Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for led strip lights not working
In today’s fast-evolving global lighting industry, LED strip lights have become indispensable for a wide array of applications—from architectural accents and retail displays to industrial installations and outdoor environments. However, the challenge of LED strip lights not working remains a critical concern that can significantly impact project timelines, operational efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. For international B2B buyers operating across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the root causes and solutions behind these failures is essential for securing reliable products and maintaining competitive advantage.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted aspects influencing LED strip light performance, including types and materials, manufacturing standards, quality control protocols, and supplier reliability. It further explores market dynamics and cost considerations tailored for diverse regional requirements and infrastructure conditions. By addressing common technical pitfalls—such as improper installation, power supply mismatches, and connector failures—this resource equips buyers with actionable insights to mitigate risks.
Key areas covered include:
– Varieties of LED strip lights suited for different environments (waterproof, tunable white, high CRI)
– Critical manufacturing and QC checkpoints that ensure durability and performance
– Supplier evaluation strategies emphasizing transparency and compliance
– Cost-benefit analysis aligned with regional market trends and logistics
– Frequently asked questions that clarify installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting
Armed with this knowledge, B2B buyers from regions like South Africa and the UK can confidently navigate supplier negotiations, optimize procurement, and ultimately secure LED strip lighting solutions that deliver consistent, long-lasting results in their markets.
Understanding led strip lights not working Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Supply Failure | LED strips fail to light due to incompatible or faulty drivers | Commercial lighting, retail displays, architectural | + Easy to diagnose – Requires matching voltage & wattage |
| Connector and Wiring Issues | Loose, damaged, or incorrect connectors causing intermittent/no light | Installation projects, event lighting, signage | + Simple fix with connectors – Can cause downtime if not pre-checked |
| LED Chip or PCB Damage | Individual LEDs or entire segments not working due to physical damage or manufacturing defect | Industrial lighting, manufacturing facilities | + Long lifespan if quality assured – Replacement may require full strip swap |
| Overloading and Voltage Drop | Dimming or non-functioning LEDs at strip ends due to excessive length or insufficient power | Large-scale architectural, outdoor installations | + Enables long runs – Requires careful power planning and segmentation |
| Environmental Exposure Failure | Moisture, dust, or heat causing strip malfunction, especially in non-waterproof variants | Outdoor, marine, or harsh-environment projects | + Waterproof variants available – Higher upfront cost and installation complexity |
Power Supply Failure
Power supply issues are among the most common causes of LED strip lights not working. For B2B buyers, ensuring the power supply matches the LED strip’s voltage and wattage requirements is critical to avoid failure. This type is particularly relevant in commercial and architectural projects where consistent illumination is essential. Buyers should prioritize reliable, certified power supplies and consider regional voltage standards to minimize compatibility issues and downtime.
Connector and Wiring Issues
Faulty or loose connectors, improper wiring, or poor soldering can cause LED strips to malfunction. This problem often arises during installation or maintenance phases, especially in event lighting or signage. B2B buyers should source high-quality connectors and consider pre-assembled wiring harnesses to reduce installation errors. Training installation teams and verifying connections before final commissioning can save costs related to troubleshooting and repairs.
LED Chip or PCB Damage
Physical damage or manufacturing defects in the LED chips or printed circuit boards (PCBs) can lead to partial or full strip failure. This is a significant consideration for industrial or manufacturing environments where equipment robustness is paramount. Buyers should work with suppliers offering stringent quality controls and warranty coverage. For ease of maintenance, modular strip designs that allow segment replacement can be advantageous.
Overloading and Voltage Drop
When LED strips are installed in long runs without adequate power distribution, voltage drop can cause LEDs at the far end to dim or fail. This issue is common in large-scale architectural or outdoor installations. B2B purchasers must plan power supplies and segment lengths carefully, possibly incorporating multiple injection points or higher-voltage strips. Proper design minimizes energy waste and ensures uniform lighting, critical for customer satisfaction in commercial projects.
Environmental Exposure Failure
LED strips exposed to moisture, dust, or extreme temperatures may fail if not designed for such conditions. Waterproof (IP65+) or even submersible (IP68) strips are essential for outdoor, marine, or industrial applications. Buyers targeting these markets should prioritize strips with appropriate ingress protection ratings and compatible accessories. Although these variants have higher upfront costs, they reduce long-term replacement and maintenance expenses in harsh environments.
Key Industrial Applications of led strip lights not working
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of led strip lights not working | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail & Visual Merchandising | Identifying and troubleshooting LED strip light failures in display lighting | Ensures consistent product presentation and customer attraction | Seek suppliers with reliable technical support and quick replacement policies; consider IP-rated strips for humid climates in Africa or South America |
| Hospitality & Interior Design | Diagnosing LED strip lighting issues in ambient and accent lighting | Maintains ambiance and customer experience, reducing downtime costs | Prioritize energy-efficient, dimmable LED strips with warranty and local service centers in Europe and Middle East markets |
| Manufacturing & Warehousing | Monitoring LED strip lighting in safety and operational zones | Enhances workplace safety and productivity by ensuring proper illumination | Source durable, industrial-grade LED strips with robust connectors and power supplies suited for harsh environments in South Africa and Middle East |
| Automotive & Transport | Addressing LED strip failures in vehicle interior and exterior lighting | Improves vehicle safety and aesthetic appeal, critical for fleet operators | Choose LED strips compliant with international automotive standards and capable of withstanding vibration and temperature extremes |
| Event Management & Exhibition | Managing LED strip lighting faults in temporary setups and stages | Guarantees reliable, flexible lighting solutions for dynamic event environments | Opt for modular, easy-to-install LED strips with quick connectors and adaptable power options suitable for South American and European markets |
Retail & Visual Merchandising
In retail environments, LED strip lights are crucial for highlighting products and creating inviting displays. When LED strips fail, it disrupts visual appeal and can negatively impact sales. Businesses in Africa and South America must emphasize sourcing LED strips with strong after-sales support and IP ratings to handle humidity. Quick troubleshooting and replacement are essential to minimize downtime and maintain consistent lighting quality, which is vital for attracting customers and showcasing merchandise effectively.
Hospitality & Interior Design
Hotels, restaurants, and lounges rely heavily on LED strip lighting for mood and accent lighting. Non-functional LED strips can degrade the guest experience and lead to costly repairs. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should focus on energy-efficient, dimmable LED strips that offer longevity and come with solid warranties. Additionally, local service availability reduces downtime, ensuring that lighting enhances ambiance without frequent disruptions.
Manufacturing & Warehousing
LED strip lights are used extensively for safety markings and operational illumination in manufacturing plants and warehouses. Failure of these lights can compromise worker safety and slow operations. International buyers, especially in South Africa and the Middle East, need to source industrial-grade LED strips designed to withstand dust, moisture, and temperature fluctuations. Reliable connectors and power supplies are critical to ensure continuous operation in demanding environments.
Automotive & Transport
LED strips are increasingly integrated into vehicle interiors and exteriors for both functional and decorative purposes. Failures can affect safety signals and brand image, particularly for commercial fleets. Buyers should prioritize LED strips compliant with automotive industry standards and capable of enduring vibration and temperature extremes common in transport sectors. This is particularly relevant for suppliers targeting markets in Europe and South America where stringent regulations apply.
Event Management & Exhibition
Temporary event setups depend on flexible and reliable LED strip lighting to create dynamic atmospheres. Failures can disrupt event schedules and damage reputations. B2B buyers in South America and Europe should select modular LED strips with quick-connect features and adaptable power options to facilitate fast installation and troubleshooting. Durability and ease of maintenance are key to managing the unpredictable conditions of event environments.
Related Video: How To Set Up Govee RGB LED Strip Lights With Corners Angles And More Tips
Strategic Material Selection Guide for led strip lights not working
When addressing the issue of LED strip lights not working, the choice of materials used in manufacturing and installation plays a critical role in product reliability and performance. International B2B buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must consider material properties aligned with environmental conditions, regulatory standards, and cost-efficiency to minimize failures and maximize longevity.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Coating
Key Properties: PVC is widely used as an insulating and protective coating for LED strip lights due to its good electrical insulation, moderate temperature resistance (typically up to 60°C), and flexibility. It offers decent resistance to moisture and chemicals but is less effective under prolonged UV exposure.
Pros & Cons: PVC is cost-effective and easy to manufacture, making it a popular choice for indoor LED strips. However, it can become brittle over time in harsh climates, especially in high UV or extreme temperature environments, which are common in parts of Africa and the Middle East. Its flammability and potential release of harmful gases during combustion are also concerns in strict regulatory markets like the UK and EU.
Impact on Application: PVC-coated strips are suitable for indoor applications or protected outdoor environments. They are less ideal for direct outdoor exposure or industrial settings with chemical exposure, where degradation can cause malfunction.
International Considerations: Buyers in Europe and the UK must ensure PVC materials comply with RoHS and REACH directives limiting hazardous substances. In Africa and South America, where climate extremes vary, selecting PVC with UV stabilizers or opting for alternative coatings may be necessary to prevent premature failure.
Silicone Encapsulation
Key Properties: Silicone offers excellent thermal stability (operating up to 200°C), superior flexibility, and outstanding resistance to UV, moisture, and chemical exposure. It provides effective waterproofing, making it ideal for outdoor and harsh environment applications.
Pros & Cons: Silicone encapsulation significantly enhances LED strip durability and longevity but comes at a higher manufacturing cost and complexity. It is less rigid than PVC, which can complicate certain mounting or installation scenarios.
Impact on Application: Ideal for outdoor, industrial, and marine environments common in South Africa, Middle East, and coastal regions of Europe. Silicone’s resistance to extreme temperatures and chemicals reduces the risk of LED strip lights not working due to environmental degradation.
International Considerations: Silicone materials generally meet international standards such as ASTM and DIN for thermal and chemical resistance. Buyers should verify certifications and ensure suppliers provide documentation for compliance with local electrical and safety standards, especially in regulated markets like the EU.
Aluminum Backing/Heat Sink
Key Properties: Aluminum is commonly used as a backing material or integrated heat sink in LED strip lights. It offers excellent thermal conductivity, helping dissipate heat generated by LEDs, which is crucial for maintaining performance and preventing failure.
Pros & Cons: Aluminum improves LED lifespan by reducing thermal stress but increases product weight and cost. It requires precise manufacturing to ensure proper adhesion and electrical isolation to avoid short circuits.
Impact on Application: Particularly beneficial in high-power LED strips and installations in warm climates such as the Middle East and parts of South America. Proper heat management reduces the likelihood of LED strips not working due to overheating.
International Considerations: Aluminum components must comply with corrosion resistance standards (e.g., ASTM B209, EN 573) to suit humid or coastal environments. Buyers should consider anodized or coated aluminum variants to enhance durability in regions with high humidity or salt exposure.
Copper Conductors
Key Properties: Copper is the standard conductor material in LED strip lights due to its excellent electrical conductivity and flexibility. It supports efficient current flow, reducing voltage drop and improving overall LED performance.
Pros & Cons: Copper is durable and widely available but is susceptible to oxidation and corrosion if not properly protected, which can cause connectivity issues leading to LED strip failure. It also adds to the cost compared to cheaper alternatives like aluminum conductors.
Impact on Application: Essential for reliable electrical performance in all applications, especially in regions with unstable power supplies such as parts of Africa and South America. Proper insulation and protective coatings are critical to prevent corrosion-related failures.
International Considerations: Compliance with international electrical standards (IEC, DIN) and quality certifications (e.g., UL, CE) is vital. Buyers should ensure copper purity and plating quality to meet local safety and performance requirements, particularly in Europe and the UK.
| Material | Typical Use Case for led strip lights not working | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC Coating | Indoor and protected outdoor LED strip insulation | Cost-effective, easy to manufacture | Limited UV and temperature resistance | Low |
| Silicone Encapsulation | Outdoor, industrial, and marine environments | Excellent thermal and chemical resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum Backing | Heat dissipation in high-power LED strips | Superior thermal management | Increased weight and cost | Medium |
| Copper Conductors | Electrical conduction in all LED strip types | High electrical conductivity | Susceptible to corrosion without protection | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide equips international B2B buyers with actionable insights to mitigate LED strip light failures by choosing materials that align with their specific environmental conditions, regulatory frameworks, and cost constraints. Prioritizing materials like silicone encapsulation and aluminum backing for harsh climates or copper conductors for reliable electrical performance can significantly reduce downtime and enhance product satisfaction.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for led strip lights not working
Manufacturing Processes for LED Strip Lights: Ensuring Reliability and Performance
The production of LED strip lights, particularly those designed to minimize failure such as “LED strip lights not working,” involves a series of precise manufacturing stages. Each phase is critical to achieving durable, high-quality lighting solutions that meet the demands of international B2B buyers, especially in markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Material Preparation
Material quality directly impacts the longevity and performance of LED strip lights. This stage involves sourcing high-grade components such as:
- LED chips (commonly SMD types like 3528, 5050, or COB modules) from reputable manufacturers.
- Flexible printed circuit boards (FPCBs) that provide the substrate for LED placement, designed for optimal heat dissipation and flexibility.
- Resistors, capacitors, and connectors with precise electrical specifications.
- Encapsulation materials such as silicone or epoxy for waterproofing and protection.
Material batches undergo incoming quality control (IQC), where suppliers’ certifications and physical inspections ensure compliance with technical specifications.
2. Forming and Circuit Board Assembly
In this phase, the FPCB is prepared and the LEDs and electronic components are mounted using surface mount technology (SMT):
- Solder paste application: Automated machines apply solder paste to designated pads.
- Pick-and-place machines: Precisely position LEDs and components.
- Reflow soldering: A controlled heating process melts the solder paste, securing components firmly to the board.
Automation here reduces human error, ensuring consistent placement and solder quality. Some manufacturers incorporate laser cutting or die-cutting to shape strips accurately.
3. Assembly and Connection
After forming the LED modules, assembly involves:
- Attaching connectors or terminals for power supply compatibility.
- Integrating waterproofing layers (IP65, IP67, or IP68 rated coatings) for outdoor or humid environment applications.
- Adding adhesive backing for easy installation.
This stage often involves manual inspection combined with automated tests to verify connection integrity.
4. Finishing and Packaging
Final touches include:
- Applying protective films or casings.
- Labeling with batch numbers and certifications.
- Packaging tailored for safe international transport, considering humidity, temperature, and mechanical stress during shipment.
Quality Assurance: Critical for Preventing LED Strip Lights Failures
Quality assurance (QA) in LED strip light manufacturing is a multi-tiered process designed to detect faults that could cause the product to fail in the field, such as the common issue of “LED strip lights not working.” B2B buyers must understand these QA processes to select reliable suppliers.
Key International and Industry Standards
- ISO 9001: The global benchmark for quality management systems, ensuring consistent production processes and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: Mandatory for products sold within the European Economic Area, confirming compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- RoHS Compliance: Restricts hazardous substances, critical for environmental and regulatory adherence.
- UL Certification: Important for electrical safety, especially for North American markets but increasingly recognized worldwide.
- IP Ratings (Ingress Protection): Define the degree of protection against dust and water ingress, vital for outdoor or industrial applications.
- API and Other Regional Standards: Certain regions may require specific certifications related to electrical or environmental standards; buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East should verify these with suppliers.
Quality Control Checkpoints
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials and components before production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Real-time monitoring during assembly, including solder joint inspections and component placement accuracy.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of finished products before shipment.
Each checkpoint uses defined criteria to accept or reject batches, ensuring only products meeting specifications proceed.
Common Testing Methods
- Electrical Testing: Verifies voltage, current, and power consumption to match design parameters.
- Functional Testing: Ensures all LEDs light up correctly, without flickering or dimming.
- Thermal Testing: Assesses heat dissipation under operational conditions to prevent overheating.
- Environmental Testing: Simulates humidity, temperature extremes, and water exposure to confirm IP ratings.
- Mechanical Testing: Checks flexibility, adhesion of components, and durability of connectors.
Verifying Supplier Quality: Practical Guidance for International B2B Buyers
For buyers in regions such as South Africa, Brazil, UAE, and the UK, verifying supplier quality is essential to mitigate risks associated with LED strip lights not working. Here are actionable steps:
-
Request Documentation and Certifications: Always obtain ISO 9001 certificates, CE declarations of conformity, RoHS reports, and test data. Confirm these documents are current and issued by accredited bodies.
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Where possible, perform on-site factory audits focusing on manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and worker training. Remote virtual audits can be alternatives if travel is restricted.
-
Third-Party Inspection: Engage independent inspection agencies to verify product quality before shipment. These inspections can include random sampling and destructive testing to ensure reliability.
-
Sample Evaluation: Order pre-production samples and conduct in-house testing aligned with your operational environment to identify potential failures early.
-
Review Production Capacity and Lead Times: Confirm the supplier can maintain quality at scale and meet delivery schedules, especially for large projects.
Quality Assurance Nuances for Different Regions
-
Africa and South America: Buyers should pay close attention to product durability under variable climates (high humidity, dust, temperature swings). Waterproofing and robust thermal management are essential. Local standards may be less stringent, so international certifications become critical.
-
Middle East: High ambient temperatures require LED strips with superior heat dissipation and IP65+ waterproof ratings due to dust and sand exposure. Certifications such as IEC and UL are valued.
-
Europe (e.g., UK): Strict adherence to CE, RoHS, and WEEE directives is mandatory. Buyers often expect detailed technical documentation and traceability for compliance and sustainability concerns.
Conclusion
For international B2B buyers sourcing LED strip lights, understanding the detailed manufacturing processes and rigorous quality assurance protocols is fundamental to avoiding product failures like “LED strip lights not working.” By prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate adherence to international standards, maintain robust QC checkpoints, and welcome verification through audits and third-party inspections, buyers can secure reliable, high-performance LED lighting solutions tailored to their regional needs and industry requirements.
Related Video: LED Light Making Process | How LED Lights Made Inside Factory | Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for led strip lights not working Sourcing
Cost Components in LED Strip Lights Sourcing
When sourcing LED strip lights, especially in contexts where product reliability is critical (e.g., avoiding issues like “LED strip lights not working”), understanding the detailed cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
- Materials: The primary cost driver includes high-quality LEDs, flexible PCB substrates, resistors, connectors, and protective coatings (e.g., waterproofing). Premium materials with better heat dissipation and durability increase costs but reduce failure rates.
- Labor: Skilled labor is required for assembly, soldering, quality checks, and packaging. Labor costs vary significantly by manufacturing location, impacting total sourcing prices.
- Manufacturing Overhead: This covers factory utilities, equipment depreciation, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing lines with automation can lower overhead per unit.
- Tooling: Initial costs for custom molds, dies, and assembly jigs may be required for specialized LED strips or connectors. These are amortized over production volumes.
- Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes including electrical testing, visual inspections, and burn-in testing add to costs but are critical to avoid non-functional products.
- Logistics: Freight, customs duties, and insurance costs vary widely depending on shipping modes (air, sea), origin, and destination countries. For international buyers, these can significantly impact landed costs.
- Margin: Suppliers incorporate profit margins based on market positioning, order size, and relationship with buyers.
Key Price Influencers for LED Strip Lights
Several factors directly influence the final pricing offered by suppliers:
- Order Volume / Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically reduce per-unit costs due to economies of scale and better bargaining power. Buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consolidate demand where possible to leverage this.
- Specifications and Customization: Custom lengths, color temperatures, waterproof ratings (IP65, IP68), or integrated smart controls increase complexity and cost. Standardized products are more cost-efficient.
- Material Quality and Certifications: LED strips with certified components (e.g., RoHS, CE, UL) command higher prices but assure compliance with international safety and environmental standards.
- Supplier Location and Capabilities: Suppliers in Asia often offer competitive pricing but may require longer lead times. European suppliers might have higher prices but offer faster turnaround and localized support.
- Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (FOB, CIF, DDP) affects logistics costs and risk allocation. Buyers should clarify terms to avoid unexpected charges.
Practical Buyer Tips for Cost-Effective Sourcing
- Negotiate Beyond Price: Focus on total value including warranty terms, after-sales service, and payment conditions rather than just unit price.
- Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider installation costs, energy efficiency, maintenance, and failure rates. Higher upfront costs for quality can reduce long-term expenses.
- Leverage Local Import Regulations: Understand tariffs, taxes, and import documentation requirements in your country (e.g., South Africa’s customs or the UK’s post-Brexit regulations) to minimize delays and extra fees.
- Request Samples and Test: Always validate product functionality through samples to avoid sourcing defective batches that cause “LED strip lights not working” issues.
- Consolidate Shipments: Group orders to reduce logistics costs and environmental footprint, especially for buyers in remote or less accessible regions.
- Understand Pricing Nuances: Prices may fluctuate with raw material costs (like copper and semiconductor chips), currency exchange rates, and global supply chain disruptions.
Indicative Pricing Disclaimer
Pricing for LED strip lights varies widely based on the above factors and market conditions. For example, basic non-waterproof 5-meter LED strips may range from $10 to $30 per unit at wholesale volumes, whereas customized, high-CRI or waterproof variants with smart controls can exceed $50 per unit. Buyers should request detailed quotes tailored to their specifications and intended volumes.
By carefully analyzing these cost components and price influencers, international B2B buyers—particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—can optimize sourcing strategies to secure reliable, cost-efficient LED strip lighting solutions that minimize operational risks and maximize return on investment.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Spotlight on Potential led strip lights not working Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘led strip lights not working’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for led strip lights not working
Critical Technical Properties for LED Strip Lights
When evaluating LED strip lights, especially to troubleshoot or prevent issues such as non-functionality, understanding the following technical properties is essential for B2B buyers:
-
Voltage and Current Rating
LED strips commonly operate at 12V or 24V DC. Matching the strip’s voltage with the correct power supply is crucial to avoid underperformance or damage. Current rating per meter affects power consumption and heat generation. For buyers, specifying correct voltage/current ensures compatibility and longevity, minimizing returns and warranty claims. -
IP Rating (Ingress Protection)
The IP rating defines resistance to dust and water. For example, IP20 is suitable for indoor, dry environments, while IP65 or higher protects against moisture and outdoor conditions. Selecting the right IP rating is critical for buyers targeting diverse climates such as humid Middle Eastern or rainy European markets, reducing failure rates due to environmental exposure. -
LED Chip Quality and Material Grade
The quality of LEDs (e.g., Cree, Nichia) and substrate materials (flexible PCB copper thickness, silicone coating) influence brightness, color consistency, and durability. Buyers should prioritize high-grade components to ensure stable performance and reduce flickering or partial failures. -
Cuttable Length and Segment Design
LED strips are designed with specific cut points, usually every 3-6 LEDs, allowing customization of length without damaging the circuit. Understanding segment design helps buyers plan installations accurately and avoid electrical faults caused by improper cutting or connections. -
Thermal Management
Effective heat dissipation through materials like aluminum backing or mounting channels prevents overheating, which can cause LED failure. Buyers should consider thermal properties to maintain operational efficiency and extend product lifespan, particularly in high-temperature regions. -
Color Rendering Index (CRI)
CRI measures the quality of light in rendering colors naturally. High CRI (80+) is important in retail or hospitality sectors where accurate color perception is vital. Buyers focusing on quality lighting solutions should specify appropriate CRI levels to meet end-user expectations.
Key Trade Terminology for LED Strip Light Procurement
Understanding industry jargon streamlines communication and negotiation with suppliers, ensuring clarity and efficient transactions:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to manufacturers producing LED strips that other brands rebrand and sell. For buyers, OEM sourcing can offer cost advantages and customization options but requires due diligence on quality and compliance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest quantity a supplier will accept per order. MOQ impacts pricing, inventory management, and cash flow. Buyers in emerging markets or with smaller projects should negotiate MOQs to match demand without overstocking. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal inquiry sent to suppliers to obtain pricing, lead times, and specifications. Well-structured RFQs help buyers compare offers effectively and ensure suppliers understand technical requirements to avoid costly misunderstandings. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms defining responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs. Common terms include FOB (Free On Board) and DDP (Delivered Duty Paid). Knowing Incoterms empowers buyers to control logistics costs and risks, crucial for cross-border transactions. -
IP Rating Codes
Industry shorthand indicating waterproof and dustproof levels (e.g., IP20, IP65). Buyers must specify required IP codes in procurement documents to ensure product suitability for intended environments. -
Dimmability
Indicates whether LED strips support brightness control via compatible drivers or controllers. For projects requiring ambiance control or energy savings, buyers should confirm dimmability features upfront.
By mastering these technical specifications and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions, reduce product failures, and optimize supply chain efficiency across varied regional markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the led strip lights not working Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global LED strip lighting market has seen rapid expansion driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient and versatile lighting solutions across commercial, residential, and industrial sectors. However, issues such as LED strip lights not working remain a significant challenge, especially for international B2B buyers who must navigate diverse quality standards, installation complexities, and supply chain variabilities. Key market drivers include urbanization, smart building trends, and government incentives promoting green energy solutions.
For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, sourcing reliable LED strip lights requires careful attention to product specifications, voltage compatibility (commonly 12V or 24V), and IP ratings for environmental resistance. In markets such as South Africa and the UK, demand is rising for waterproof and high-CRI (Color Rendering Index) strips suited for harsh climates and premium lighting applications. The adoption of smart lighting controls and wireless dimmers is also accelerating, adding complexity but enabling higher-value integrations.
Emerging sourcing trends emphasize modular LED strip connectors as alternatives to soldering, reducing installation errors that cause non-functionality. Additionally, buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers with robust technical support and quality certifications to mitigate risks of defective products. Regional logistics challenges necessitate partnerships with distributors offering local warehousing or reliable shipping to ensure timely delivery.
Understanding the root causes of LED strip lights not working — such as power supply mismatches, faulty connectors, or improper installation — enables buyers to specify comprehensive product bundles including power supplies, controllers, and mounting accessories. This holistic sourcing approach reduces downtime and enhances end-user satisfaction, critical for maintaining competitive advantage in dynamic markets.
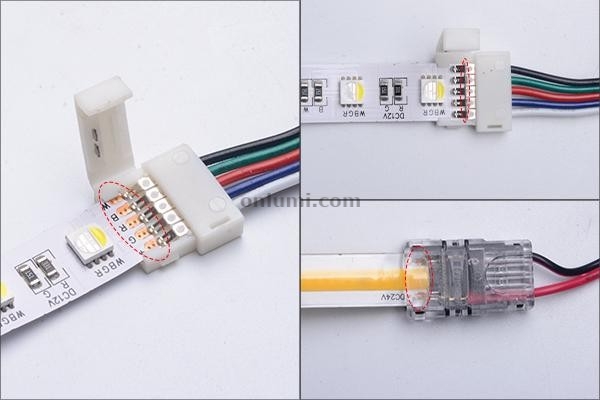

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is rapidly becoming a central concern in the LED strip lighting sector, particularly for B2B buyers seeking to align procurement with corporate social responsibility goals. LED lighting offers significant energy savings over traditional lighting, but the environmental impact of manufacturing, materials, and end-of-life disposal must be considered to ensure truly green solutions.
Ethical sourcing involves verifying that suppliers adhere to responsible labor practices, minimize hazardous substances, and utilize recyclable or low-impact materials such as lead-free solder and halogen-free substrates. Certifications like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), CE marking, and ENERGY STAR are critical benchmarks that international buyers should require to ensure compliance with regional regulations and market expectations.
In regions with growing regulatory scrutiny—Europe being a leader—demand for eco-friendly LED strips with longer lifespans and lower failure rates reduces waste and total cost of ownership. Sustainable packaging and supply chain transparency are additional factors influencing supplier selection, especially for environmentally conscious buyers in the Middle East and South America.
By partnering with manufacturers who invest in green technologies and circular economy principles, B2B buyers can reduce the incidence of product failures (such as LED strips not working) caused by substandard components or poor quality control. This proactive approach supports brand reputation, reduces operational risks, and contributes to global efforts to decarbonize the lighting industry.
Brief Evolution and History
LED strip lights originated in the early 2000s as flexible, low-voltage lighting solutions primarily used for accent and decorative purposes. Early models faced challenges with durability and electrical reliability, leading to frequent issues such as non-functionality after installation. Over time, advancements in LED chip technology, improved circuit design, and the introduction of waterproof coatings expanded their applications into outdoor, industrial, and architectural lighting.
The integration of smart controls and color-changing capabilities further transformed the market, creating demand for more sophisticated power supplies and connectors. This evolution has prompted suppliers to innovate around installation ease and product reliability to address common failure points.
For international B2B buyers, understanding this progression highlights the importance of sourcing from established manufacturers who incorporate lessons learned from past challenges to minimize operational disruptions and ensure consistent performance across global markets.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of led strip lights not working
-
How can I effectively vet LED strip light suppliers to avoid quality and reliability issues?
When sourcing LED strip lights internationally, prioritize suppliers with verifiable certifications such as CE, RoHS, and UL to ensure compliance with safety and quality standards. Request product samples to test performance and durability before large orders. Check supplier track records through references, reviews, and trade platforms. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, working with suppliers who understand regional standards and have local support or distribution channels can reduce risk and improve after-sales service. -
What customization options are typically available for LED strip lights, and how do they impact lead times?
Common customization options include color temperature, IP rating (waterproofing), strip length, LED density, and control interfaces (e.g., DMX, wireless). Custom branding and packaging are also possible. Custom orders usually require longer lead times, often 4-8 weeks, depending on complexity and supplier capacity. Early communication of specifications and flexibility on MOQ can facilitate smoother production. International buyers should confirm customization feasibility upfront to align with project timelines and budget constraints. -
What are typical Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) and payment terms for LED strip light suppliers catering to international B2B buyers?
MOQs vary widely but typically start from 100-500 meters per order for standard LED strips. Customized products often have higher MOQs. Payment terms commonly involve 30% upfront deposit with balance paid upon shipment or delivery. Letters of credit and escrow services provide additional security for international buyers. Negotiating MOQs and payment terms is possible, especially for repeat orders or long-term partnerships. Buyers should consider currency exchange fluctuations and banking regulations in their region when planning payments. -
How important are quality assurance processes and certifications for LED strip lights in international trade?
QA processes and certifications are critical to ensure product safety, longevity, and regulatory compliance across markets. Certifications like CE (Europe), RoHS (hazardous substances), UL (North America), and IEC standards provide confidence in product reliability. Suppliers with ISO 9001 quality management systems typically maintain consistent manufacturing standards. For buyers in regions with strict import regulations, verifying these certifications helps avoid customs delays and costly returns. Insist on documented QA reports and batch testing results during supplier evaluation. -
What logistical considerations should international B2B buyers keep in mind when importing LED strip lights?
Buyers should consider shipping methods (air vs. sea), customs clearance procedures, import duties, and VAT applicable in their countries. Packaging must ensure protection against moisture and mechanical damage during transit, especially for sensitive LED components. Lead times can be affected by port congestion or seasonal demand spikes. Partnering with freight forwarders experienced in electronics and LED products can streamline delivery. Buyers should also plan for potential delays and factor them into project schedules to avoid operational disruptions. -
How can B2B buyers handle disputes or quality issues with LED strip light suppliers effectively?
Establish clear contractual terms covering product specifications, quality standards, delivery timelines, and dispute resolution mechanisms before order confirmation. Use purchase orders and formal agreements to document expectations. If issues arise, promptly communicate with the supplier and provide evidence such as photos or test reports. Utilizing third-party inspection services pre-shipment can minimize disputes. In case of unresolved conflicts, arbitration or mediation under international trade rules (e.g., ICC guidelines) can be pursued. Maintaining professional relationships encourages cooperative problem-solving. -
Are there specific challenges when sourcing LED strip lights for markets in Africa, South America, or the Middle East?
Yes, challenges include variable power supply standards, import restrictions, and differing climate conditions requiring robust waterproofing and heat resistance. Suppliers must provide products compatible with local voltage and frequency to avoid malfunction. Logistics can be complicated by less-developed infrastructure or customs bureaucracy, causing delays. Language barriers and payment system limitations may also impact negotiations. Partnering with suppliers familiar with these regional nuances and providing localized support can significantly improve procurement success. -
What technological features should international buyers prioritize to ensure LED strip lights do not malfunction post-installation?
Prioritize LED strips with stable power supply compatibility (12V or 24V options), high-quality connectors (preferably solderless for ease of installation), and reliable controllers supporting dimming or color control if needed. Waterproofing (IP65 or above) is essential for outdoor or humid environments. Verify that the supplier uses high-quality LEDs with good heat dissipation design to prevent premature failure. Additionally, ensure that installation guidelines are clear and that accessories like mounting channels and connectors are included to reduce installation errors that often cause failures.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for led strip lights not working
Ensuring the reliable operation of LED strip lights is critical for B2B buyers seeking to deliver consistent value in their projects and products. Common issues such as improper installation, inadequate power supply, or substandard connectors can lead to failures that disrupt timelines and inflate costs. Strategic sourcing—selecting reputable manufacturers, verifying product specifications, and leveraging quality accessories like certified connectors—plays a pivotal role in mitigating these risks.
For international buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local market conditions alongside global supplier capabilities enables smarter procurement decisions. Prioritizing suppliers with robust technical support and proven quality assurance helps avoid common pitfalls and ensures compatibility with regional electrical standards and environmental conditions.
Looking ahead, the LED lighting market continues to evolve with innovations in smart controls and energy efficiency. Buyers who integrate these emerging technologies with reliable sourcing strategies will enhance their competitive edge and sustainability credentials. Engage proactively with trusted suppliers, invest in thorough quality validation, and adopt best practices in installation and maintenance to secure long-term operational success. This approach not only prevents functional issues but also maximizes ROI in dynamic international markets.
