Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for led strip connection diagram
Understanding the intricacies of LED strip connection diagrams is essential for businesses aiming to deploy reliable, efficient, and scalable lighting solutions. As LED technology continues to revolutionize commercial and industrial lighting worldwide, mastering the connection schematics ensures optimal performance, safety, and ease of maintenance. For international B2B buyers, particularly in dynamic markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this knowledge is a strategic asset that directly influences procurement success and project outcomes.
This comprehensive guide delves deep into the technical and commercial facets of LED strip connection diagrams. It covers a broad spectrum of topics including the various types of LED strips—single color, RGB, addressable, and tunable white—along with essential materials and components like power supplies, connectors, and wiring standards. You will also find detailed insights on manufacturing best practices, quality control protocols, and how to evaluate suppliers to ensure compliance with international standards and local regulations.
Beyond technical guidance, the guide provides actionable market intelligence—highlighting cost structures, supply chain considerations, and regional market trends—to empower buyers from Mexico, Colombia, Nigeria, UAE, Germany, and beyond. A curated FAQ section addresses common challenges and clarifies complex installation scenarios, helping buyers mitigate risks and optimize their investment.
By equipping you with this knowledge, the guide enables confident decision-making, facilitating the sourcing of high-quality, cost-effective LED strip solutions tailored to your region’s unique electrical and environmental requirements. Whether you are specifying products for new installations or upgrading existing systems, understanding LED strip connection diagrams is your first step toward achieving lighting excellence on a global scale.
Understanding led strip connection diagram Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Series (End-to-End) Wiring | LED strips connected end-to-end in a single continuous line | Short runs, simple commercial installations | + Simple installation, cleaner wiring – Limited length, voltage drop, single failure point |
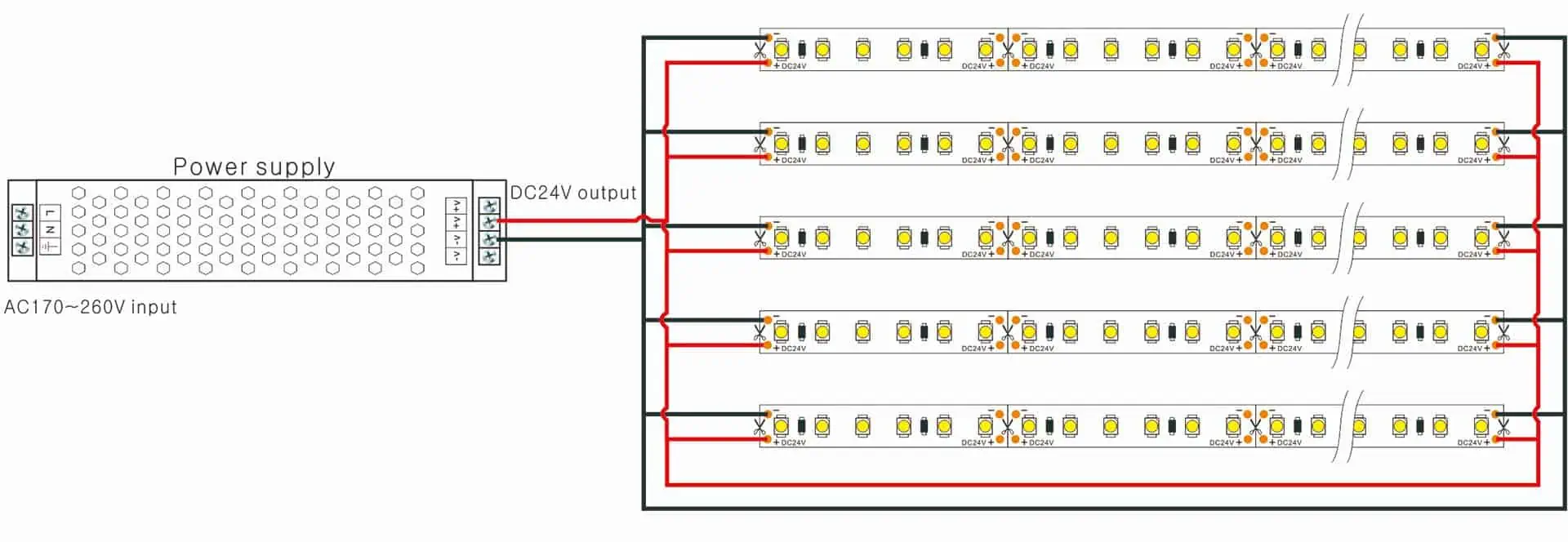
| Parallel Wiring | Multiple LED strips connected individually to a common power source | Long runs, high-brightness, complex layouts | + Consistent brightness, longer runs – More wiring complexity, higher initial cost |
| Power Injection Wiring | Additional power supplied at intervals along the strip to mitigate voltage drop | Large-scale installations, long continuous runs | + Maintains brightness uniformity – Requires careful planning, more connection points |
| Dimmable Wiring with Controllers | Integration of dimmable drivers and controllers (PWM, 0-10V, DALI) | Retail, hospitality, architectural lighting | + Flexible lighting control – Increased system complexity, higher upfront investment |
| Addressable LED Strip Wiring | Individually controllable LEDs with complex data wiring | Entertainment, advertising, dynamic displays | + Highly customizable effects – Requires advanced controllers, higher cost and expertise |
Series (End-to-End) Wiring
This traditional wiring approach connects LED strips sequentially from one end to the other, suitable for short runs typically under 5 meters for 12V systems. It is favored for its simplicity and minimal wiring requirements, making it cost-effective for straightforward commercial projects. However, voltage drop and brightness inconsistency increase with length, and a failure in one segment can affect the entire chain. B2B buyers should consider this for small-scale or temporary installations where cost and ease of setup outweigh scalability.
Parallel Wiring
Parallel wiring connects each LED strip segment directly to a centralized power supply, effectively minimizing voltage drop and ensuring uniform brightness across long runs. This type is essential for commercial and industrial projects requiring runs beyond 5 meters or complex lighting layouts. Though installation complexity and wiring costs are higher, the reliability and maintenance ease make it a preferred choice for professional buyers in sectors such as retail and hospitality, where consistent lighting quality is critical.
Power Injection Wiring
Power injection involves adding power feeds at multiple points along an LED strip to combat voltage drop in ultra-long installations. This method is particularly important for large-scale architectural or industrial lighting projects that exceed the maximum recommended length for single power feeds. Buyers should plan for additional wiring, connectors, and power supplies, increasing initial investment but significantly improving system longevity and brightness uniformity, crucial for high-profile installations.
Dimmable Wiring with Controllers
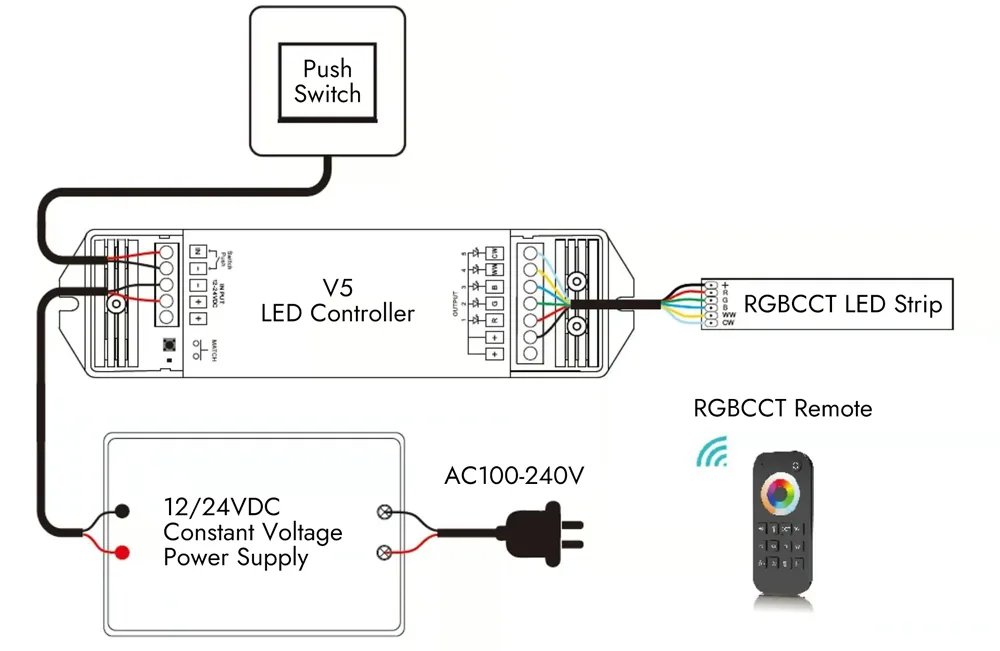
Integrating dimmable LED drivers and control systems (such as PWM, 0-10V, or DALI) enables precise brightness adjustment, energy savings, and enhanced ambiance control. This wiring variation is vital for retail, hospitality, and corporate environments where lighting flexibility impacts customer experience and operational efficiency. B2B buyers must evaluate controller compatibility, dimming protocols, and installation expertise, balancing upfront costs against long-term benefits like energy efficiency and user control.
Addressable LED Strip Wiring
Addressable LED strips feature individually controllable LEDs via complex wiring that carries both power and data signals. This setup is ideal for dynamic lighting effects in entertainment venues, advertising displays, and architectural features demanding high customization. While offering unparalleled visual impact, these systems require specialized controllers and technical knowledge, resulting in higher costs and complexity. Buyers targeting innovative, interactive lighting solutions should prioritize supplier expertise and after-sales support.
Related Video: Large Language Models (LLMs) – Everything You NEED To Know
Key Industrial Applications of led strip connection diagram
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of led strip connection diagram | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail & Commercial | Illuminated display cases and shelving lighting | Enhances product visibility and customer experience, driving sales | Requires flexible wiring solutions for varied layouts; attention to voltage drop and parallel wiring to ensure consistent brightness in large retail spaces |
| Hospitality & Leisure | Ambient and accent lighting in hotels, restaurants, and lounges | Creates inviting atmospheres and improves guest satisfaction | Needs dimmable and color-tunable LED strips with reliable connectors for ease of maintenance and customization |
| Manufacturing & Warehousing | Task lighting and safety pathway illumination | Improves worker safety and operational efficiency | Robust wiring diagrams that accommodate long runs and power injection for consistent illumination in large facilities |
| Automotive & Transportation | Interior cabin and exterior accent lighting on vehicles and vessels | Enhances aesthetic appeal and functional lighting | Requires compact, vibration-resistant connection methods and compliance with regional electrical standards |
| Architectural & Urban Development | Façade lighting and public space illumination | Highlights architectural features and increases nighttime safety | Must support weatherproof connections and scalable wiring configurations for large-scale outdoor installations |
Retail & Commercial Lighting
In retail environments, LED strip connection diagrams guide the installation of illuminated display cases and shelving lighting to highlight products effectively. Proper wiring ensures even brightness and prevents voltage drop issues that can cause uneven lighting, which is critical for enhancing product appeal. Buyers from regions like South America and Africa should prioritize parallel wiring configurations and select wire gauges that accommodate longer runs typical in large retail stores. Flexible connectors and modular wiring are essential to adapt to diverse store layouts and facilitate maintenance.
Hospitality & Leisure Ambiance
Hotels, restaurants, and leisure venues leverage LED strip connection diagrams to implement ambient and accent lighting that creates mood and ambiance. These applications often require dimmable and color-tunable LED strips controlled via sophisticated wiring setups. For international buyers, especially in the Middle East and Europe, sourcing dimmable drivers compatible with regional dimming protocols (e.g., DALI, 0-10V) is vital. The wiring diagram must ensure easy access for upgrades and repairs, supporting long-term operational flexibility and guest experience enhancement.
Manufacturing & Warehousing Safety Lighting
Industrial facilities utilize LED strip connection diagrams to install task lighting and safety pathway illumination. These environments demand robust wiring solutions that support long cable runs with power injection points to maintain consistent brightness and prevent voltage drop. B2B buyers in Africa and South America should consider wire gauge selection carefully to handle high current loads and environmental conditions such as heat and dust. Durable connectors and clear wiring schematics reduce downtime and simplify maintenance in demanding operational settings.
Automotive & Transportation Lighting
The automotive and transportation sectors apply LED strip connection diagrams for interior cabin lighting and exterior accent illumination on vehicles and vessels. Wiring must accommodate compact spaces and resist vibration and environmental stress. International buyers need to ensure that connection methods comply with local electrical and safety standards. Selecting vibration-resistant connectors and secure soldered joints is essential to maintain system reliability and aesthetic quality in harsh operational conditions.
Architectural & Urban Development Lighting
LED strip connection diagrams are critical in architectural façade lighting and public space illumination projects. These applications require weatherproof wiring and scalable connection schemes that can cover large outdoor areas. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should focus on sourcing IP-rated connectors and wiring materials suitable for exposure to elements. The diagrams must support flexible power injection and parallel wiring to guarantee uniform illumination across expansive surfaces, enhancing both aesthetic appeal and public safety.
Related Video: How to Use LED Strip Light Connectors
Strategic Material Selection Guide for led strip connection diagram
When selecting materials for LED strip connection diagrams, it is essential to consider factors such as electrical performance, environmental durability, manufacturing complexity, and regulatory compliance. The choice of materials directly influences the reliability, safety, and longevity of LED lighting installations, especially in demanding commercial and industrial environments across diverse international markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Copper Conductors
Key Properties:
Copper is widely regarded as the industry standard for electrical conductors due to its excellent electrical conductivity (approximately 5.8×10^7 S/m), high thermal conductivity, and good mechanical flexibility. It exhibits strong corrosion resistance when properly insulated and can withstand temperatures typically up to 105°C in PVC insulation and even higher with specialized coatings.
Pros & Cons:
Copper wiring offers low electrical resistance, minimizing voltage drop and heat generation, which is critical for maintaining LED brightness and system efficiency. It is relatively easy to solder and connect with various terminals and connectors, facilitating flexible installation designs. However, copper is more expensive than alternatives like aluminum and requires careful handling to avoid oxidation during manufacturing. Its weight is also higher, which may affect large-scale installations.
Impact on Application:
Copper is ideal for both 12V and 24V LED strip systems, especially in commercial projects requiring long wire runs or parallel wiring to reduce voltage drop. It performs well in environments with moderate to high ambient temperatures and is compatible with most insulation types used in LED wiring.
International B2B Considerations:
Copper wiring must meet international standards such as ASTM B170, DIN EN 13601, or JIS C 3605, which are recognized in Europe, Asia, and increasingly in African and South American markets. Buyers in regions like Mexico and Colombia should ensure suppliers provide certification to these standards to guarantee quality and compliance with local electrical codes.
Tinned Copper Wire
Key Properties:
Tinned copper wire is copper wire coated with a thin layer of tin to enhance corrosion resistance, especially in humid or chemically aggressive environments. It maintains the electrical and thermal conductivity of copper while offering improved solderability and longer lifespan in harsh conditions.
Pros & Cons:
The tin coating protects against oxidation and extends the wire’s durability in coastal or industrial atmospheres, making it suitable for outdoor or semi-outdoor LED installations. It is slightly more expensive than bare copper but reduces maintenance costs by preventing corrosion-related failures. However, the tin layer can wear off under mechanical stress, so proper handling is necessary.
Impact on Application:
Tinned copper wires are preferred in Middle Eastern and African markets where high humidity, salt air, or chemical exposure is common. They are also advantageous in South American tropical climates for outdoor LED strip lighting. This material supports reliable long-term connections in LED strip power distribution and control wiring.
International B2B Considerations:
Ensure tinned copper wire complies with IEC 60228 Class 5 or Class 6 for flexible conductors, widely accepted in Europe and increasingly in emerging markets. Buyers should verify supplier adherence to environmental and quality certifications to meet import regulations and local standards.
Aluminum Conductors
Key Properties:
Aluminum wire is lighter and less expensive than copper but has lower electrical conductivity (about 61% of copper) and reduced mechanical strength. It requires larger cross-sectional areas to carry the same current and is more prone to oxidation, which can increase contact resistance if not properly treated.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum’s cost advantage and light weight make it attractive for large-scale or budget-sensitive projects. However, it demands specialized connectors and anti-oxidation treatments to ensure reliable electrical connections. It is less flexible and more brittle than copper, complicating installation and maintenance.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is generally less favored for LED strip wiring due to its conductivity limitations and connection challenges. It may be used in power distribution wiring feeding LED systems in large industrial setups where weight and cost are critical, but not typically for the fine wiring of LED strips themselves.
International B2B Considerations:
Buyers should confirm compliance with ASTM B230 or DIN EN 50182 standards for aluminum conductors. In regions such as Europe and the Middle East, aluminum wiring may face stricter regulatory scrutiny, so thorough technical evaluation and testing are necessary before procurement.
PVC Insulation
Key Properties:
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is the most common insulation material for LED strip wiring, offering good electrical insulation, flame retardance, and chemical resistance. It typically withstands temperatures up to 70-105°C depending on formulation and provides mechanical protection against abrasion.
Pros & Cons:
PVC insulation is cost-effective, widely available, and easy to manufacture. It is suitable for indoor and dry environments but may degrade under prolonged UV exposure or extreme heat. Its flexibility supports easy routing of wires in complex LED strip layouts.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for indoor commercial and residential LED strip installations in Europe, South America, and parts of Africa where ambient conditions are controlled. For outdoor or harsh environments, PVC may require additional protective measures or be replaced with more robust materials.
International B2B Considerations:
PVC insulation must comply with RoHS and REACH regulations in Europe and meet local fire safety standards such as IEC 60332-1. Buyers in emerging markets should verify the insulation’s chemical composition and flame retardant rating to ensure safety and regulatory acceptance.
Silicone Insulation
Key Properties:
Silicone insulation offers superior thermal stability (up to 200°C), excellent flexibility, and outstanding resistance to UV radiation, moisture, and chemicals. It maintains elasticity over a wide temperature range, making it suitable for dynamic or outdoor installations.
Pros & Cons:
Silicone-insulated wires are highly durable and reliable for harsh environments but come at a higher cost than PVC. Manufacturing complexity is increased due to specialized extrusion processes. It is less common but preferred for premium or industrial-grade LED strip wiring.
Impact on Application:
Highly recommended for outdoor, industrial, or Middle Eastern installations where temperature extremes and UV exposure are concerns. Its flexibility also benefits installations requiring frequent bending or movement.
International B2B Considerations:
Compliance with UL 1441 and IEC 60811 standards is critical for silicone-insulated wiring. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East often require these certifications for commercial projects. For African and South American markets, silicone insulation can be a differentiator for high-end, durable LED strip solutions.
| Material | Typical Use Case for led strip connection diagram | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Standard wiring for indoor/outdoor LED strip power and control lines |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for led strip connection diagram
Manufacturing Processes for LED Strip Connection Diagrams
The production of LED strip connection diagrams involves a series of precise and highly controlled manufacturing stages to ensure optimal functionality, safety, and durability. For B2B buyers, understanding these stages is crucial to assess supplier capabilities and product quality.
1. Material Preparation
This initial phase involves sourcing and preparing raw materials critical to LED strip connections:
- Copper Foil and Flexible PCB Substrates: High-purity copper with excellent conductivity is laminated onto flexible substrates such as polyimide or PET films, forming the electrical pathways.
- Conductive Adhesives and Soldering Materials: Selection of solder alloys or conductive adhesives that meet RoHS and environmental compliance is vital.
- Connectors and Terminals: Precision manufacturing of connectors, often via injection molding combined with metal stamping, ensures reliable mechanical and electrical contact.
Material quality at this stage directly affects the performance and longevity of the LED strip wiring system.
2. Forming and Circuit Patterning
Once raw materials are ready, the key forming processes take place:
- Photolithography and Etching: Circuit patterns for the connection diagram are created on the flexible PCB by applying photoresist masks followed by chemical etching to remove unwanted copper.
- Laser Cutting and Punching: Precision cutting techniques define strip dimensions and connector placement areas to tight tolerances, critical for seamless integration.
- Surface Treatment: To enhance solderability and corrosion resistance, surfaces are treated with HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling), ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), or OSP (Organic Solderability Preservative).
These techniques ensure the electrical paths are accurately formed with minimal defects.
3. Assembly
Assembly integrates all components to create a functional LED strip connection system:
- Soldering and Connector Attachment: Automated or manual soldering attaches connectors and wires to the circuit pads, with processes such as reflow soldering for consistency.
- Encapsulation and Insulation: Protective coatings or silicone encapsulation are applied to safeguard connections from moisture, dust, and mechanical strain.
- Quality Marking: Serial numbers, batch codes, and certification marks are printed or laser engraved for traceability.
Assembly precision is essential to prevent connection failures and maintain signal integrity.
4. Finishing and Packaging
Final steps prepare the product for shipment and installation:
- Functional Testing: Basic electrical continuity and insulation resistance tests verify correct assembly.
- Labeling and Documentation: Clear product labels and connection diagrams are included, tailored for international standards and languages.
- Packaging: Anti-static, moisture-resistant packaging protects components during transit, especially important for buyers in humid or challenging climates.
This stage ensures the product arrives ready for professional installation.
Quality Assurance and Control (QA/QC) Framework
Robust quality assurance is fundamental to delivering LED strip connection diagrams that meet international expectations and regulatory requirements. B2B buyers should evaluate supplier QC rigor and compliance.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: The global benchmark for quality management systems, ensuring consistent manufacturing and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking (Europe): Confirms compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental directives.
- RoHS Compliance: Restricts hazardous substances in electrical components, critical for environmental and regulatory adherence.
- UL or IEC Certifications: Recognize electrical safety and performance standards applicable to LED wiring systems.
- Industry-Specific Standards: Depending on application, certifications such as API (American Petroleum Institute) for industrial environments may be relevant.
Understanding these standards helps buyers verify supplier legitimacy and product safety.
QC Checkpoints
Quality control typically involves multiple inspection stages:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Verification of raw materials and components for conformity with specifications before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing to catch defects early, including solder joint inspection and dimensional accuracy.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of finished products for electrical performance, durability, and visual defects.
Each checkpoint reduces risks of failure and ensures consistent product quality.
Common Testing Methods
- Electrical Continuity and Insulation Resistance Testing: Confirms no open circuits or shorts in connections.
- Voltage Drop Measurement: Ensures wiring meets design specifications to prevent brightness inconsistency.
- Mechanical Stress Testing: Simulates bending and flexing to verify connection durability.
- Thermal Cycling: Assesses performance under temperature fluctuations common in diverse environments.
- Visual and Microscopic Inspection: Detects soldering defects, corrosion, or physical damage.
These tests are essential to guarantee reliability in demanding commercial and industrial installations.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control for International B2B Buyers
For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where sourcing may involve cross-border complexities, verifying supplier QC processes is a strategic priority.
Conducting Supplier Audits
- On-site Factory Audits: Evaluating manufacturing facilities, QC processes, and workforce competence provides direct insight into supplier capabilities.
- Process and Documentation Review: Assessing compliance with ISO 9001 or other certifications and reviewing quality manuals and inspection records.
- Sample Testing: Requesting product samples for independent lab testing to verify claims.
Regular audits build trust and reduce supply chain risks.
Reviewing QC Reports and Certifications
- Production and Inspection Reports: Detailed batch-level reports including IQC, IPQC, and FQC results help track quality trends.
- Third-Party Certification: Certification from internationally recognized bodies (e.g., TÜV, SGS, Intertek) adds credibility.
- Compliance Declarations: Documentation confirming adherence to RoHS, CE, and other relevant standards.
Buyers should insist on transparent reporting to facilitate compliance with local regulations.
Considering Regional QC and Certification Nuances
- Import Regulations: Some countries require local certification or type approval (e.g., INMETRO in Brazil, SASO in Saudi Arabia) beyond international standards.
- Environmental Conditions: Suppliers should demonstrate that their manufacturing and QC processes account for climatic factors such as high humidity or temperature prevalent in regions like Africa or the Middle East.
- Language and Documentation: Clear, multilingual technical documentation and connection diagrams reduce installation errors in diverse markets.
- After-Sales Support and Warranty: Comprehensive support and warranty policies aligned with regional expectations enhance buyer confidence.
Understanding these regional factors helps buyers select suppliers capable of delivering compliant and durable LED strip connection solutions.
Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers
- Prioritize suppliers with transparent, standardized manufacturing processes and internationally recognized quality certifications.
- Insist on detailed QC checkpoints covering material inspection, in-process monitoring, and final testing.
- Utilize factory audits and third-party testing to independently verify supplier quality claims.
- Consider local regulatory requirements and environmental conditions when evaluating product suitability.
- Ensure suppliers provide clear connection diagrams and installation documentation tailored for your market.
By thoroughly vetting manufacturing processes and quality assurance frameworks, international B2B buyers can secure reliable LED strip connection diagrams that meet performance, safety, and regulatory demands across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Related Video: LED Light Making Process | How LED Lights Made Inside Factory | Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for led strip connection diagram Sourcing
When sourcing LED strip connection diagrams and associated components, international B2B buyers must navigate a multifaceted cost structure influenced by technical specifications, supplier conditions, and logistical complexities. Understanding these cost drivers and pricing influencers is essential for optimizing procurement strategies, particularly for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including markets like Mexico and Colombia.
Key Cost Components in LED Strip Connection Diagram Sourcing
-
Materials: Core materials include copper wiring, connectors, soldering supplies, insulation, and PCB substrates for custom connection boards. Quality and certification standards (e.g., RoHS, CE) significantly impact material costs. Premium-grade copper and flame-retardant insulation raise upfront expenses but improve reliability and compliance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely by region and complexity. Skilled labor is needed for precision wiring, soldering, and assembly, especially for diagrams requiring custom wiring harnesses or multi-connection points. Automated processes may reduce costs in high-volume manufacturing but are less common for specialized diagrams.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: Includes factory utilities, equipment depreciation, and indirect labor. Overhead rises with complexity and customization, such as multi-voltage or RGB-compatible connection diagrams.
-
Tooling and Setup: Initial tooling for custom connectors or specialized cable assemblies can add significant upfront costs, particularly for low to medium order quantities. Tooling amortization is a key factor in unit pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing for electrical continuity, insulation integrity, and adherence to voltage/current specifications ensures reliability. Certifications for international markets add to QC expenses but are necessary for compliance and warranty assurance.
-
Logistics and Import Duties: Shipping costs, customs duties, and import taxes vary by origin and destination. Buyers in Africa and South America often face higher tariffs and longer transit times, increasing landed costs.
-
Supplier Margin: Includes profit markups reflecting supplier risk, market positioning, and after-sales support. Margins tend to shrink with higher volumes but may increase for highly customized or expedited orders.
Influential Pricing Factors
-
Order Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale and amortized tooling. Buyers should assess if suppliers offer tiered pricing or discounts for repeat business.
-
Technical Specifications and Customization: Complex diagrams with multi-voltage support, integrated dimming controls, or RGB wiring demand more materials and labor, increasing prices. Standardized diagrams are more cost-effective but may not suit all applications.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Compliance with international safety and environmental standards is non-negotiable for many markets. Certified components cost more but reduce risks of import rejection or product failure.
-
Supplier Reputation and Location: Established suppliers with proven quality control and delivery reliability may charge premiums but reduce total cost of ownership (TCO). Proximity to the buyer can reduce logistics costs and lead times.
-
Incoterms and Payment Terms: Terms such as FOB, CIF, or DDP affect who bears shipping risks and costs. Buyers should negotiate favorable terms aligning with their logistics capabilities and risk tolerance.
Practical Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing
-
Leverage Volume Negotiations: Consolidate orders to unlock price breaks, but balance inventory costs. Consider forming purchasing consortia with regional partners to increase bargaining power.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond unit price, factor in quality, warranty, after-sales support, and potential downtime costs due to poor connections or voltage drops.
-
Prioritize Certified Suppliers: Certifications reduce compliance risks, especially for Europe and Middle East markets with strict import regulations.
-
Request Detailed Cost Breakdowns: Transparent supplier quotes help identify cost-saving opportunities, such as alternative materials or simplified wiring configurations.
-
Plan for Logistics Complexity: Account for customs clearance times and tariffs in Africa and South America. Engage freight forwarders experienced with local regulations to minimize delays and costs.
-
Use Incoterms Strategically: For buyers with strong local logistics, FOB or EXW terms can reduce costs. Less experienced buyers may prefer DDP for end-to-end supplier-managed shipping.
-
Consider Modular Designs: Modular connection diagrams that allow easy replacement or upgrades can lower long-term maintenance costs.
Indicative Pricing Disclaimer
Pricing for LED strip connection diagrams varies widely based on specifications, order size, and supplier location. Typical unit costs may range from a few cents for basic connectors to several dollars for custom multi-connection wiring assemblies. Buyers should obtain multiple quotes and validate supplier capabilities before committing. All cost data should be considered indicative and subject to negotiation and market fluctuations.
By understanding the granular cost components and market dynamics, international B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions that balance upfront expenditure with long-term system reliability and compliance, ensuring optimal value in their LED strip connection diagram procurement.
Spotlight on Potential led strip connection diagram Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘led strip connection diagram’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for led strip connection diagram
Understanding the critical technical properties and trade terminology related to LED strip connection diagrams empowers international B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions, especially when dealing with suppliers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here, we outline the essential specifications and key industry terms that facilitate clear communication and successful transactions.
Key Technical Properties for LED Strip Connection Diagrams
-
Voltage Rating (12V / 24V DC)
LED strips operate on low-voltage direct current, commonly 12V or 24V. Selecting the correct voltage rating ensures compatibility with power supplies and controllers, avoiding performance issues or damage. For buyers, verifying voltage compatibility upfront reduces costly returns and installation delays. -
Wire Gauge (AWG) and Current Capacity
Wire gauge indicates the thickness of the conductor and directly affects the current-carrying capability and voltage drop over distance. Thicker wires (lower AWG numbers) minimize voltage drop and heat buildup, critical for maintaining consistent brightness and safety in commercial installations. Buyers should specify wire gauge based on total length and current requirements to ensure compliance with local electrical standards. -
Connection Type (Soldered, Connector, Terminal Block)
The method used to join LED strips and wiring impacts installation reliability and maintenance. Soldered joints offer strong, permanent connections but require skilled labor, whereas connectors and terminal blocks enable faster installation and easier replacement. Understanding these options helps buyers negotiate appropriate product configurations based on project complexity and labor availability. -
IP Rating (Ingress Protection)
The IP rating defines the LED strip’s resistance to dust and moisture (e.g., IP20, IP65, IP67). For outdoor or humid environments common in many international markets, higher IP ratings are essential to ensure longevity and reduce warranty claims. Buyers must match IP ratings to the installation environment to avoid premature failures. -
Color Temperature and CRI (Color Rendering Index)
Color temperature (measured in Kelvins) and CRI affect the visual quality of lighting. For commercial and architectural projects, selecting LED strips with appropriate color specs ensures aesthetic goals and user comfort. Buyers should confirm these parameters to align with end-user expectations and regulatory requirements. -
Tolerance and Quality Grade
Tolerance refers to allowable variations in electrical or physical parameters. Quality grades (e.g., industrial vs. consumer-grade) affect durability and performance consistency. For large-scale B2B orders, specifying tighter tolerances and higher quality grades reduces variability, simplifies quality control, and enhances brand reputation.
Common Trade Terminology in LED Strip Procurement
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to suppliers who produce LED strips or components that other brands re-label and sell. OEM partnerships allow buyers to customize products and benefit from cost efficiencies while maintaining brand identity. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest amount a supplier is willing to sell per order. Understanding MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory planning, especially for emerging markets or smaller distributors seeking scalable orders. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal inquiry sent to suppliers to obtain price and delivery terms. Well-structured RFQs with clear technical specs and quantities enable competitive bidding and reduce procurement cycle times. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms defining responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs between buyers and sellers (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP). Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers manage logistics risk and cost transparency in cross-border transactions. -
Lead Time
The period from order confirmation to product delivery. Accurate knowledge of lead times supports project scheduling and avoids costly downtime, particularly when sourcing from distant manufacturing hubs. -
Power Injection
A technique to maintain uniform brightness in long LED strip runs by supplying power at multiple points. Awareness of power injection options enables buyers to specify designs that meet demanding commercial lighting requirements.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can optimize their procurement strategies, ensure product performance, and build strong supplier relationships tailored to diverse market needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the led strip connection diagram Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global LED strip connection diagram sector is experiencing robust growth driven by expanding applications in commercial, industrial, and architectural lighting. For international B2B buyers, particularly from emerging and diverse markets like Africa, South America (e.g., Mexico, Colombia), the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the evolving market dynamics is crucial for effective sourcing and project execution.
Key Market Drivers:
– Energy Efficiency Demand: LED technology’s low power consumption and long lifespan are pushing adoption in regions with rising energy costs and sustainability mandates. This creates strong demand for reliable LED strip connection solutions that optimize performance and reduce maintenance.
– Urbanization & Infrastructure Growth: Rapid urban development in Africa and South America is fueling demand for commercial and public lighting projects requiring scalable and flexible LED strip wiring systems.
– Technological Advancements: Integration of smart lighting controls, dimming capabilities, and RGB/RGBW options necessitates sophisticated connection diagrams. B2B buyers increasingly seek suppliers who provide detailed technical documentation and adaptable wiring configurations to support smart building initiatives.
– Supply Chain Localization: Buyers in the Middle East and Europe are focusing on reducing lead times and logistics costs by sourcing from regional manufacturers who comply with international standards. This trend supports just-in-time inventory and reduces exposure to global supply chain disruptions.
Emerging Sourcing Trends:
– Modular and Pre-assembled Wiring Solutions: To reduce installation time and errors, suppliers are offering modular connectors and pre-terminated cables designed for parallel wiring configurations favored in commercial settings.
– Customization & Technical Support: Vendors providing tailored connection diagrams, wire gauge recommendations, and power injection strategies gain competitive advantage, especially for complex layouts in large-scale projects.
– Compliance with International Electrical Standards: Compliance with IEC, UL, and CE standards is increasingly demanded by European and Middle Eastern buyers, ensuring safety and interoperability across diverse installations.
For B2B buyers, partnering with suppliers that combine technical expertise, flexible product offerings, and responsive support is key to navigating the complexities of LED strip connection wiring in evolving market environments.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability considerations are becoming central to procurement decisions in the LED strip connection diagram sector. Environmental impact reduction, ethical sourcing, and compliance with green certifications are no longer optional but critical for international B2B buyers aiming to align with global sustainability goals.
Environmental Impact:
– LED strips and their connection components (wires, connectors, power supplies) involve materials like copper, plastics, and semiconductors. Sourcing from manufacturers who use recycled or sustainably sourced copper and low-toxicity plastics reduces environmental footprint.
– Energy-efficient wiring configurations (e.g., parallel wiring with appropriate wire gauge) minimize voltage drop and power loss, directly contributing to lower operational energy consumption over the system’s lifetime.
Ethical Supply Chains:
– Buyers from Africa, South America, and the Middle East increasingly require transparency in supplier labor practices and conflict-free sourcing, especially for copper and electronic components.
– Partnering with suppliers committed to fair labor standards and environmental stewardship reduces reputational risks and supports sustainable development in sourcing regions.
Green Certifications & Standards:
– Certifications such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals), and Energy Star are essential indicators of product sustainability and safety.
– Adopting LED strip connection products that comply with these certifications ensures regulatory compliance in Europe and facilitates market entry in environmentally conscious regions.
Actionable Insight:
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers offering full lifecycle transparency, from raw material extraction to product end-of-life recycling programs. Engaging in supplier audits and requesting environmental product declarations (EPDs) can further validate sustainability claims.
Evolution and Historical Context
The evolution of LED strip connection diagrams reflects the broader advancement of LED lighting technology from simple decorative applications to sophisticated, integrated lighting systems. Initially, LED strips were wired in simple series configurations suitable for short runs and low-power applications. However, as commercial and industrial demand grew, the industry shifted towards parallel wiring with centralized power distribution to overcome voltage drop challenges and improve system reliability.
The introduction of advanced connectors, power injection techniques, and compatibility with smart controllers has transformed LED strip wiring into a specialized discipline requiring detailed technical knowledge. This progression has been driven by the need for scalable, energy-efficient, and maintainable lighting solutions that meet diverse regional electrical standards and environmental regulations.
For international B2B buyers, understanding this historical context aids in selecting future-proof wiring strategies and suppliers that can support complex, high-performance LED lighting projects across multiple geographies.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of led strip connection diagram
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers of LED strip connection diagrams for international sourcing?
To vet suppliers, request detailed technical documentation and certifications such as CE, RoHS, and UL to ensure compliance with international safety and quality standards. Verify their experience with international projects, especially in your region (Africa, South America, Middle East, Europe). Request references or case studies from similar B2B clients. Conduct virtual or onsite audits if possible, and confirm their after-sales support capabilities. Prioritize suppliers who provide clear wiring schematics, customization options, and technical consultation to minimize risks in complex installations. -
Is it possible to customize LED strip connection diagrams to meet specific regional electrical standards?
Yes, customization is critical for compliance with local voltage, wiring color codes, and safety regulations. Reputable suppliers offer tailored diagrams compatible with regional AC mains voltages (e.g., 220V/240V common in Europe and Africa) and low-voltage DC requirements (12V or 24V). They should also accommodate specific installation environments, such as high ambient temperatures or hazardous locations. Engage suppliers early to discuss your project’s technical requirements, enabling them to provide precise connection diagrams that integrate with local electrical codes and installation practices. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for purchasing LED strip connection diagrams and related hardware?
MOQs for connection diagrams themselves are generally flexible or non-existent, but associated components like connectors, power supplies, and wiring kits often have MOQs ranging from 100 to 500 units depending on the supplier. Lead times can vary between 2 to 6 weeks, influenced by customization level and shipping logistics. For international buyers in regions like South America or the Middle East, plan for additional time due to customs clearance and transport. Negotiate MOQs with suppliers and explore consolidated shipments to optimize costs and delivery schedules. -
What payment terms are commonly accepted for international B2B transactions involving LED strip connection diagrams?
Suppliers typically offer payment terms such as 30-50% upfront deposit with balance before shipment or upon delivery. Letters of credit (L/C) and bank transfers (T/T) are preferred for secure international transactions. For new relationships, smaller initial orders with prepayment may be required. Established buyers may negotiate net 30 or 60-day terms. Always confirm currency exchange policies and ensure clear invoicing to avoid delays. Utilizing escrow services or trade assurance platforms can add security, particularly when dealing with suppliers in different continents. -
How can I ensure the quality assurance and certification of LED strip connection diagrams and related components?
Request supplier-provided quality certificates such as ISO 9001 for manufacturing processes, and product-specific certifications like CE, UL, or RoHS for electrical safety and environmental compliance. Insist on factory test reports, including voltage drop tests and durability under expected environmental conditions. For large projects, consider third-party inspections or laboratory testing of samples before bulk purchase. Verify the supplier’s traceability system for components, ensuring consistent quality across shipments, critical for maintaining long-term reliability in commercial installations. -
What logistics considerations should international buyers be aware of when importing LED strip connection diagrams and accessories?
LED strip connection diagrams are typically digital files, but associated hardware requires careful logistics planning. Choose suppliers with experience shipping to your region, offering Incoterms like FOB or CIF to manage risk and cost transparency. Check compatibility of packaging with customs regulations in your country to avoid delays. Consider consolidated shipments to reduce freight costs. Factor in local import duties, taxes, and potential quarantine inspections. Collaborate with freight forwarders familiar with electronics to streamline customs clearance and ensure timely delivery. -
How should disputes over LED strip connection diagrams or related hardware be managed in international B2B transactions?
Establish clear contractual terms specifying technical specifications, delivery timelines, payment terms, and dispute resolution mechanisms before order confirmation. Use internationally recognized arbitration clauses (e.g., ICC or LCIA) to resolve conflicts efficiently. Maintain detailed communication records, including emails and technical approvals. If discrepancies arise, engage technical experts to assess the diagrams or hardware against agreed standards. Early mediation can prevent escalation. Additionally, consider sourcing from suppliers with strong reputations and responsive customer service to minimize potential disputes. -
Are there specific challenges for B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe regarding LED strip connection diagrams?
Yes, regional challenges include variations in electrical standards (e.g., voltage, frequency), import regulations, and infrastructure limitations affecting installation. Language barriers and time zone differences can complicate technical communication. Supply chain disruptions may impact lead times, especially in remote areas. Buyers should prioritize suppliers offering localized technical support, multilingual documentation, and flexible logistics solutions. Understanding regional certification requirements and working with partners experienced in these markets will facilitate smoother procurement and installation processes.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for led strip connection diagram
Optimizing LED strip connection systems requires a clear understanding of wiring configurations, power requirements, and connection methods. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, prioritizing parallel wiring with appropriate wire gauge selection ensures consistent brightness and system reliability across varied installation environments. Selecting quality power supplies and incorporating effective power injection strategies minimize voltage drop, reducing maintenance costs and enhancing long-term operational efficiency.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in securing components that meet international safety standards, offer durability under diverse climatic conditions, and support scalable installation designs. Buyers should focus on suppliers who provide detailed technical documentation, customization options, and reliable after-sales support to accommodate complex commercial and industrial projects.
Looking ahead, the growing demand for energy-efficient, smart lighting solutions underscores the importance of integrating advanced controllers and dimmable drivers compatible with global standards. B2B buyers are encouraged to engage with manufacturers and distributors who demonstrate innovation in LED technologies and are responsive to regional regulatory requirements. By doing so, businesses can future-proof their lighting infrastructure, optimize costs, and deliver superior outcomes to their clients across multiple markets.
