precise dimming and color control, which can significantly reduce power consumption in commercial lighting installations compared to traditional systems.
- Ethical supply chains: Establishing traceability is essential to ensure components are sourced from conflict-free regions, especially regarding critical raw materials like rare earth elements used in LEDs. Partnering with suppliers who maintain transparent labor practices and comply with international standards (e.g., ISO 14001 for environmental management) safeguards brand reputation.
- Green certifications: Buyers should seek products certified under recognized eco-labels such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals), and ENERGY STAR. These certifications guarantee compliance with environmental regulations and promote sustainable manufacturing.
- Circular economy initiatives: Engaging suppliers who offer recycling programs or refurbishing options for Raspberry Pi boards and LED components supports waste reduction and aligns with corporate social responsibility goals.
For regions like Europe and the Middle East, where regulatory frameworks around electronic waste and sustainability are increasingly stringent, compliance is not only a legal obligation but a competitive advantage. African and South American buyers can leverage sustainable sourcing to access new markets and partnerships aligned with global ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) trends.
Brief Evolution and Historical Context
The convergence of LED strip technology with Raspberry Pi controllers marks a significant evolution in programmable lighting solutions. LED strips, initially used for basic decorative lighting, have undergone rapid innovation with the introduction of RGB and individually addressable LEDs such as WS2812B “Neopixels.” Concurrently, the Raspberry Pi platform, launched in 2012 as an affordable single-board computer, revolutionized embedded control by offering accessible programming and connectivity options.
This synergy has enabled businesses to move beyond static lighting to dynamic, networked systems capable of real-time interaction and complex visual effects. Over the last decade, improvements in LED chip efficiency, Raspberry Pi processing power, and open-source software ecosystems have expanded the application scope from hobbyist projects to industrial-grade deployments.
For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution helps identify the most advanced and cost-effective solutions available today, while anticipating future innovations such as AI-driven lighting control and integration with smart city infrastructure.
Related Video: Raspberry Pi LED Matrix Display
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of led strip with raspberry pi
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers of LED strips compatible with Raspberry Pi for international B2B sourcing?
To ensure supplier reliability, verify company credentials such as business licenses and export certifications relevant to your region (e.g., CE for Europe, RoHS compliance). Request product samples and technical datasheets to assess quality and compatibility with Raspberry Pi models. Check references from previous international clients and review third-party audits or factory inspection reports. For African, South American, Middle Eastern, and European markets, partner with suppliers experienced in cross-border trade and familiar with local import regulations to minimize compliance risks. -
What customization options are typically available for LED strips integrated with Raspberry Pi, and how can I negotiate these?
Common customizations include LED chip type (e.g., SMD5050 vs. WS2812B), strip length, power ratings, connector types, and software compatibility. Some suppliers also offer pre-installed MOSFET drivers or tailored firmware for specific applications. When negotiating, clearly specify your technical requirements and intended use cases to avoid misunderstandings. Request a prototype or pilot batch before full production. Leverage volume commitments to negotiate pricing and customization lead times, especially when sourcing from suppliers in Asia for distribution in Africa, South America, or Europe. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for LED strip with Raspberry Pi solutions, and how do payment terms vary internationally?
MOQs can range from 100 to 500 units depending on customization complexity and supplier capacity. Lead times generally span 4 to 8 weeks, factoring in production, testing, and shipping. International buyers should clarify if suppliers have regional warehouses or fulfillment centers to reduce delivery times. Payment terms often include a 30% deposit upfront and balance before shipment; however, trusted buyers might negotiate net 30 or net 60 terms. Use escrow services or letters of credit for higher-value transactions to mitigate payment risks across regions like the Middle East or South America. -
What quality assurance certifications should I demand to ensure product safety and reliability for global markets?
Request compliance with international standards such as CE (Europe), UL or ETL (North America), RoHS (hazardous substances), and FCC (electromagnetic compatibility). For LED strips powered via Raspberry Pi, ensure the MOSFETs and power supplies meet relevant electrical safety standards. Suppliers should provide test reports, including thermal performance and lifespan testing. Certificates of conformity and factory inspection reports help validate quality. This is especially critical when importing to regulated markets like the UK or the European Union. -
How can I optimize logistics and shipping for bulk orders of LED strips with Raspberry Pi controllers to regions like Africa and South America?
Choose suppliers with experience in international freight forwarding and customs clearance in your target markets. Consolidate shipments to reduce per-unit freight costs and consider sea freight for large volumes, balancing speed and budget. Verify packaging robustness to protect sensitive electronics during transit and account for local import tariffs and taxes in your cost analysis. Engage local customs brokers familiar with import regulations in Kenya, Brazil, or the Middle East to avoid delays. Establish clear Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) to delineate responsibilities and reduce disputes. -
What dispute resolution mechanisms are recommended when dealing with international suppliers of LED strip and Raspberry Pi products?
Incorporate clear dispute resolution clauses in contracts, specifying jurisdiction and arbitration venues (e.g., ICC arbitration in Switzerland). Use detailed purchase agreements covering product specifications, delivery timelines, and quality acceptance criteria to minimize misunderstandings. Retain all communications and quality inspection reports as evidence. For suppliers in Asia or Europe, consider involving third-party inspection agencies before shipment. Payment terms tied to satisfactory inspection can incentivize compliance. Promptly address issues through negotiation before escalating to formal dispute channels. -
How do I ensure software compatibility and support for LED strips controlled by Raspberry Pi in a B2B context?
Confirm that the supplier provides or supports open-source or documented control libraries compatible with popular Raspberry Pi OS versions. Verify the availability of example code, APIs, and technical support to facilitate integration into your applications. For complex LED strips like WS2812B Neopixels, ensure timing and voltage requirements match your Raspberry Pi model. International buyers should request multilingual documentation and consider suppliers offering remote technical assistance or training to streamline deployment across diverse markets. -
Are there specific considerations for sourcing LED strips with Raspberry Pi in emerging markets like Kenya or Brazil?
Emerging markets may face challenges such as limited local technical expertise, import restrictions, and fluctuating currency rates. Prioritize suppliers with local or regional representation to ease after-sales support and warranty claims. Consider modular kits with clear assembly instructions to reduce dependence on specialized labor. Factor in extended lead times due to customs and infrastructure limitations. Engage with local industry associations or trade bodies to better understand regulatory frameworks and optimize supply chain resilience in these regions.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for led strip with raspberry pi
The integration of LED strips with Raspberry Pi technology offers international B2B buyers a versatile, customizable solution for a wide range of lighting and display applications. Key sourcing considerations include selecting high-quality LED components such as SMD5050 or WS2812B chips, ensuring compatible power supplies, and procuring logic-level MOSFETs for efficient control. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate technical reliability, provide clear component specifications, and support local or regional distribution to optimize lead times and reduce costs.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Strategic sourcing is crucial for mitigating risks associated with electronic component variability and supply chain disruptions. Establishing relationships with reputable manufacturers and distributors enables buyers to negotiate favorable terms, secure consistent quality, and access technical support—essential for scalable projects and innovative deployments. Additionally, leveraging modular kits and pre-tested assemblies can accelerate time-to-market while ensuring compatibility with Raspberry Pi platforms.
Looking ahead, the growing demand for smart lighting solutions in emerging markets presents significant growth opportunities. Buyers are encouraged to actively engage with suppliers offering cutting-edge LED strip technologies and integrated control systems. Embracing strategic partnerships and investing in supplier development will empower businesses to deliver differentiated, cost-effective solutions that meet evolving customer needs across diverse international markets.
