Guide to Led Strip And Power Supply
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for led strip and power supply
- Understanding led strip and power supply Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of led strip and power supply
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for led strip and power supply
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for led strip and power supply
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for led strip and power supply Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential led strip and power supply Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for led strip and power supply
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the led strip and power supply Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of led strip and power supply
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for led strip and power supply
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for led strip and power supply
The LED strip and power supply sector is at the forefront of modern lighting innovation, offering unparalleled flexibility, energy efficiency, and design versatility that meet the evolving demands of commercial, industrial, and architectural projects worldwide. For international B2B buyers—especially those from dynamic markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—mastering the complexities of this market is essential to secure high-quality, cost-effective solutions that align with regional standards and application needs.
This comprehensive guide delivers an authoritative resource to navigate the diverse landscape of LED strips and their power supplies. It covers critical aspects including the variety of LED strip types (from single-color to advanced addressable and COB models), the impact of materials and technical specifications on performance and durability, and the rigorous manufacturing and quality control processes that ensure product reliability. Additionally, it provides in-depth analysis of supplier ecosystems, cost structures, market trends, and sustainability considerations, tailored to the unique challenges faced by international buyers.
By equipping decision-makers with detailed knowledge and practical insights, this guide empowers businesses to make informed sourcing choices—balancing innovation, quality, and price. Whether upgrading existing installations or launching new projects, buyers will gain the confidence to evaluate suppliers effectively, understand technical trade-offs, and anticipate market shifts. Ultimately, this resource is designed to unlock competitive advantages and drive successful procurement strategies in the global LED strip and power supply market.
Understanding led strip and power supply Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Color LED Strip | Emits uniform single color; simple circuitry | Retail displays, accent lighting, signage | Pros: Cost-effective, easy installation; Cons: Limited color options, less dynamic lighting effects |
| RGB and RGBW LED Strip | Combines red, green, blue LEDs; RGBW adds dedicated white LEDs | Hospitality, event venues, architectural | Pros: Versatile color range, dynamic effects; Cons: Higher cost, requires compatible controllers |
| Addressable LED Strip | Individually controllable LEDs with integrated ICs | Entertainment, advertising, smart buildings | Pros: Pixel-level control, complex animations; Cons: Complex setup, higher technical skill needed |
| Waterproof LED Strip | IP65-IP68 rated, sealed with silicone or epoxy | Outdoor lighting, marine, industrial | Pros: Durable in harsh environments; Cons: Reduced flexibility, higher price point |
| Constant Voltage & Constant Current Power Supplies | Constant voltage (12V/24V) or constant current (350mA+) output | All LED strip types, industrial lighting | Pros: Matches LED requirements for safety and longevity; Cons: Incorrect type can cause LED damage |
Single-Color LED Strip
Single-color LED strips are the most straightforward type, offering a consistent light output in one color such as warm white or cool white. Their simplicity makes them highly cost-effective and easy to deploy across large-scale projects, especially in retail or signage applications where dynamic color changes are not required. B2B buyers should prioritize quality of LEDs and PCB copper thickness to ensure longevity, especially in regions with varying power stability. These strips are ideal for buyers seeking reliable, budget-friendly lighting solutions with minimal complexity.
RGB and RGBW LED Strip
RGB LED strips enable mixing of red, green, and blue LEDs to produce millions of colors, while RGBW strips add a dedicated white LED to improve white light quality and pastel tones. This versatility suits commercial spaces like hotels, restaurants, and architectural projects requiring mood lighting or dynamic ambiance. Buyers from diverse markets should consider controller compatibility and power supply capacity to handle the increased load. RGBW strips, although pricier, offer superior color accuracy and are preferred where white light quality is critical.
Addressable LED Strip
Addressable LED strips integrate IC chips allowing each LED to be controlled independently, enabling intricate lighting patterns, animations, and effects. This type is favored in entertainment, advertising displays, and smart building projects where customization and interactivity are paramount. For B2B buyers, understanding the communication protocols (e.g., SPI, DMX) and ensuring supplier quality control are essential to avoid operational issues. These strips require specialized controllers and technical expertise, representing a higher investment but unlocking advanced lighting capabilities.
Waterproof LED Strip
Waterproof LED strips are coated with protective materials to achieve IP65 to IP68 ratings, making them suitable for outdoor, marine, or industrial environments exposed to moisture and dust. Buyers targeting markets in Africa, the Middle East, or South America, where humidity and weather conditions vary, must prioritize IP rating certification and robustness. While waterproof strips tend to be less flexible and more expensive than non-waterproof variants, their durability justifies the cost for applications requiring reliable outdoor performance.
Constant Voltage & Constant Current Power Supplies
Power supplies for LED strips come mainly in constant voltage (typically 12V or 24V DC) and constant current (usually measured in milliamps) types. Constant voltage supplies are common for standard LED strips, simplifying installation and scaling. Constant current supplies are preferred for high-power or COB LED strips to ensure consistent brightness and prevent LED damage. For international buyers, selecting the correct power supply type and ensuring compliance with local electrical standards (e.g., CE, UL) is critical to maintain safety and system longevity across diverse regional infrastructures.
Related Video: 10 Mental Models Explained
Key Industrial Applications of led strip and power supply
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of led strip and power supply | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail & Commercial | Accent and display lighting in stores and showrooms | Enhances product visibility, improves customer experience, and drives sales | High CRI for color accuracy, dimmability, energy efficiency, and compliance with local safety standards |
| Hospitality & Leisure | Ambient and decorative lighting in hotels, restaurants, and entertainment venues | Creates inviting atmospheres, supports brand aesthetics, and reduces energy costs | Waterproof rating for humid environments, flexible design, and reliable power supply with surge protection |
| Manufacturing & Warehousing | Task lighting and safety illumination on assembly lines and storage areas | Improves worker productivity, enhances safety, and reduces downtime | Robust IP rating for dusty or wet environments, durable power supplies, and easy installation features |
| Transportation & Infrastructure | Under-cabinet, pathway, and signage lighting in airports, railways, and tunnels | Increases visibility, guides passengers safely, and lowers maintenance costs | Long lifespan LEDs, energy-efficient power supplies, and compliance with regional electrical standards |
| Agriculture & Horticulture | Supplemental grow lighting and environmental control lighting in greenhouses | Boosts crop yields, enables controlled growth conditions, and saves energy | Specific spectrum LEDs, waterproof and dustproof strips, and stable power supply with voltage regulation |
Retail & Commercial Lighting
In retail environments across Europe, Africa, and South America, LED strips paired with reliable power supplies are widely used to accentuate products and displays. High color rendering index (CRI) LED strips ensure that merchandise colors appear vibrant and true to life, which is critical for customer decision-making. Adjustable dimming capabilities allow retailers to tailor lighting intensity for different times of day or promotional events, enhancing ambiance while optimizing energy use. International buyers should prioritize sourcing LED strips with certifications that meet regional safety and efficiency standards, such as CE in Europe or local equivalents in emerging markets.
Hospitality & Leisure
Hotels, restaurants, and entertainment venues in the Middle East and Europe leverage LED strip lighting to create immersive and dynamic atmospheres. Waterproof and flexible LED strips are essential for areas with high humidity or outdoor terraces. These lighting systems not only elevate the guest experience but also contribute to significant energy savings over traditional lighting solutions. For B2B buyers, sourcing durable power supplies with surge protection is crucial to ensure longevity and reduce maintenance in regions prone to electrical fluctuations.
Manufacturing & Warehousing
Industrial facilities in South America and Africa rely on LED strip lighting for task illumination along assembly lines and in storage areas. Bright, consistent lighting improves worker accuracy and safety, reducing errors and accidents. LED strips with high IP ratings withstand dusty, oily, or moist conditions common in these sectors. Power supplies must be robust, capable of handling variable loads, and easy to install to minimize operational disruptions. Buyers should also consider suppliers offering customization options to fit specific industrial layouts.
Transportation & Infrastructure
Airports, railway stations, and tunnels in Europe and the Middle East use LED strip lighting extensively for under-cabinet lighting, pathway illumination, and signage. These installations require long-lasting LEDs and energy-efficient power supplies to minimize maintenance and operational costs. Compliance with strict regional electrical and safety standards is mandatory. International buyers must ensure products can handle voltage variations and offer consistent performance in diverse climatic conditions.
Agriculture & Horticulture
In controlled environment agriculture across Africa and South America, LED strips provide targeted supplemental lighting to optimize photosynthesis and growth cycles. Specialized LED strips emitting specific light spectrums support various plant stages, improving yields and quality. Waterproof and dustproof features are essential to withstand humid and soil-rich environments. Stable power supplies with voltage regulation ensure uninterrupted operation, critical for maintaining crop health. Buyers should work with manufacturers experienced in horticultural lighting to ensure product suitability.
Related Video: How to Choose the Right LED Power Supply
Strategic Material Selection Guide for led strip and power supply
Key Materials for LED Strip and Power Supply Components: An In-Depth Analysis
1. Flexible Printed Circuit Board (FPCB) – Polyimide and Copper Layers
The FPCB is the foundational substrate for LED strips, typically composed of polyimide film with embedded copper layers ranging from 1oz to 4oz thickness. Polyimide offers excellent thermal stability, withstanding temperatures up to 260°C, which is crucial during soldering and operation. Copper layers provide electrical conductivity and influence heat dissipation, directly impacting LED lifespan and performance.
Pros:
– High flexibility for curved or irregular installations.
– Excellent heat resistance and electrical conductivity.
– Lightweight and thin, enabling discreet lighting designs.
Cons:
– Polyimide can be more expensive than alternative substrates like polyester.
– Requires precise manufacturing to avoid delamination or copper oxidation.
Application Impact:
Ideal for indoor and outdoor LED strips requiring bending and shaping, especially in architectural and decorative lighting. The copper thickness should be matched to current load requirements to prevent overheating.
International Buyer Considerations:
Buyers in regions with high ambient temperatures (e.g., Middle East, Africa) should prioritize FPCBs with thicker copper layers (3oz or higher) for better heat management. Compliance with IPC standards (e.g., IPC-2223 for flexible circuits) is common globally, but buyers in Europe and the UK should verify RoHS and REACH compliance to meet environmental regulations.
2. Aluminum Profiles and Heat Sinks
Aluminum is widely used for LED strip housings and heat sinks due to its excellent thermal conductivity (around 205 W/mK), lightweight nature, and corrosion resistance. Profiles often come anodized for enhanced surface durability and aesthetic appeal.
Pros:
– Superior heat dissipation prolongs LED life and maintains brightness.
– Provides mechanical protection and structural support.
– Corrosion-resistant, suitable for humid or outdoor environments.
Cons:
– Higher material and processing cost compared to plastic alternatives.
– Requires precise extrusion and finishing processes, adding to lead time.
Application Impact:
Essential for high-power LED strips and outdoor installations where heat buildup and environmental exposure are concerns. Aluminum profiles also facilitate easier mounting and integration into architectural elements.
International Buyer Considerations:
In Europe and the UK, anodized aluminum profiles must meet EN 12373 standards for corrosion resistance. Buyers in coastal or high-humidity regions like South America and parts of Africa should specify marine-grade anodizing or powder coating for enhanced durability. Import tariffs on aluminum may affect cost competitiveness in some African and Middle Eastern markets.
3. Silicone and Polyurethane Coatings (Waterproofing Materials)
Waterproof LED strips use silicone or polyurethane encapsulation to achieve IP65 to IP68 ratings, protecting against moisture, dust, and chemical exposure. Silicone offers flexibility and UV resistance, while polyurethane provides superior abrasion resistance.
Pros:
– Enables outdoor and wet environment applications.
– Protects against dust, chemicals, and UV degradation.
– Maintains flexibility for curved installations.
Cons:
– Adds cost and complexity to manufacturing.
– Silicone may attract dust and dirt, requiring periodic cleaning.
– Polyurethane coatings can be less flexible, limiting bending radius.
Application Impact:
Crucial for outdoor signage, landscape lighting, and industrial environments with exposure to water or chemicals. Choice of coating depends on specific environmental stressors and mechanical demands.
International Buyer Considerations:
Buyers in tropical climates (e.g., Southeast Asia, parts of Africa) should prioritize UV-stabilized silicone coatings. Compliance with IEC 60529 for IP ratings is standard internationally. For Middle Eastern markets, resistance to sand and dust ingress is critical. European buyers may require REACH-compliant materials to meet stringent chemical safety standards.
4. Power Supply Enclosures – ABS Plastic vs. Metal (Steel or Aluminum)
Power supplies for LED strips require protective enclosures that balance thermal management, electrical insulation, and mechanical durability. ABS plastic enclosures are common for indoor use due to their electrical insulation and cost-effectiveness, while metal enclosures (steel or aluminum) offer superior heat dissipation and robustness.
Pros of ABS Plastic:
– Lightweight and cost-effective.
– Good electrical insulation properties.
– Easy to mold into complex shapes.
Cons of ABS Plastic:
– Lower heat dissipation, may require internal thermal management.
– Less impact and UV resistant, unsuitable for harsh outdoor environments.
Pros of Metal Enclosures:
– Excellent thermal conductivity, reducing overheating risk.
– Enhanced mechanical protection and electromagnetic shielding.
– Suitable for outdoor or industrial applications.
Cons of Metal Enclosures:
– Higher cost and weight.
– Requires grounding and insulation considerations.
Application Impact:
Indoor commercial lighting projects often use ABS enclosures for power supplies, while outdoor or industrial settings demand metal enclosures for durability and heat management.
International Buyer Considerations:
Buyers in Europe and the UK should ensure compliance with EN 60529 for enclosure ingress protection and CE marking for electrical safety. In regions with high ambient temperatures (Middle East, Africa), metal enclosures are preferred to avoid thermal failures. South American buyers should consider local standards like INMETRO for electrical safety certification.
Summary Table of Materials for LED Strip and Power Supply
| Material | Typical Use Case for led strip and power supply | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyimide FPCB with Copper Layers | Flexible LED strip substrates requiring heat dissipation | High thermal stability and flexibility | Higher cost than polyester; delicate handling | Medium |
| Aluminum Profiles and Heat Sinks | Structural housing and heat dissipation for LED strips | Excellent heat dissipation and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and processing complexity | High |
| Silicone/Polyurethane Coatings | Waterproofing for outdoor and industrial LED strips | Provides IP65-IP68 protection and UV resistance | Adds cost; silicone attracts dust; polyurethane less flexible | Medium |
| ABS Plastic and Metal Enclosures | Power supply housing for indoor (ABS) and outdoor (metal) | ABS: cost-effective and insulating; Metal: durable and thermally efficient | ABS: poor heat dissipation; Metal: higher cost and weight | ABS: Low; Metal: Medium-High |
This material selection guide empowers international B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific regional requirements, environmental conditions, and application needs. Prioritizing compliance with local and international standards ensures product reliability and market acceptance across Africa, South America, the Middle East,
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for led strip and power supply
The manufacturing of LED strips and their corresponding power supplies involves highly specialized processes designed to ensure performance, reliability, and safety. For international B2B buyers, especially those operating in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes and the associated quality assurance measures is vital to selecting dependable suppliers and mitigating risks.
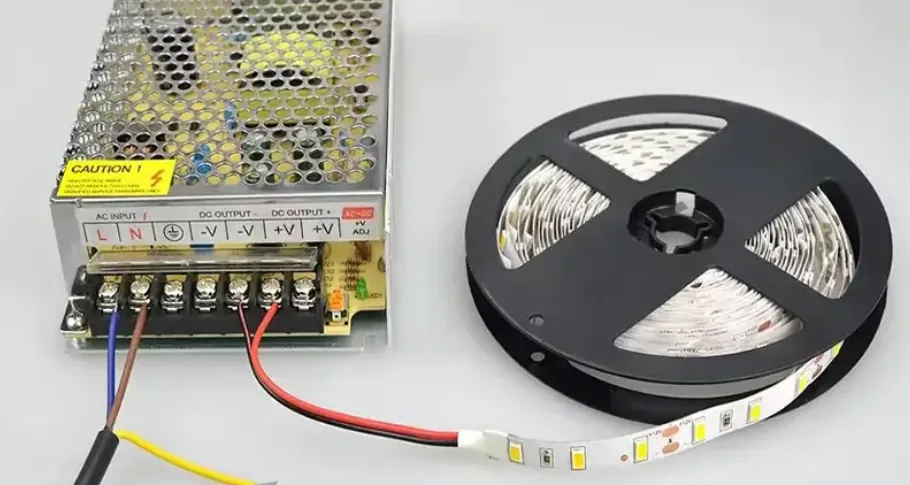
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Core Manufacturing Processes for LED Strips and Power Supplies
1. Material Preparation
The production journey begins with sourcing and preparing raw materials. For LED strips, this primarily involves manufacturing flexible printed circuit boards (FPCBs) with copper layers that provide electrical pathways and heat dissipation. High-quality copper weight (e.g., 2oz to 4oz) and flexible substrates are chosen based on the application’s durability and thermal requirements. In power supplies, key components such as transformers, capacitors, and semiconductors undergo rigorous selection to meet voltage and current specifications.
2. Component Mounting and Assembly
LEDs are mounted onto the FPCB using Surface Mount Technology (SMT), which places SMD (Surface Mount Device) LEDs like 2835 or 5050 types precisely on the board. This step requires automated pick-and-place machines for accuracy and speed. For power supplies, assembly involves soldering electronic components onto printed circuit boards, often using wave soldering or reflow soldering techniques to ensure strong, reliable connections.
3. Wiring and Integration
Once LEDs are mounted, wiring connects the LEDs in series or parallel circuits as per design requirements. For addressable LED strips, integrated circuits (ICs) are embedded to enable individual LED control. Power supplies are integrated with input/output terminals, protective devices, and sometimes cooling elements like heat sinks or fans. This stage is critical for ensuring electrical safety and functional integrity.
4. Protective Coating and Finishing
To enhance durability, LED strips often receive protective coatings such as silicone or epoxy encapsulation, granting water resistance (IP65 to IP68 ratings) suitable for outdoor or humid environments. Power supplies are typically enclosed in metal or plastic casings to prevent electrical hazards and facilitate heat dissipation. Final finishing may also include labeling, packaging, and inclusion of connectors or accessories.
Quality Assurance Framework and Standards
International and Industry Standards
– ISO 9001: The cornerstone of quality management systems, ISO 9001 certification ensures consistent manufacturing quality and continuous improvement. Suppliers adhering to this standard demonstrate robust process control and documentation.
– CE Marking: Mandatory for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE certification confirms compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental requirements. LED strips and power supplies with CE marking assure buyers of conformity to stringent regulations.
– RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): This directive limits hazardous materials in electrical products, critical for compliance in European markets and increasingly demanded worldwide.
– UL and ETL (for power supplies): Safety certifications from Underwriters Laboratories (UL) or Electrical Testing Laboratories (ETL) are important for North American and global buyers, verifying that power supplies meet electrical safety standards.
– API and Other Regional Certifications: Depending on the buyer’s region, additional certifications such as IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards or local approvals might be required, especially for power supplies.
Quality Control Checkpoints Throughout Production
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
Raw materials and components are inspected upon arrival. This includes verifying PCB thickness and copper weight, LED binning for color and brightness consistency, and component authenticity for power supply parts. IQC prevents defective inputs from entering production.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
During assembly, IPQC involves monitoring solder joints, alignment of LEDs, and circuit continuity. Automated optical inspection (AOI) and manual checks ensure that defects are detected early. For power supplies, electrical parameters such as voltage stability and thermal performance are tested at this stage.
Final Quality Control (FQC)
Completed LED strips and power supplies undergo comprehensive testing before packaging. This includes:
– Electrical Testing: Verification of voltage, current, and power consumption against specifications.
– Functional Testing: Ensuring LEDs light correctly, dimming functions operate, and addressable controls respond as expected.
– Environmental Testing: For waterproof strips, IP rating tests confirm resistance to dust and moisture. Thermal cycling and vibration tests may be conducted on power supplies.
– Safety Tests: Insulation resistance, leakage current, and overload protection tests for power supplies ensure end-user safety.
Testing Methods and Tools Commonly Employed
- Spectroradiometers and Luminance Meters: Measure brightness, color temperature, and CRI (Color Rendering Index) of LED strips.
- Electrical Load Testers: Assess power supply performance under various load conditions.
- AOI Machines: Detect soldering defects and component misplacements on PCBs.
- Environmental Chambers: Simulate temperature and humidity extremes to verify product durability.
- IP Testing Equipment: Spray nozzles and immersion tanks for waterproofing validation.
How B2B Buyers Can Verify Supplier Quality Assurance
Supplier Audits
Conduct on-site audits or remote video inspections focusing on production lines, QC laboratories, and warehouse management. Evaluate the supplier’s adherence to documented procedures and certifications.
Review of QC Documentation
Request detailed quality control records including IQC reports, in-process inspection logs, and final test certificates. Suppliers should provide traceability for batches and components.
Third-Party Inspection and Testing
Engage independent inspection agencies to conduct pre-shipment inspections, sample testing, and compliance verification. This adds a layer of impartial assurance, especially important for buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East, where local regulatory oversight may vary.
Sample Evaluation
Order prototype or pilot batches to test in real-world conditions before committing to large orders. This allows assessment of product consistency, performance, and compatibility with local standards.
QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers
- Regional Regulatory Alignment: Buyers in Europe and the UK must prioritize CE marking and RoHS compliance. Meanwhile, markets in Africa and South America may require additional certifications or approvals aligned with local authorities. Understanding these nuances helps avoid customs delays and market entry barriers.
- Voltage and Frequency Compatibility: Power supplies must match the voltage (e.g., 110V, 220V) and frequency (50Hz, 60Hz) standards of the buyer’s region to ensure safe and efficient operation.
- Environmental Considerations: For buyers in humid or outdoor markets (Middle East coastal areas, parts of Africa), waterproofing and thermal management are critical. Insist on suppliers providing IP rating test results and thermal performance data.
- Sustainability and Compliance: Increasingly, buyers from Europe and progressive markets demand eco-friendly manufacturing processes and materials free from hazardous substances. Verify supplier adherence to environmental standards and certifications.
By gaining a thorough understanding of these manufacturing and quality assurance aspects, international B2B buyers can confidently evaluate LED strip and power supply suppliers, ensuring product reliability, compliance, and long-term partnership success. This knowledge is particularly valuable for buyers navigating diverse market requirements and regulatory landscapes across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Related Video: LED Light Making Process | How LED Lights Made Inside Factory | Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for led strip and power supply Sourcing
When sourcing LED strips and power supplies for international B2B purposes, particularly across diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, a thorough understanding of the cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential to optimize procurement strategies and ensure competitive advantages.
Key Cost Components in LED Strip and Power Supply Manufacturing
-
Materials:
The raw materials—LED chips (e.g., SMD 2835, 5050), flexible PCBs with varying copper thickness, resistors, capacitors, and power supply components—constitute the bulk of the cost. Higher-grade materials, such as high-purity copper PCBs or premium LED chips with superior CRI and brightness, increase costs but enhance product longevity and performance. -
Labor:
Labor costs vary significantly depending on the manufacturing location. Chinese factories typically offer cost advantages due to established supply chains and skilled labor, but labor costs are rising. Buyers should weigh labor cost savings against quality and delivery reliability. -
Manufacturing Overhead:
Includes factory utilities, maintenance, equipment depreciation, and administrative expenses. Efficient factories with modern automation often pass savings to buyers through better economies of scale. -
Tooling and Setup:
Initial tooling for custom LED strip designs or power supply configurations can be substantial, especially for addressable or specialty strips. This cost is amortized over production volume, making larger orders more cost-effective. -
Quality Control (QC):
Rigorous testing for brightness uniformity, waterproof ratings (IP65-IP68), electrical safety, and certifications (CE, RoHS, UL) adds to costs but reduces risks of returns and warranty claims. -
Logistics and Duties:
International shipping fees, customs duties, and import taxes affect landed costs. Incoterms chosen (FOB, CIF, DDP) determine who bears these costs and risks, impacting the final price. -
Supplier Margin:
Factory profit margins typically range from 10% to 30%, influenced by order size, product complexity, and market demand.
Influencing Factors on Pricing
-
Order Volume and MOQ:
Larger orders benefit from scale economies and reduced per-unit costs. Minimum order quantities (MOQs) vary by supplier and product type, impacting upfront investment. -
Technical Specifications and Customization:
More advanced features—such as addressable LEDs, higher IP ratings, or specific color temperatures—increase costs. Custom packaging and branding also raise prices. -
Material Quality and Certifications:
Products with international certifications command premium pricing but facilitate smoother market entry and compliance. -
Supplier Reputation and Location:
Established suppliers with robust quality systems may price higher but offer lower risk. Factories closer to the buyer’s market can reduce shipping times and costs. -
Incoterms and Payment Terms:
The choice of Incoterms affects cost transparency and risk allocation. Favorable payment terms (e.g., letters of credit) may influence pricing negotiations.
Practical Tips for International B2B Buyers
-
Negotiate Beyond Price:
Engage suppliers on payment terms, lead times, and after-sales support. Volume discounts, bundled deals (LED strips plus power supplies), and long-term contracts can yield cost benefits. -
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO):
Consider product durability, energy efficiency, warranty conditions, and potential rework costs. Cheaper upfront prices may lead to higher lifecycle costs. -
Understand Regional Pricing Nuances:
For buyers in Africa and South America, factor in longer shipping times and customs complexities. In Europe and the Middle East, strict certification requirements may justify paying a premium. -
Leverage Sourcing Hubs:
Sourcing from major manufacturing centers (e.g., China) remains cost-effective but requires due diligence on supplier reliability and compliance with local regulations. -
Plan for Logistics and Currency Fluctuations:
Lock in shipping schedules and payment currencies where possible to mitigate cost volatility.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for LED strips and power supplies fluctuate due to raw material markets, technological advances, and geopolitical factors. The cost components and pricing influencers outlined here serve as an indicative framework to guide procurement decisions rather than fixed price points.
By dissecting the comprehensive cost structure and understanding pricing levers, international B2B buyers can strategically source LED strips and power supplies that balance cost, quality, and compliance—ensuring optimal value across diverse global markets.
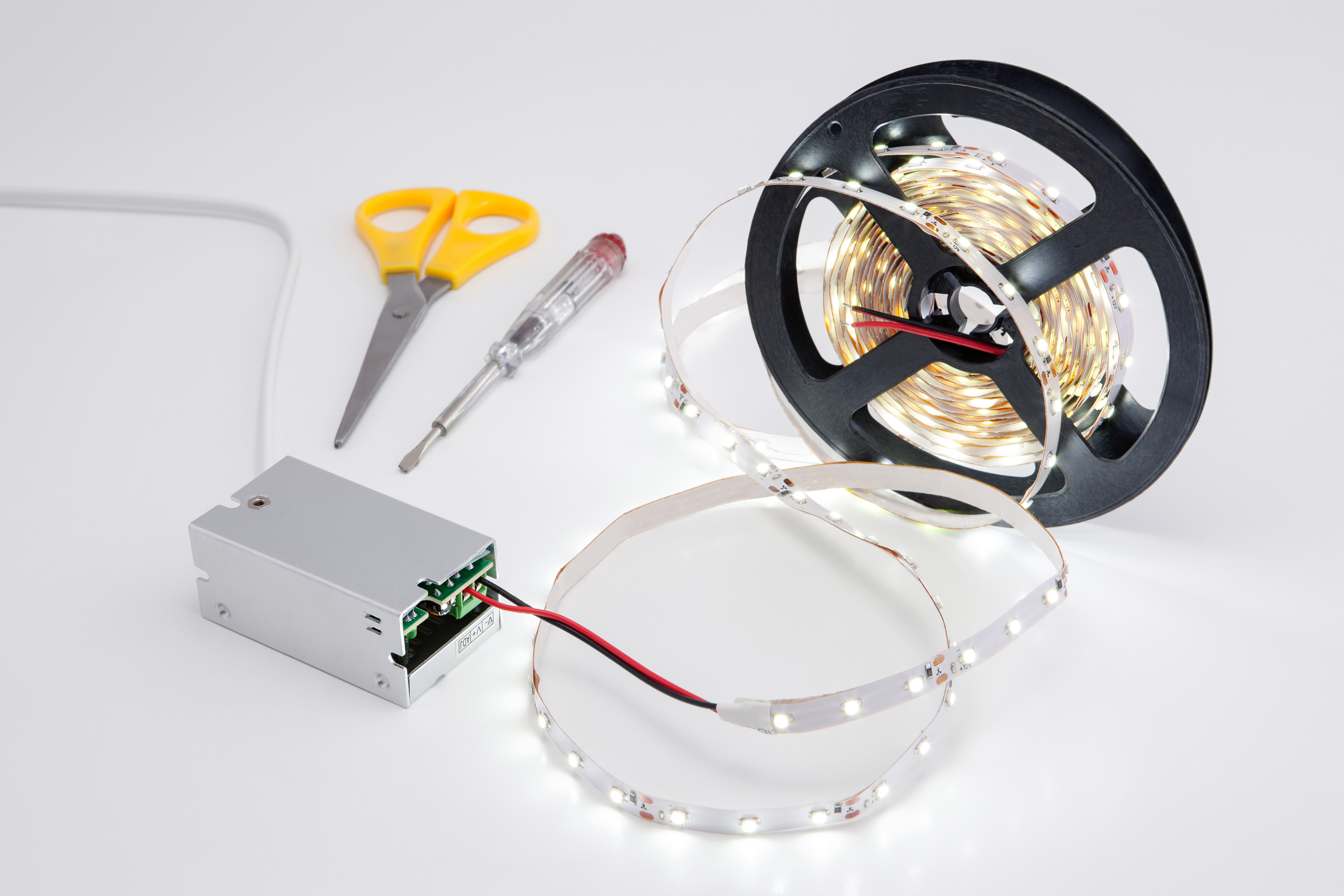

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Spotlight on Potential led strip and power supply Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section offers a look at a few manufacturers active in the ‘led strip and power supply’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct their own extensive due diligence before any engagement. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for led strip and power supply
Critical Technical Properties for LED Strips and Power Supplies
Understanding key technical specifications is essential for B2B buyers to ensure product compatibility, longevity, and performance, especially when sourcing internationally.
-
Material Grade of PCB (Printed Circuit Board)
LED strips commonly use flexible PCBs made from materials like polyimide with copper layers measured in ounces (e.g., 2oz, 3oz copper). Higher copper weight improves heat dissipation and durability, reducing thermal stress and extending strip lifespan. For buyers in warm or industrial climates, selecting strips with thicker copper layers is crucial to maintain reliability. -
Voltage and Current Ratings
LED strips typically operate at 12V or 24V DC, while power supplies can range from low-voltage DC to 110V/220V AC input. Choosing the correct voltage ensures safe operation and prevents premature failure. Current ratings determine maximum strip length per power supply; exceeding these can cause voltage drops and uneven brightness. Buyers must verify voltage compatibility with their electrical infrastructure and intended application. -
IP Rating (Ingress Protection)
This rating classifies the strip’s resistance to dust and water — for example, IP20 (indoor, no water protection), IP65 (water-resistant), IP67/IP68 (waterproof). International buyers targeting outdoor or humid environments, such as in Middle Eastern or tropical African markets, should prioritize higher IP ratings to avoid corrosion and electrical hazards. -
Color Temperature and CRI (Color Rendering Index)
Color temperature (measured in Kelvins) affects lighting ambiance — from warm white (2700K) to cool white (6500K). CRI indicates how accurately colors appear under the LED light; values above 80 are preferred for retail, art, and hospitality sectors where true color representation is critical. Buyers should align these properties with project requirements to optimize visual impact. -
Dimmability and Control Compatibility
The ability to dim or adjust LED brightness can be essential for energy savings and mood setting. Common dimming protocols include PWM (Pulse Width Modulation), 0-10V, and DALI. For advanced applications, addressable LED strips allow pixel-level control via specialized controllers. Buyers should confirm controller compatibility to avoid costly integration issues. -
Tolerance and Quality Standards
Manufacturing tolerance refers to allowable variations in electrical and physical properties, such as voltage fluctuation or LED placement accuracy. Tight tolerances ensure consistent performance across batches. International buyers should request quality certifications (e.g., CE, RoHS) and inquire about factory quality control to minimize defects and returns.
Key Trade Terms Every B2B Buyer Should Know
Familiarity with common trade terminology facilitates smoother negotiations, clearer contracts, and better supplier relationships.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to manufacturers that produce products or components sold under another company’s brand. Many LED strips and power supplies are OEM products, allowing buyers to customize branding and specifications. Understanding OEM capabilities helps buyers negotiate bespoke solutions and bulk pricing. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell in one order. MOQs can vary widely depending on product complexity and factory scale. Buyers from emerging markets should clarify MOQs early to balance inventory costs and order feasibility. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal inquiry sent to suppliers requesting price, lead time, and terms for specified products. Well-prepared RFQs with clear technical requirements enable suppliers to provide accurate and comparable quotes, accelerating decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms defining responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs between buyer and seller. Common terms include FOB (Free on Board), CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight), and DDP (Delivered Duty Paid). Knowing Incoterms helps buyers control logistics costs and reduce import risks. -
Lead Time
The period from order confirmation to delivery. This can be affected by production capacity, customs clearance, and shipping. Buyers in fast-growing markets should negotiate realistic lead times to align with project timelines and avoid costly delays. -
Batch Testing / QC (Quality Control)
Refers to the supplier’s process of inspecting products before shipment. Buyers should request documentation of batch testing protocols and consider third-party inspections to ensure product consistency and compliance with agreed standards.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions, optimize cost-efficiency, and reduce supply chain risks in the LED strip and power supply market. This knowledge is particularly valuable for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe who face diverse environmental conditions and regulatory landscapes.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the led strip and power supply Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global LED strip and power supply market is experiencing robust growth driven by increasing adoption across commercial, residential, industrial, and architectural sectors. Energy efficiency mandates, smart building initiatives, and the rise of IoT-enabled lighting solutions are key catalysts shaping demand. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these drivers is critical to aligning procurement strategies with evolving market needs.
Emerging trends include:
- Integration of Addressable LED Technology: Addressable LED strips allow pixel-level control, enabling dynamic lighting effects and enhanced customization. This is increasingly favored in retail, entertainment, and urban infrastructure projects, offering buyers opportunities to differentiate their offerings.
- Shift Toward Higher Voltage and Longer Runs: 24V and even 48V LED strips are gaining traction due to reduced voltage drop and longer uninterrupted runs, simplifying installation and reducing total system costs.
- Smart Controls and Connectivity: Demand for LED strips compatible with wireless protocols (e.g., Zigbee, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth) is rising, enabling seamless integration into smart lighting ecosystems. Buyers must consider compatibility with control systems to future-proof installations.
- Regional Sourcing Diversification: While China remains a dominant manufacturing hub, buyers in emerging markets increasingly explore suppliers from Southeast Asia (Vietnam, Thailand), Eastern Europe, and Turkey to mitigate geopolitical risks and shipping delays.
- Focus on Quality and Compliance: International buyers emphasize certifications such as CE, RoHS, UL, and IEC standards to ensure safety and performance. This trend is particularly strong in Europe and the UK, where regulatory scrutiny is high.
For B2B buyers in Africa and South America, cost-effectiveness combined with durability in harsh environmental conditions (high humidity, dust) is paramount. Middle Eastern markets prioritize high IP-rated waterproof LED strips for outdoor and architectural applications. European buyers focus on high CRI and energy-efficient power supplies to meet stringent environmental and aesthetic standards.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has emerged as a decisive factor in the procurement of LED strips and power supplies. Buyers worldwide are under increasing pressure to reduce carbon footprints and ensure ethical supply chains. For B2B buyers, particularly those in environmentally conscious markets like Europe and progressive regions in South America and the Middle East, sustainability translates into several actionable sourcing criteria:
- Material Selection: Opting for LED strips manufactured with low-toxicity, recyclable materials and power supplies designed for energy efficiency (high power factor, low standby power) reduces environmental impact.
- Certifications and Standards: Compliance with global eco-labels such as Energy Star, TUV Green Mark, and RoHS ensures that products meet environmental and safety benchmarks. These certifications also facilitate access to markets with strict import regulations.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Buyers increasingly demand full visibility into manufacturing practices, including labor conditions, sourcing of raw materials (e.g., conflict-free minerals), and carbon emissions. Partnering with suppliers who provide sustainability reports and third-party audits mitigates reputational risks.
- End-of-Life Management: Encouraging suppliers to offer recycling programs or take-back schemes for LED strips and power supplies supports circular economy initiatives and reduces e-waste.
- Energy Efficiency Focus: Selecting power supplies with high efficiency ratings (80 PLUS certification or better) and LED strips with optimized luminous efficacy helps reduce operational energy costs and aligns with corporate sustainability goals.
For international buyers in emerging markets, educating suppliers on sustainability expectations and gradually integrating green procurement practices can yield competitive advantages and improve market positioning.
Brief Evolution and Historical Context
The LED strip lighting industry has evolved significantly since the early 2000s when rigid, single-color LED modules dominated the market. Advances in surface mount technology (SMT) and flexible printed circuit boards (FPCB) enabled the development of versatile, energy-efficient LED strips capable of producing a wide spectrum of colors and customizable effects.
The emergence of addressable LED strips in the 2010s marked a technological leap, allowing individual LED control and complex animations previously unattainable with traditional lighting. Concurrently, power supply units evolved from basic transformers to sophisticated, compact drivers with improved efficiency, dimmability, and smart integration capabilities.
This evolution reflects a broader industry trend toward highly customizable, intelligent lighting solutions that cater to diverse applications — from decorative retail displays to large-scale architectural projects. Understanding this historical context helps B2B buyers appreciate the value proposition of modern LED strip and power supply technologies and anticipate future innovation trajectories.
Related Video: International Trade and Supply Chains
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of led strip and power supply
-
How can I effectively vet LED strip and power supply suppliers for international B2B purchases?
Supplier vetting should start with verifying their manufacturing capabilities, certifications (such as ISO 9001, CE, RoHS), and product quality records. Request factory audits or third-party inspection reports to confirm production standards. Evaluate their experience with international shipping and compliance with destination country regulations. Checking references from other international buyers, especially within your region, provides valuable insights. Finally, assess their communication responsiveness and after-sales support to ensure smooth collaboration throughout the supply chain. -
What customization options are typically available for LED strips and power supplies, and how can I ensure they meet my project requirements?
Most manufacturers offer customization on LED type, color temperature, IP rating (waterproofing), length, voltage, and connectors. For power supplies, options include voltage, wattage, efficiency ratings, and certifications. To ensure alignment with your needs, provide detailed technical specifications and application context to the supplier upfront. Request prototypes or samples for testing before committing to large orders. Clear documentation and signed technical agreements mitigate risks of miscommunication, especially when dealing with long-distance suppliers. -
What are common minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for international orders of LED strips and power supplies?
MOQs vary widely depending on product complexity and supplier scale but typically range from 500 to 2,000 meters for LED strips and 100 to 500 units for power supplies. Lead times usually span 3 to 8 weeks, factoring in production, quality checks, and shipping. Buyers from Africa, South America, and the Middle East should also account for customs clearance delays. Negotiating flexible MOQs or phased deliveries is possible with established suppliers, helping manage inventory and cash flow more effectively. -
Which quality assurance measures and certifications should I require to ensure reliable LED strip and power supply products?
Demand suppliers provide proof of compliance with international safety and quality standards such as CE, RoHS, UL, and FCC. Insist on detailed quality control protocols, including in-line inspections, burn-in tests, and final product testing for electrical safety and performance consistency. Request test reports or certificates from accredited labs. For critical applications, consider third-party factory audits or pre-shipment inspections to verify quality before dispatch. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing LED strips and power supplies internationally?
Understand the shipping options (air, sea, express courier) and their cost-time trade-offs. LED strips are lightweight but can be fragile; ensure suppliers use secure packaging to prevent damage during transit. Verify Incoterms to clarify cost and risk responsibilities. Also, research import duties, taxes, and local regulations in your country to avoid unexpected costs or delays. Working with freight forwarders experienced in electronics and negotiating consolidated shipments can optimize your supply chain efficiency. -
How should payment terms be structured to minimize risk when sourcing LED strips and power supplies internationally?
Standard B2B payment terms include a 30% deposit upfront and 70% balance upon shipment or receipt of documents. Letters of Credit (LC) and escrow services offer higher security for large orders. Avoid full prepayment unless dealing with highly trusted partners. Using trade assurance platforms or third-party escrow services can protect both parties. Clear contract terms on payment milestones, delivery timelines, and penalties for non-compliance help manage financial risk. -
What steps can I take to resolve disputes related to product quality or delivery issues with international LED strip suppliers?
First, maintain clear communication and document all agreements and correspondence. Upon quality or delivery disputes, request photographic or video evidence and arrange for independent third-party inspection if necessary. Refer to the contract’s dispute resolution clause, which often recommends negotiation or mediation before arbitration. Leveraging trade platforms with dispute resolution support or involving local trade chambers can also facilitate amicable settlements. Always have legal counsel review contracts to protect your interests. -
How can I ensure compliance with environmental and safety regulations when importing LED strips and power supplies into my country?
Familiarize yourself with local regulations concerning electrical safety, electromagnetic compatibility, and hazardous substances restrictions (e.g., RoHS compliance). Request conformity certificates and test reports from suppliers as proof of compliance. For markets like the EU or UK, CE marking is mandatory, while other regions may require additional certifications. Partner with suppliers who prioritize sustainable manufacturing and use eco-friendly materials to future-proof your supply chain and meet increasingly stringent regulatory demands.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for led strip and power supply
The LED strip and power supply market presents vast opportunities for international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Strategic sourcing is paramount to securing products that balance quality, cost-efficiency, and technological innovation. Understanding critical technical factors—such as LED types, IP ratings, power specifications, and dimming capabilities—enables buyers to align product choices with their unique operational needs and environmental conditions.
Key takeaways for buyers include:
- Prioritize suppliers with robust manufacturing processes and transparent quality control to ensure product reliability and longevity.
- Evaluate power supply compatibility meticulously to optimize system performance and safety.
- Consider emerging trends like addressable LED strips and COB technology for applications demanding high customization and superior light uniformity.
- Assess supplier sustainability practices and compliance with international standards to future-proof investments.
Looking ahead, the global LED lighting landscape will continue evolving rapidly, driven by innovation and growing demand for energy-efficient solutions. Buyers who adopt a strategic, informed sourcing approach will be best positioned to capitalize on these trends, unlocking competitive advantages in their markets. Engage proactively with reputable manufacturers and leverage comprehensive technical insights to make decisions that foster long-term success and sustainability in your lighting projects.
