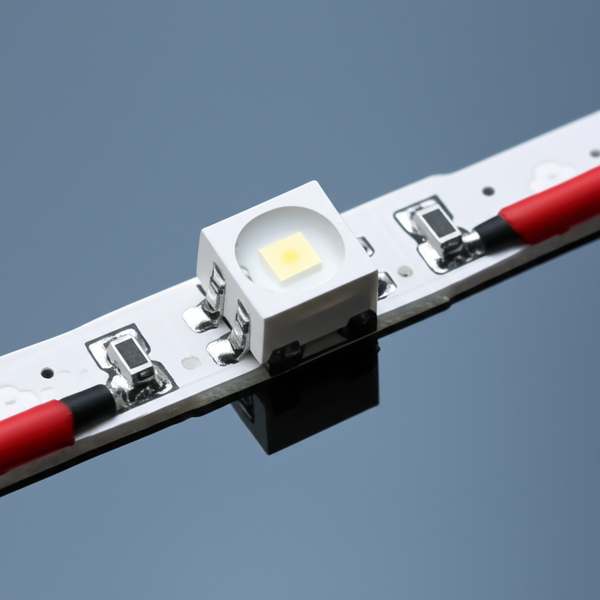
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for addressable led
Addressable LED technology is rapidly transforming the lighting landscape across industries worldwide, offering unprecedented levels of customization, efficiency, and dynamic visual appeal. For international B2B buyers—especially those operating in diverse and fast-growing markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—understanding the nuances of addressable LED solutions is essential to sourcing products that align with specific operational needs and regional market conditions.
This comprehensive guide demystifies the complexities of addressable LED strips, providing a detailed overview of their types, embedded integrated circuits (ICs), material compositions, and manufacturing and quality control standards. It also explores the global supplier ecosystem, cost structures, and key market trends shaping demand and innovation. By addressing common technical questions and procurement challenges, the guide equips buyers with actionable insights to navigate supplier selection, evaluate product specifications, and optimize total cost of ownership.
Whether sourcing for architectural projects in the UK, entertainment venues in the Middle East, or retail installations in South America and Africa, this resource empowers decision-makers to confidently assess the compatibility, scalability, and long-term value of addressable LED products. Emphasizing global best practices and regional considerations, the guide supports strategic purchasing decisions that reduce risk, enhance product performance, and unlock new possibilities for lighting design and functionality.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Understanding addressable led Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| WS2812B (Built-in IC) | Individually addressable LEDs with embedded IC, 5V operation | Dynamic architectural lighting, retail displays, entertainment venues | Pros: High resolution control, widely supported; Cons: Lower voltage limits length and power |
| WS2811 (External IC) | External IC controlling 3 LEDs each, 12V operation | Outdoor signage, large-scale installations, stage lighting | Pros: Higher voltage for longer runs, easier maintenance; Cons: Lower pixel density, less granular control |
| SK6812 (Built-in IC, RGBW) | RGB plus white LEDs for enhanced color rendering, 5V | Hospitality lighting, museums, premium retail spaces | Pros: Better white light options, versatile color mixing; Cons: Slightly higher cost, 5V power limits |
| DMX512 Controlled (External IC) | Industry-standard protocol, supports complex multi-channel control | Professional stage lighting, architectural projects, large events | Pros: Protocol standardization, scalable; Cons: Requires specialized controllers, higher complexity |
| APA102 (Built-in IC) | SPI protocol with separate clock and data lines, 5V operation | High-speed animation, video walls, interactive displays | Pros: Fast refresh rates, reliable data transmission; Cons: More complex wiring, higher cost |
WS2812B (Built-in IC)
WS2812B strips integrate an IC within each LED, allowing precise individual control at a 5V power level. This type is ideal for projects requiring high pixel density and fine detail, such as architectural accents or retail displays where dynamic color changes enhance customer engagement. B2B buyers should consider power limitations for longer runs and ensure compatible controllers are available. WS2812B’s widespread adoption makes sourcing and support globally accessible, beneficial for buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
WS2811 (External IC)
WS2811 uses an external IC controlling groups of three LEDs, operating typically at 12V. This higher voltage reduces voltage drop over long distances, making it suitable for outdoor signage, large-scale installations, and stage lighting where durability and ease of maintenance are priorities. B2B buyers should assess installation environments and power infrastructure compatibility. While offering less granularity in control, the robustness and longer wiring distances make WS2811 strips a cost-effective choice for expansive commercial projects.
SK6812 (Built-in IC, RGBW)
The SK6812 is a built-in IC LED strip that adds a dedicated white LED to the RGB mix, enabling richer color palettes and more natural white lighting. This feature is especially valuable in hospitality, museums, and upscale retail environments where lighting quality significantly impacts ambiance and product presentation. Buyers should weigh the slightly increased cost against the benefit of improved color rendering and the 5V power limitation, which may require more segmented installations or power injections.
DMX512 Controlled (External IC)
DMX512 addressable LED strips adhere to a global lighting control standard, enabling highly scalable and synchronized multi-channel lighting setups. These are preferred for professional stage lighting, architectural projects, and large events where precise, reliable control over thousands of LEDs is necessary. B2B buyers must consider the need for specialized DMX controllers and technical expertise for integration. The protocol’s universality ensures interoperability, an important factor for international projects spanning multiple regions.
APA102 (Built-in IC)
APA102 strips use a SPI protocol with separate clock and data lines, which supports fast refresh rates and stable data transmission. This makes them ideal for high-speed animations, video walls, and interactive displays demanding real-time responsiveness. For B2B buyers, APA102 offers superior performance but requires more complex wiring and higher upfront costs. Suitable for technology-forward businesses in Europe and the Middle East, this type supports advanced applications where lighting is part of an interactive or multimedia system.
Related Video: How do you use Addressable LED strips? What is ARGB LED?
Key Industrial Applications of addressable led
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of addressable led | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail & Commercial Spaces | Dynamic in-store displays and signage | Enhances customer engagement through customizable, vibrant lighting; drives sales and brand recognition | Compatibility with control systems, durability for extended use, energy efficiency, and ease of installation |
| Entertainment & Events | Stage lighting and immersive visual effects | Enables complex lighting sequences and synchronized effects; improves audience experience and event impact | High refresh rate ICs, robust controllers, and reliable power supplies suitable for international standards |
| Architecture & Urban Design | Façade lighting and public art installations | Creates iconic landmarks with programmable color and animation; supports branding and tourism initiatives | Weather-resistant strips, IP rating, long cable runs, and local voltage compatibility |
| Transportation & Automotive | Interior ambient lighting and exterior signaling | Improves passenger experience and vehicle aesthetics; supports safety through dynamic signaling | Compliance with automotive standards, vibration resistance, and integration with vehicle control units |
| Hospitality & Leisure | Mood lighting in hotels, restaurants, and casinos | Customizable ambiance that enhances guest satisfaction and operational flexibility | Flexible strip lengths, easy maintenance, and compatibility with smart control systems |
Retail & Commercial Spaces
In retail environments across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, addressable LED strips are transforming in-store displays and signage. Their ability to individually control each LED allows for dynamic color changes and animations that attract customers and highlight promotions. Businesses benefit from increased foot traffic and brand differentiation. Buyers should prioritize energy-efficient strips with durable construction that can withstand long operating hours. Compatibility with existing control systems and ease of installation are critical to minimize downtime and installation complexity.
Entertainment & Events
Addressable LEDs are essential in the entertainment sector for stage lighting, concerts, and event production. They enable highly customizable lighting effects synchronized with music or performances, creating immersive experiences that captivate audiences. For B2B buyers in diverse international markets, selecting LED strips with high refresh rates and reliable controllers ensures smooth animations without flicker. Power supply quality and adherence to local electrical standards are important for safety and performance, especially in regions with varying voltage and frequency.
Architecture & Urban Design
Architectural projects and urban installations leverage addressable LEDs to illuminate building façades and public art with programmable light shows. This application supports city branding and tourism by creating visually striking landmarks. Buyers from regions with harsh climates must source LED strips with high IP ratings and weather resistance. Additionally, long cable runs and local voltage compatibility are essential to accommodate large-scale installations while maintaining consistent color and brightness.
Transportation & Automotive
In transportation, addressable LEDs are used for interior ambient lighting and exterior dynamic signaling on vehicles. These lighting solutions improve passenger comfort and vehicle aesthetics while enhancing safety through attention-grabbing signals. International B2B buyers should ensure compliance with automotive standards such as vibration resistance and electromagnetic compatibility. Integration capability with vehicle control units is a key factor to enable seamless operation within complex automotive systems.
Hospitality & Leisure
Hotels, restaurants, and casinos utilize addressable LED strips to create adaptable mood lighting that can be tailored to different times of day or events. This flexibility enhances guest experiences and supports operational efficiency. Buyers should focus on flexible strip lengths and easy maintenance features to accommodate varied interior layouts. Compatibility with smart lighting control systems enables centralized management, which is particularly valuable for large hospitality chains operating across multiple countries.
Related Video: Power Diode (Basics, Structure, Characteristics, Working, Applications, Biasing & Types) Explained
Strategic Material Selection Guide for addressable led
When selecting materials for addressable LED products, especially for international B2B buyers targeting diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the material properties and their impact on performance and compliance is critical. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in addressable LED manufacturing: Flexible Printed Circuit Boards (FPCBs), Silicone, Polyurethane, and Aluminum.
Flexible Printed Circuit Boards (FPCBs)
Key Properties:
FPCBs are typically made from polyimide or polyester films, offering excellent flexibility, high temperature resistance (up to 260°C for polyimide), and good electrical insulation. They withstand moderate mechanical stress and are resistant to chemicals and moisture to some extent.
Pros & Cons:
FPCBs provide excellent design flexibility, allowing complex LED layouts and compact installations. They are lightweight and support high-density LED placement. However, polyimide-based FPCBs can be more expensive than polyester alternatives and require precise manufacturing processes. They may be susceptible to damage under extreme bending or sharp folds.
Impact on Application:
FPCBs are ideal for dynamic, curved, or compact LED installations such as architectural lighting, wearable tech, and automotive interiors. Their temperature tolerance makes them suitable for environments with fluctuating temperatures.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions with high ambient temperatures (Middle East, parts of Africa) should prioritize polyimide-based FPCBs for better thermal stability. Compliance with international standards such as IPC-6013 (for flexible circuits) and ASTM D150 (dielectric properties) is essential. European buyers often require RoHS and REACH compliance, while South American markets may emphasize durability under humidity.
Silicone (Encapsulation and Coating)
Key Properties:
Silicone is widely used as an encapsulant or protective coating for addressable LEDs, offering excellent UV resistance, flexibility, and high thermal stability (typically up to 200°C). It provides superior moisture and dust protection with good electrical insulation.
Pros & Cons:
Silicone encapsulation enhances durability, especially in outdoor and harsh environments, by protecting LEDs from corrosion and physical damage. It is flexible and maintains clarity over time. However, silicone coatings increase production costs and may complicate repair or recycling processes.
Impact on Application:
Silicone-coated LED strips are preferred for outdoor installations, marine environments, and industrial settings where exposure to moisture, salt, or dust is common.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Regions with high UV exposure (Middle East, parts of Africa) benefit from silicone’s UV stability. Buyers should verify compliance with standards like ASTM D4329 (UV resistance) and IEC 60529 (IP rating for ingress protection). In Europe, certifications such as CE marking and RoHS are critical. Silicone’s higher cost may be a consideration for budget-sensitive markets in South America.
Polyurethane (Protective Sheathing)
Key Properties:
Polyurethane offers robust mechanical protection with good abrasion resistance, flexibility, and moderate temperature tolerance (typically up to 120°C). It provides excellent resistance to oils, solvents, and chemicals.
Pros & Cons:
Polyurethane sheathing protects LED strips from mechanical wear and chemical exposure, making it suitable for industrial applications. It is less expensive than silicone but offers lower UV resistance and thermal stability. Polyurethane coatings may yellow over time when exposed to sunlight.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for indoor industrial environments or areas with chemical exposure but limited direct sunlight. It is often used in factory automation, warehouses, or automotive under-hood lighting.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in industrial hubs of Europe and South America may favor polyurethane for cost-effective durability. However, in high UV regions like the Middle East, additional UV stabilizers or alternative materials are recommended. Compliance with ASTM D2240 (hardness), ISO 527 (tensile properties), and local chemical safety standards is important.
Aluminum (Heat Dissipation Substrate)
Key Properties:
Aluminum is commonly used as a substrate or heat sink material for addressable LED strips, providing excellent thermal conductivity (up to 205 W/m·K), mechanical strength, and corrosion resistance when anodized.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum substrates significantly improve LED lifespan by dissipating heat efficiently, enabling higher brightness and longer operation. They are lightweight and relatively low cost but require precise machining and anodizing for corrosion protection. Aluminum is rigid and less flexible than polymer substrates.
Impact on Application:
Best suited for high-power LED installations, architectural lighting, and environments where heat management is critical. It is less suitable for flexible or curved installations.
Considerations for International Buyers:
European and Middle Eastern buyers often demand anodized aluminum meeting EN 12373 or DIN 17611 standards for corrosion resistance. African and South American buyers should consider local climate corrosion factors and verify compliance with ASTM B221 or ISO 6361. Aluminum offers a cost-effective solution for durable, high-performance LED products.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for addressable led | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flexible Printed Circuit Board (FPCB) | Flexible, high-density LED layouts in architectural and wearable lighting | High flexibility, thermal resistance, compact design | Higher cost, sensitive to extreme bending | Medium |
| Silicone | Outdoor, marine, and industrial LED encapsulation | Excellent UV and moisture resistance, flexibility | Increased production cost, repair complexity | High |
| Polyurethane | Protective sheathing in industrial indoor environments | Good abrasion and chemical resistance, cost-effective | Lower UV resistance, potential yellowing | Low |
| Aluminum | Heat dissipation substrate for high-power LED strips | Superior thermal management, mechanical strength | Rigid, less flexible, requires anodizing | Low to Medium |
This guide equips international B2B buyers with insights to strategically select materials that balance performance, durability, cost, and compliance, tailored to their regional market demands and application requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for addressable led
The manufacturing and quality assurance of addressable LEDs are critical factors for international B2B buyers aiming to procure reliable, high-performance lighting solutions. Understanding the production lifecycle and quality control (QC) protocols enables buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and ensure compliance with regional and global standards.
Manufacturing Process of Addressable LEDs
The production of addressable LED strips involves several precise stages, each requiring specialized techniques and equipment to ensure product functionality, durability, and customization capabilities.
1. Material Preparation
- Raw Materials: High-quality flexible printed circuit boards (FPCBs), LEDs (commonly SMD types like 5050 or 3535), integrated circuits (ICs) such as WS2812B or TM512AC, resistors, capacitors, and solder paste.
- Procurement: Sourcing components from reputable suppliers is essential. Many manufacturers emphasize lead-free (RoHS compliant) materials to meet environmental regulations.
- Inspection: Incoming Quality Control (IQC) tests raw materials for dimensional accuracy, electrical properties, and visual defects before production.
2. Circuit Forming and PCB Fabrication
- FPCB Manufacturing: Flexible circuit boards are fabricated using copper etching and layering processes tailored for flexibility and electrical reliability.
- IC and LED Mounting: Surface-mount technology (SMT) machines place LEDs and ICs onto the FPCB with precision. Placement accuracy is crucial for consistent signal transmission and electrical performance.
- Soldering: Reflow soldering ensures strong mechanical and electrical connections between components and the board.
- Cleaning: Post-solder cleaning removes flux residues to prevent corrosion and maintain conductivity.
3. Assembly and Integration
- Data Line Integration: Addressable LEDs require data lines for individual control; careful wiring and testing of these lines ensure proper signal flow.
- Encapsulation: Some strips receive silicone or epoxy coatings for waterproofing, enhancing durability in outdoor or humid environments.
- Cutting and Packaging: Strips are cut to standard or custom lengths, with connectors attached for ease of installation.
4. Finishing and Customization
- Color Calibration: Final adjustments to LED brightness and color balance may be performed using specialized equipment to meet design specifications.
- Labeling and Documentation: Each batch is labeled with batch numbers and certification marks to facilitate traceability.
- Packaging: Protective packaging is designed to prevent damage during shipping, often including anti-static bags and cushioning.
Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) Framework
For B2B buyers, particularly those importing addressable LEDs into diverse markets, understanding the QC framework helps ensure the products meet international quality and safety standards.
Relevant International and Industry Standards
- ISO 9001: This globally recognized standard for quality management systems (QMS) ensures manufacturers maintain consistent production quality and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: Mandatory for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE certification verifies compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection requirements.
- RoHS Compliance: Restricts hazardous substances in electronic products, critical for European and many global markets.
- UL Certification: Ensures electrical safety and fire hazard resistance, highly regarded in North America and increasingly recognized worldwide.
- API and IEC Standards: Pertinent for electrical and electronic equipment, including LED components, ensuring interoperability and safety.
- Regional Requirements: Some countries in Africa, the Middle East, and South America may have additional local certification or import regulations buyers should verify.
QC Checkpoints in Manufacturing
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Verifies raw materials and components upon receipt to prevent defective parts entering production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during assembly, IPQC includes solder joint inspections, component placement accuracy, and functional testing of partial assemblies.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Post-assembly inspections focus on overall product functionality, appearance, and packaging integrity.
Common Testing Methods
- Electrical Testing: Validates voltage, current, and signal integrity for each LED and IC to ensure proper addressability and color accuracy.
- Visual Inspection: Automated optical inspection (AOI) systems detect soldering defects, component misalignment, and surface damage.
- Environmental Testing: Includes thermal cycling, humidity resistance, and waterproofing tests to simulate real-world operating conditions.
- Durability Testing: Bending tests for flexible strips and adhesion tests for coatings verify mechanical robustness.
- EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) Testing: Ensures LED strips do not emit or suffer from electromagnetic interference, critical for sensitive commercial environments.
How B2B Buyers Can Verify Supplier QC Effectiveness
Due diligence in supplier quality assurance is essential for buyers to avoid costly returns, delays, or regulatory issues.
Supplier Audits
- Factory Audits: On-site evaluations assess manufacturing capabilities, equipment, workforce skills, and compliance with ISO and safety standards.
- Process Audits: Focus on specific production stages and QC procedures to confirm consistency and adherence to documented processes.
Documentation and Reporting
- Quality Control Reports: Comprehensive IQC, IPQC, and FQC reports should be provided with batch shipments.
- Test Certificates: Including CE, RoHS, UL, and other relevant certifications with detailed test data.
- Traceability Records: Enable tracking of components and production batches for accountability and recall management if needed.
Third-Party Inspection Services
- Engaging independent inspection agencies to conduct pre-shipment inspections or in-line audits offers unbiased verification of product quality and compliance.
- These services often include functional tests, packaging checks, and conformity assessments according to buyer specifications.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
Understanding regional regulatory environments and certification acceptance is vital for seamless market entry.
- Africa: Regulatory frameworks vary widely; some countries require local certification or import approvals. Buyers should verify if CE or UL marks are recognized or if additional testing is necessary.
- South America: Countries like Brazil and Argentina have specific electrical safety standards; compliance with IEC or UL may facilitate importation, but local certification could be mandated.
- Middle East: Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries increasingly harmonize with international standards, but buyers should confirm conformity with local standards and certifications like SASO in Saudi Arabia.
- Europe (UK & EU): Post-Brexit, UKCA marking is required alongside or instead of CE for UK markets. Buyers must ensure compliance with both marks where applicable.
- Thailand and Southeast Asia: While many accept CE and UL certifications, local authorities may require additional documentation or testing, particularly for electrical safety and electromagnetic compatibility.
Actionable Insights for B2B Buyers
- Specify QC Requirements Early: Clearly communicate required certifications, testing protocols, and inspection plans in contracts.
- Request Sample Testing: Before large orders, conduct lab testing on samples to verify electrical performance, color accuracy, and durability.
- Partner with Experienced Suppliers: Prioritize manufacturers with proven track records, ISO 9001 certification, and transparent QC reporting.
- Leverage Technology: Use digital tools for remote factory audits and real-time QC data sharing to overcome geographic challenges.
- Plan for Regional Compliance: Engage local consultants or certification bodies to navigate country-specific requirements efficiently.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing and quality assurance landscape of addressable LEDs, international B2B buyers can secure high-quality, compliant products that meet their functional and regulatory needs, ensuring successful project outcomes and long-term partnerships.
Related Video: LED Light Making Process | How LED Lights Made Inside Factory | Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for addressable led Sourcing
When sourcing addressable LEDs for international B2B projects, understanding the detailed cost structure and pricing influencers is essential for optimizing procurement strategies and ensuring competitive margins. Addressable LED products involve a multifaceted cost composition, shaped by technical specifications, manufacturing complexity, and global supply chain dynamics.
Key Cost Components in Addressable LED Sourcing
-
Materials: The primary cost driver includes LED chips (often RGB or RGBW), integrated circuits (ICs) either built-in or external, flexible printed circuit boards (FPCBs), and protective coatings. Premium chipsets like WS2812B or SK6812 command higher prices due to superior color control and reliability. Raw material prices fluctuate based on semiconductor supply and copper costs.
-
Labor and Manufacturing Overhead: Assembly of addressable LED strips requires precision, especially for soldering ICs and LEDs onto flexible boards. Labor costs vary significantly by region, with lower wages in Asia compared to Europe or the Middle East. Overhead includes factory utilities, quality control processes, and equipment depreciation.
-
Tooling and Setup: Initial investment in tooling, such as stencil printers and pick-and-place machines, impacts unit cost, particularly for smaller production runs. Custom designs or unique IC integration may require additional setup fees.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing for LED functionality, color accuracy, and signal integrity is vital. QC costs rise with tighter tolerances and certifications (e.g., CE, RoHS, UL), which are often mandatory for European and Middle Eastern markets.
-
Logistics and Import Duties: Freight charges, customs clearance, and import tariffs significantly affect landed costs. Buyers in Africa and South America should anticipate higher logistics expenses and possible delays, influencing inventory planning.
-
Margin: Suppliers factor in profit margins depending on order size, client relationship, and market competition. Margins tend to be tighter for large-volume contracts but can increase for highly customized or expedited orders.
Influential Pricing Factors
-
Order Volume and Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ): Larger volumes typically reduce per-unit costs due to economies of scale. However, some suppliers impose MOQs that may be challenging for smaller buyers in emerging markets.
-
Technical Specifications and Customization: Higher LED density (LEDs per meter), advanced IC types (e.g., dual-signal WS2813 vs. single-signal WS2812B), and additional features like RGBW or dim-to-warm functionality increase cost. Custom firmware or proprietary controllers further add to pricing.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Certified components that meet international standards often carry premiums but reduce risks related to regulatory compliance, especially in the UK and EU.
-
Supplier Reliability and Location: Established suppliers with proven quality and after-sales support command higher prices but reduce project risks. Proximity to manufacturing hubs in China, Taiwan, or South Korea can lower logistics costs and lead times.
-
Incoterms and Payment Terms: The choice of shipping terms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP) affects who bears freight and customs responsibilities, impacting overall procurement costs. Flexible payment terms can also influence pricing negotiations.
Strategic Buyer Recommendations
-
Negotiate Based on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not only unit price but also shipping, customs, warranty, and potential rework costs. For African and South American buyers, factoring in extended lead times and logistics reliability is critical.
-
Leverage Volume Consolidation: Pooling orders regionally or through buying groups can unlock better MOQs and pricing tiers.
-
Prioritize Certified Quality: Especially for buyers in Europe and the Middle East, insist on certifications to avoid costly compliance issues.
-
Request Detailed Cost Breakdowns: Transparent supplier quotes help identify cost drivers and areas for negotiation, such as tooling amortization or logistics charges.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances by Region: For example, UK buyers may face VAT and stringent environmental regulations; Middle Eastern buyers might prefer suppliers with local warehouses to reduce delivery times.
-
Plan for Currency Fluctuations: Hedging or fixed exchange rate contracts can protect against cost volatility for international transactions.
Indicative Pricing Disclaimer
Pricing for addressable LED strips varies widely based on specifications, order size, and supplier. Typical costs range from approximately $5 to $20 per meter for standard RGB addressable LED strips in bulk quantities. Custom or high-end variants with advanced ICs or additional features can exceed this range. All price references are indicative and subject to change due to global supply chain dynamics, tariffs, and material cost fluctuations.
This comprehensive understanding of the cost and pricing landscape enables international B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions, optimize budgets, and establish sustainable supplier partnerships tailored to their regional market requirements.
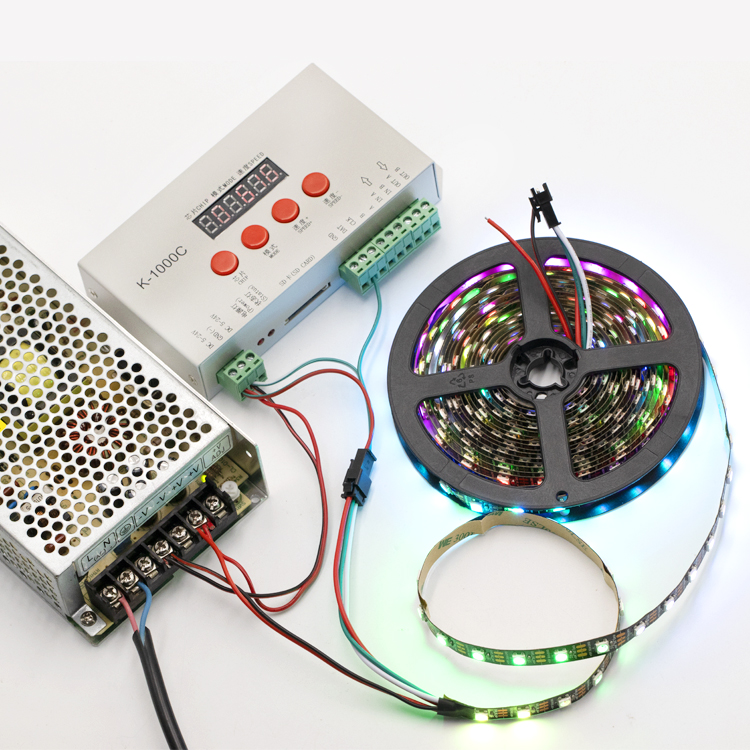

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Spotlight on Potential addressable led Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘addressable led’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for addressable led
Critical Technical Properties of Addressable LED Strips
When sourcing addressable LED strips for international B2B projects, understanding key technical specifications is essential to ensure quality, compatibility, and long-term performance. Here are the most critical properties you should evaluate:
-
LED Density (LEDs per Meter):
This indicates how many individual LEDs are placed per meter of the strip. Higher LED density offers smoother light transitions and more detailed effects, which is crucial for applications requiring intricate lighting designs such as architectural facades or entertainment venues. For budget-sensitive projects or simple accent lighting, lower densities may suffice. -
Integrated Circuit (IC) Type and Control Protocol:
Addressable LEDs embed ICs that enable individual LED control. Common IC types include WS2812B (SPI protocol) and TM512 (DMX512 protocol). SPI ICs are widely used for flexible, pixel-level control, ideal for custom animations, while DMX512 ICs suit large-scale, standardized lighting systems often used in stage or commercial installations. Selecting the correct IC type ensures compatibility with your existing controllers and software. -
Operating Voltage and Power Consumption:
Typical voltage ratings are 5V, 12V, or 24V. Lower voltages (5V) offer finer control but shorter runs before voltage drop becomes an issue. Higher voltages (12V/24V) enable longer strips with less power loss, ideal for large installations in commercial buildings or outdoor projects. Always match power supplies and controllers to the strip’s voltage to avoid performance issues or damage. -
Color Configuration and Chip Capability:
Addressable strips vary from simple RGB (Red, Green, Blue) to RGBW (including White LEDs for better white light quality) and advanced types like RGBIC that allow multiple colors on a single LED. Knowing your desired color output and effects helps prevent overspending on unnecessarily complex strips or under-specifying your lighting needs. -
Material Quality and IP Rating:
The flexible printed circuit board (FPCB) material affects durability and heat dissipation. Look for high-grade copper layers and quality soldering for longer lifespan. For outdoor or humid environments common in many African, Middle Eastern, and South American markets, IP65 or higher-rated waterproof strips are recommended to prevent corrosion and ensure safety. -
Tolerance and Signal Integrity:
Tolerance refers to how much variation in color and brightness occurs between LEDs. High-quality strips maintain uniformity, essential for professional installations where visual consistency impacts brand image. Additionally, signal integrity impacts how well control signals propagate along the strip, influencing the smoothness of animations and reducing flicker or glitches.
Common Trade Terminology for Addressable LED Procurement
Navigating international B2B transactions for addressable LEDs involves familiarity with industry jargon that impacts pricing, delivery, and contractual obligations:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer):
Refers to suppliers who produce LED strips that can be branded and customized for your company. OEM partnerships are valuable for buyers seeking unique product specifications or private labeling, allowing differentiation in competitive markets. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity):
The smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell in one order. MOQs vary widely and impact cost-efficiency. Buyers in emerging markets or smaller businesses should negotiate MOQs that align with their inventory capacity and cash flow while balancing supplier expectations. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation):
A formal inquiry sent to suppliers detailing your product requirements and requesting pricing and terms. A well-prepared RFQ speeds up the sourcing process and helps compare multiple suppliers on equal footing, critical when purchasing complex products like addressable LED strips. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms):
Standardized trade terms defining responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs between buyer and seller. Common Incoterms include FOB (Free On Board), CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight), and DDP (Delivered Duty Paid). Understanding these terms ensures clarity on who bears risk and costs during transport, reducing disputes and unexpected expenses. -
Lead Time:
The total time from placing an order to receiving the goods. Addressable LED strips with custom ICs or special waterproofing might have longer lead times. Planning accordingly helps avoid project delays, especially when coordinating multi-country logistics. -
Batch Consistency:
Refers to uniformity of product quality and color output across different production runs. For repeat orders, confirm with suppliers that batch consistency is maintained to prevent noticeable variations in lighting installations, which can affect brand reputation and customer satisfaction.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can make informed purchasing decisions that optimize cost, quality, and project success when sourcing addressable LED strips.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the addressable led Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global addressable LED market is experiencing rapid growth driven by increasing demand for customizable, energy-efficient lighting solutions across diverse industries. International B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including the UK and Thailand) are capitalizing on advancements in LED technology to enhance commercial, architectural, entertainment, and industrial applications. The ability to individually control each LED’s color and brightness provides unprecedented flexibility, making addressable LEDs a preferred choice for dynamic lighting designs and smart city projects.
Key market dynamics include a rising emphasis on digital lighting integration with IoT platforms, enabling remote control and automation that aligns with smart building trends. Buyers are increasingly seeking LED strips with advanced IC types (e.g., WS2812B, SK6812, and DMX512 compatible models) that offer high precision and reliability. The growing adoption of SPI and DMX512 protocols reflects a demand for standardized, scalable solutions that accommodate complex installations.
Sourcing trends reveal a shift towards suppliers who can provide comprehensive technical support, customization options, and adherence to international quality standards. Regions like Europe and the Middle East prioritize suppliers with strong R&D capabilities and compliance with EU and GCC regulations, while African and South American markets focus on cost-effective, durable solutions suitable for diverse environmental conditions. Supply chain resilience is also a critical consideration, with buyers favoring manufacturers that maintain robust logistics and component availability amid global disruptions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a pivotal factor for B2B buyers in the addressable LED sector, reflecting broader environmental and social governance (ESG) commitments. Addressable LEDs inherently contribute to energy savings due to their low power consumption and long lifespan, which reduces overall environmental impact. However, buyers must evaluate the entire supply chain to ensure sustainable and ethical practices.
Ethical sourcing involves selecting suppliers who demonstrate transparency in raw material procurement, particularly regarding conflict minerals and responsible labor practices. Certifications such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals), and ENERGY STAR are increasingly regarded as essential benchmarks for product quality and environmental compliance. Furthermore, sourcing addressable LEDs with lead-free solder, recyclable packaging, and reduced carbon footprints aligns with global sustainability goals.
For buyers in regions like Europe and the UK, compliance with stringent environmental regulations is non-negotiable, while emerging markets in Africa and South America are progressively adopting green procurement policies. Collaborating with suppliers who actively pursue eco-friendly innovations—such as biodegradable flexible PCBs and energy-efficient drivers—can enhance corporate reputation and meet the growing demand for “green” lighting solutions. Sustainable sourcing also mitigates risks related to regulatory penalties and supply chain disruptions, positioning buyers for long-term success.
Brief Evolution and Industry Context
Addressable LED technology has evolved significantly over the past decade, transitioning from niche, hobbyist applications to mainstream commercial use. Early iterations relied on basic RGB LEDs with limited control, whereas today’s addressable LED strips incorporate sophisticated integrated circuits (ICs) like WS2812B and SK6812, enabling individual LED control and complex programmable effects.
The industry’s maturation has been driven by improvements in IC design, flexible PCB manufacturing, and the development of universal control protocols such as DMX512 and SPI. These advances have expanded the market’s scope, making addressable LEDs indispensable in sectors ranging from entertainment and retail to smart infrastructure and automotive lighting.
For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is critical to selecting future-proof solutions that leverage the latest innovations while balancing cost, performance, and sustainability. As the technology continues to advance, buyers should anticipate ongoing improvements in energy efficiency, integration capabilities, and customization options, all of which will influence sourcing strategies and market competitiveness.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of addressable led
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers of addressable LED products for international B2B purchases?
Start by verifying the supplier’s business credentials, certifications (such as ISO, CE, RoHS), and manufacturing capabilities. Request product samples to assess quality and compatibility. Check references or reviews from other international buyers, especially those in your region. Evaluate their technical support and after-sales service responsiveness. Use platforms that offer verified supplier status and conduct factory audits if possible. This thorough vetting helps minimize risks of low-quality products and unreliable delivery. -
What customization options are typically available for addressable LED strips, and how should I specify them?
Customization can include LED density (LEDs per meter), IC type (e.g., WS2812B, WS2815), color configurations (RGB, RGBW), strip length, voltage, waterproofing, and connectors. Specify your project’s technical requirements clearly, including control protocols (SPI, DMX512), power supply compatibility, and environmental conditions. Provide detailed drawings or use case scenarios to ensure the supplier understands your needs. Early engagement on customization reduces revisions and ensures the product fits your operational requirements. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for addressable LED orders, and how can I negotiate them?
MOQs vary widely based on customization level and supplier scale but typically range from 500 to 2000 meters for standard strips. Lead times can span 3 to 8 weeks depending on order complexity and production schedules. For buyers in Africa, South America, or the Middle East, factor in additional time for shipping and customs clearance. Negotiate MOQs by consolidating orders, committing to repeat purchases, or accepting standard specifications to reduce costs. Clear communication of your timeline helps suppliers prioritize your order.
-
Which quality assurance certifications should I look for when purchasing addressable LED strips internationally?
Look for compliance with international standards such as CE (European safety), RoHS (restriction of hazardous substances), UL (safety certification), and ISO 9001 (quality management). For export to specific regions, check local requirements—for example, SASO for Saudi Arabia or INMETRO for Brazil. Request certificates of conformity and test reports for electrical safety, color consistency, and environmental durability. Verified QA certifications ensure product reliability, regulatory compliance, and smoother customs clearance. -
What are the best payment terms and methods for international B2B transactions involving addressable LEDs?
Common payment methods include Letters of Credit (L/C), Telegraphic Transfers (T/T), and Escrow services. L/Cs provide security for both parties but may incur higher bank fees. T/T is faster but riskier without trust. Negotiate partial payments—such as 30% upfront and 70% after inspection—to balance risk. For first-time suppliers, consider using trade assurance platforms or third-party inspection services. Always confirm payment terms in the contract to avoid disputes. -
How should I plan logistics and shipping for addressable LED strip orders to Africa, South America, or the Middle East?
Choose shipping methods based on cost, urgency, and order size—sea freight is cost-effective for bulk orders but slower, while air freight offers speed at a premium. Work with freight forwarders experienced in your target region to navigate customs clearance and local regulations. Verify packaging is robust to prevent damage during transit. Factor in import duties and taxes upfront. Establish clear Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) to define responsibilities and avoid unexpected costs. -
What quality control measures should I implement upon receiving addressable LED shipments?
Conduct incoming inspections for physical damage, color accuracy, LED functionality, and controller compatibility. Use sample testing to verify electrical parameters and programmability. If feasible, engage third-party inspection agencies for batch verification. Document all findings and compare them against agreed specifications. Early detection of defects enables faster resolution with suppliers and reduces operational downtime. -
How can I resolve disputes effectively if addressable LED products do not meet agreed specifications?
Maintain detailed contracts specifying technical requirements, delivery schedules, and penalties for non-compliance. Communicate issues promptly with photographic and test evidence. Negotiate solutions such as replacements, refunds, or discounts. Use mediation or arbitration clauses in contracts for formal dispute resolution. Building long-term relationships with suppliers who prioritize transparency and accountability is key to minimizing conflicts. Keep legal counsel familiar with international trade laws to support complex cases.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for addressable led
Addressable LED technology presents a transformative opportunity for businesses seeking customizable, dynamic lighting solutions. For international B2B buyers—especially those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—the strategic sourcing of addressable LEDs requires careful consideration of product specifications, IC types, voltage requirements, and compatibility with control protocols such as SPI and DMX512. Understanding these technical nuances ensures optimal performance, reduces operational risks, and enhances project outcomes.
Key takeaways for B2B buyers include:
- Prioritize suppliers offering diverse product ranges with clear technical documentation and support for various IC models to meet specific application needs.
- Evaluate the balance between cost, quality, and technological sophistication to secure lighting solutions that deliver both innovation and reliability.
- Leverage local and international partnerships to navigate supply chain complexities and optimize logistics, particularly in emerging markets.
Looking ahead, the addressable LED market is poised for growth fueled by advances in smart lighting controls and energy-efficient designs. Buyers who embrace strategic sourcing—grounded in technical expertise and market insight—will unlock competitive advantages and drive sustainable innovation in their lighting projects. Engage proactively with trusted manufacturers and stay informed on emerging technologies to capitalize on the evolving landscape of addressable LED solutions.