Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for do led strip lights use a lot of electricity
The global demand for energy-efficient lighting solutions has never been more pressing, especially for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize operational costs and sustainability. Among these solutions, LED strip lights have emerged as a versatile, stylish, and increasingly popular choice across commercial and industrial sectors. However, a critical question remains for buyers from diverse markets such as Nigeria, Poland, Brazil, or the UAE: do LED strip lights use a lot of electricity? Understanding the true energy consumption of these lighting systems is pivotal for accurate budgeting, procurement planning, and long-term cost management.
This comprehensive guide delves deeply into the technical and commercial aspects of LED strip lighting, empowering buyers to make informed sourcing decisions in a competitive global marketplace. It covers essential topics including various LED strip types and their electrical efficiencies, material quality considerations, manufacturing and quality control standards, and key supplier evaluation criteria. Additionally, the guide provides detailed insights on cost structures, market trends, and frequently asked questions that directly impact purchasing strategies.
For businesses operating in regions with fluctuating energy costs and infrastructure challenges, such as parts of Africa and South America, this knowledge is invaluable. Similarly, buyers in Europe and the Middle East benefit from understanding how LED technology advancements can reduce electricity consumption without compromising performance. By equipping international buyers with clear, actionable information, this guide facilitates smarter investments in LED strip lighting that align with both economic and environmental goals.
Understanding do led strip lights use a lot of electricity Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard LED Strip | Flexible PCB with 3528 or 5050 LEDs, varying densities | Retail lighting, office decor, residential | + Cost-effective, energy-efficient; – Limited brightness for large spaces |
| COB LED Strip | Chip-on-Board tech, continuous light output, high density | Architectural lighting, hospitality, displays | + Uniform light, high brightness; – Higher initial cost |
| RGB LED Strip | Multi-color LEDs with controllers for color changing | Event venues, advertising, entertainment | + Versatile lighting effects; – Slightly higher power consumption |
| Neon Flex LED Strip | Silicone encased, neon-like continuous lighting | Outdoor signage, facade lighting | + Weather-resistant, flexible; – Moderate power use, premium price |
| High-Density LED Strip | Very high LED count per meter, intense illumination | Industrial lighting, large commercial spaces | + Extremely bright, customizable; – Highest power consumption |
Standard LED Strip
This is the most common type, featuring 3528 or 5050 LEDs on flexible circuit boards. They balance brightness and energy consumption well, making them ideal for retail, office, and residential applications. For B2B buyers, these strips offer reliable performance at competitive prices. When purchasing, consider the LED density per meter to match illumination needs without overspending on energy.
COB LED Strip
Chip-on-Board (COB) LED strips provide a seamless, continuous light output with higher LED density than standard strips. These are favored in architectural and hospitality projects for their superior brightness and uniformity. Buyers should weigh the higher upfront cost against long-term energy savings and aesthetic benefits, especially in premium commercial environments.
RGB LED Strip
RGB strips incorporate red, green, and blue LEDs, enabling dynamic color changes via controllers. They are popular in entertainment, advertising, and event spaces where mood lighting and flexibility are crucial. For B2B procurement, ensure compatibility with control systems and assess the slightly increased power requirements due to multi-color functionality.
Neon Flex LED Strip
Encased in durable silicone, neon flex strips mimic traditional neon lighting with enhanced flexibility and weather resistance. Ideal for outdoor signage and building facades, they offer a premium look with moderate energy use. Buyers should consider environmental factors and installation complexity, as well as the higher price point relative to standard LED strips.
High-Density LED Strip
These strips pack a very high number of LEDs per meter, delivering intense illumination suitable for industrial and large commercial applications. They consume more power but provide unparalleled brightness and customization options. B2B buyers should plan for increased electrical load and cooling requirements while benefiting from their superior lighting performance.
Key Industrial Applications of do led strip lights use a lot of electricity
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of do led strip lights use a lot of electricity | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail & Commercial | Ambient and accent lighting in retail stores and shopping malls | Enhances customer experience and brand visibility with energy efficiency | Select LED strips with optimal brightness-to-power ratio; ensure compliance with local energy standards and durability for high-traffic areas |
| Hospitality & Leisure | Mood lighting in hotels, restaurants, and entertainment venues | Creates inviting atmospheres while reducing operational energy costs | Prioritize dimmable, color-adjustable LED strips; consider installation flexibility and local voltage compatibility |
| Manufacturing & Warehousing | Task lighting and safety illumination in production lines and storage areas | Improves worker safety and productivity through consistent lighting | Choose robust, long-life LED strips with low power consumption; ensure IP rating for dust and moisture resistance |
| Architecture & Urban Development | Decorative building façade lighting and public space illumination | Boosts aesthetic appeal and urban branding with energy savings | Source weather-resistant, high-efficiency LED strips; verify energy consumption specs to manage power budgets |
| Transportation & Infrastructure | Interior and exterior lighting in vehicles, stations, and airports | Enhances visibility and passenger comfort with minimal energy use | Opt for flexible, vibration-resistant LED strips; confirm compatibility with vehicle electrical systems and regional power standards |
Retail & Commercial Applications
In retail environments across markets such as Nigeria and Poland, LED strip lights are widely used for ambient and accent lighting to enhance product displays and overall store aesthetics. Despite concerns about electricity consumption, modern LED strips offer significant energy savings compared to traditional lighting, making them ideal for businesses aiming to reduce operational costs. Buyers should focus on LED strips that balance brightness and power consumption, ensuring compliance with local energy regulations and durability to withstand continuous use in busy commercial settings.
Hospitality & Leisure Sector
Hotels and restaurants in regions like South America and the Middle East utilize LED strip lights to create dynamic mood lighting that can be adjusted for different times of day or events. These applications demand LED strips that support dimming and color control without excessive power draw. International buyers must consider voltage compatibility and installation flexibility to accommodate diverse infrastructure standards. Energy-efficient LED strips reduce electricity expenses, a critical factor for hospitality businesses managing large-scale lighting installations.
Manufacturing & Warehousing
Industrial facilities require reliable task lighting that maintains worker safety and operational efficiency. LED strip lights are favored for their low heat emission and long lifespan, which reduces maintenance downtime. In environments such as warehouses in Europe or factories in Africa, sourcing LED strips with robust construction and suitable IP ratings is essential to withstand dust and moisture. Buyers should prioritize products with proven low power consumption to optimize energy budgets while ensuring consistent illumination.
Architecture & Urban Development
Urban planners and architects leverage LED strip lights for decorative façade illumination and public space lighting to enhance cityscapes with sustainable solutions. In countries with growing urban infrastructure projects, like Poland and Nigeria, energy-efficient LED strips help manage municipal electricity costs while delivering high-impact visual effects. Selecting weather-resistant LED strips with verified power consumption data allows for effective energy management and long-term durability in outdoor applications.
Transportation & Infrastructure
Transportation hubs and vehicles benefit from LED strip lights that provide clear, reliable illumination with minimal energy use. Airports, train stations, and buses in regions such as the Middle East and South America require LED strips that can endure vibrations and fluctuating electrical loads. International buyers must ensure compatibility with local electrical systems and prioritize flexible, durable LED strips that contribute to passenger comfort and operational efficiency without incurring high electricity costs.
Related Video: Do LED strip lights get hot? – Why use a profile as a heatsink?
Strategic Material Selection Guide for do led strip lights use a lot of electricity
When selecting materials for LED strip lights, especially in the context of energy consumption and efficiency, the choice of substrate, encapsulation, and conductive materials plays a crucial role. These materials influence not only the electrical performance and durability but also the overall energy efficiency and suitability for various international markets. Below is an analysis of four common materials relevant to LED strip light manufacturing and their implications for B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Flexible Printed Circuit Board (FPCB) – Polyimide or PET Substrate
Key Properties:
FPCBs typically use polyimide or polyethylene terephthalate (PET) as a flexible substrate. Polyimide offers excellent thermal stability (up to 260°C), chemical resistance, and flexibility, while PET is more cost-effective but has lower temperature tolerance (~120°C). Both materials provide good electrical insulation and mechanical durability.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: High flexibility allows for versatile installation in complex geometries; polyimide-based FPCBs withstand high temperatures during soldering and operation, enhancing longevity; PET substrates reduce costs for less demanding applications.
– Cons: Polyimide is more expensive and may require specialized manufacturing processes; PET substrates have limited heat resistance, which can affect LED lifespan under high power conditions.
Impact on Application:
FPCBs are essential for energy-efficient LED strip lights as they enable compact, lightweight designs that dissipate heat effectively, reducing power loss. Polyimide substrates are preferred for high-density, high-brightness LED strips that consume more electricity but require efficient thermal management.
International B2B Considerations:
Buyers in regions with high ambient temperatures (e.g., Middle East, parts of Africa) should prioritize polyimide-based FPCBs for durability. Compliance with standards such as UL (USA), IEC (Europe), and RoHS (global) is critical. European buyers (e.g., Poland) often require adherence to stringent environmental and safety standards, while cost-sensitive markets in South America may balance performance with PET substrates.
2. Copper Conductive Traces
Key Properties:
Copper is the standard conductive material for LED strip circuits due to its excellent electrical conductivity (~5.8×10^7 S/m) and thermal conductivity, which aids in heat dissipation.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Efficient electrical conduction reduces voltage drop and energy loss; supports high current loads, essential for longer or high-density strips; relatively abundant and recyclable.
– Cons: Copper is prone to oxidation if not properly coated, which can degrade performance; increases manufacturing complexity and cost if thicker copper layers are needed for high power strips.
Impact on Application:
High-quality copper traces ensure minimal energy waste and consistent LED brightness, critical for commercial installations where energy costs are a concern. Thicker copper layers (e.g., 2 oz vs. 1 oz) are beneficial for LED strips used in large-scale applications with higher power consumption.
International B2B Considerations:
Regions with humid or corrosive environments (e.g., coastal areas in South America or the Middle East) require copper traces with protective coatings (e.g., tin, gold plating) to prevent corrosion. Buyers should verify compliance with IPC standards for PCB manufacturing and consider local supply chain capabilities for copper sourcing.
3. Silicone or Epoxy Resin Encapsulation
Key Properties:
Encapsulation materials protect LEDs and circuits from moisture, dust, and mechanical damage. Silicone offers high flexibility, UV resistance, and excellent thermal stability, while epoxy resin provides rigid protection with good electrical insulation.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Silicone encapsulation enhances durability and is ideal for outdoor or high-humidity environments; epoxy resin is cost-effective and suitable for indoor use.
– Cons: Silicone materials are more expensive and require specialized application; epoxy can crack under thermal cycling and is less flexible, limiting installation options.
Impact on Application:
For LED strips used in energy-intensive commercial or outdoor applications, silicone encapsulation improves lifespan and reduces maintenance costs, indirectly lowering total energy expenditure by avoiding frequent replacements.
International B2B Considerations:
Buyers in regions with high UV exposure (e.g., Middle East, Africa) should prefer silicone encapsulation for outdoor installations. European markets often demand compliance with REACH and RoHS regulations for encapsulants. South American buyers may weigh cost against durability depending on the application environment.
4. Aluminum Heat Sink Backing
Key Properties:
Aluminum backing serves as a heat sink, drawing heat away from LEDs to maintain efficiency and prolong lifespan. Aluminum alloys used typically offer good thermal conductivity (~205 W/m·K) and corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Enhances thermal management, critical for LED strips with higher wattage; lightweight and relatively low cost; improves energy efficiency by reducing thermal degradation.
– Cons: Adds to manufacturing complexity and cost; rigid backing limits flexibility; corrosion can be an issue if not anodized or coated.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum-backed LED strips are suited for industrial and commercial installations where energy efficiency and longevity justify the added cost. Effective heat dissipation reduces power consumption by maintaining optimal LED operating temperatures.
International B2B Considerations:
In humid or corrosive environments (e.g., coastal regions in Africa and South America), anodized aluminum or additional protective coatings are essential. European buyers expect compliance with EN standards for material safety and environmental impact. Middle Eastern buyers should consider aluminum grades that withstand high temperatures and dust exposure.
| Material | Typical Use Case for do led strip lights use a lot of electricity | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyimide or PET FPCB | Flexible LED strips requiring thermal stability and durability | High thermal resistance and flexibility | Higher cost (polyimide) or lower heat tolerance (PET) | Medium (Polyimide), Low (PET) |
| Copper Conductive Traces | Electrical conduction in all LED strip types, especially high-density strips | Excellent conductivity and heat dissipation | Susceptible to oxidation without coating | Medium |
| Silicone or Epoxy Resin Encapsulation | Protection for LED strips in harsh or outdoor environments | Superior moisture and UV resistance (silicone) | Higher cost and complexity (silicone), rigidity (epoxy) | Medium (Epoxy), High (Silicone) |
| Aluminum Heat Sink Backing | Heat dissipation in high-power LED strip installations | Efficient thermal management | Adds rigidity and cost, potential corrosion |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for do led strip lights use a lot of electricity
Manufacturing Processes for LED Strip Lights: Key Stages and Techniques
The production of LED strip lights, designed to be energy-efficient lighting solutions, involves several critical stages that ensure both performance and reliability. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers assess supplier capabilities and product quality.
-
Material Preparation
This initial phase involves sourcing and preparing raw materials such as flexible printed circuit boards (FPCBs), LED chips (commonly 3528, 5050, or COB types), resistors, and adhesives. Quality of raw materials directly impacts energy efficiency and product lifespan. Suppliers typically procure semiconductor-grade LED chips from reputable manufacturers to ensure consistent brightness and low power consumption. -
Forming and Circuit Fabrication
The flexible PCB is fabricated with copper traces designed to carry electrical current efficiently across the strip. Advanced photolithography and etching techniques are employed to create precise circuit patterns that minimize resistance and power loss. The flexibility of the PCB allows for versatile installation without compromising electrical integrity.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Component Assembly
Automated pick-and-place machines mount LED chips and other electronic components onto the PCB. This step requires high precision to avoid defects that could increase power consumption or reduce light output. Soldering, often done via reflow ovens, ensures secure electrical connections with minimal thermal damage to components. -
Encapsulation and Finishing
To protect LED strips from environmental factors such as moisture and dust, manufacturers apply silicone or epoxy coatings. This encapsulation also enhances durability without compromising flexibility or light diffusion. Adhesive backing is applied for easy installation, followed by cutting the strips into standard lengths.
Quality Assurance and Control: Ensuring Energy-Efficient Performance
Robust quality control (QC) is essential to guarantee LED strip lights meet energy consumption claims and international safety standards. B2B buyers must understand the QC framework suppliers implement to ensure product consistency and compliance.
International and Industry Standards
- ISO 9001: This global standard for quality management systems (QMS) ensures that manufacturers maintain consistent production processes, from raw material inspection to final product testing.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE certification confirms conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- RoHS Compliance: Restricts hazardous substances in electronic products, critical for environmental sustainability and regulatory acceptance in Europe and other regions.
- UL Certification: Widely recognized in North America and increasingly valued globally, UL tests electrical safety and product reliability.
- IEC Standards: International Electrotechnical Commission standards, such as IEC 62717 for LED modules, provide detailed guidelines on performance and safety.
Quality Control Checkpoints
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials, especially LED chips and PCBs, undergo rigorous inspection for defects, electrical characteristics, and compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During assembly, automated optical inspection (AOI) systems and manual checks detect soldering defects, misalignment, and circuit integrity issues that could affect power consumption.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Finished LED strips are tested for brightness, color temperature, power draw, and longevity. Visual inspection ensures proper encapsulation and physical integrity.
Common Testing Methods
- Electrical Testing: Verifies voltage, current, and wattage to confirm energy consumption matches product specifications.
- Lumen Output Measurement: Ensures light intensity meets advertised levels without excessive power use.
- Thermal Testing: Checks heat dissipation, as overheating can increase energy consumption and reduce lifespan.
- Environmental Stress Testing: Simulates humidity, temperature fluctuations, and mechanical stress to guarantee durability in diverse climates, a key consideration for buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East.
- Safety and EMC Testing: Confirms the product does not emit harmful electromagnetic interference and meets electrical safety requirements.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control for International B2B Buyers
For buyers in regions such as Nigeria, Poland, Brazil, or the UAE, verifying supplier QC processes is critical to minimize risks related to product failure, inefficiency, or non-compliance with local regulations.
- Factory Audits: On-site evaluations by buyer representatives or third-party inspection firms help assess manufacturing capabilities, QC systems, and adherence to international standards.
- Review of Quality Documentation: Suppliers should provide ISO 9001 certificates, test reports, and compliance documents (e.g., CE, RoHS, UL). Buyers must verify the authenticity and currency of these documents.
- Third-Party Testing and Inspection: Independent labs can perform product testing to validate energy consumption claims and safety standards, providing unbiased assurance.
- Sample Testing: Procuring pre-production or pilot samples allows buyers to conduct in-house or local laboratory tests, particularly for power consumption, brightness, and durability under regional environmental conditions.
- Continuous Quality Monitoring: Establishing regular quality checkpoints during large orders can help detect deviations early, ensuring consistent product performance.
Quality Assurance Nuances for Global Markets
- Africa and the Middle East: High ambient temperatures and humidity levels necessitate LED strips with robust encapsulation and thermal management. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with proven environmental stress testing to ensure long-term energy efficiency.
- South America: Regulatory frameworks can vary widely; thus, buyers should confirm that products meet both international and local standards to avoid import complications.
- Europe (e.g., Poland): Strict compliance with EU directives such as RoHS and CE is mandatory. Buyers benefit from suppliers with transparent certification and traceability systems.
- Logistics and After-Sales Support: Efficient supply chain management and accessible technical support are critical for international buyers to address potential QC issues promptly.
By thoroughly understanding manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, international B2B buyers can confidently select LED strip light suppliers who deliver products that are not only energy-efficient but also durable, safe, and compliant with global standards. This strategic insight supports sustainable procurement decisions that align with both budgetary and environmental objectives.
Related Video: LED Light Making Process | How LED Lights Made Inside Factory | Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for do led strip lights use a lot of electricity Sourcing
Understanding the cost and pricing dynamics of LED strip lights, especially in the context of their electricity consumption, is crucial for international B2B buyers aiming to maximize value while controlling operational expenses. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the key factors influencing cost structures and pricing, along with actionable advice tailored for buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Key Cost Components in LED Strip Light Production
-
Materials
The primary cost driver is the raw materials—LED chips (commonly 3528, 5050, or COB types), flexible PCB substrates, resistors, adhesives, and protective coatings. Higher-grade materials, such as premium semiconductor chips or waterproof casings, increase both efficiency and durability but raise initial costs. Buyers should assess the trade-off between upfront material costs and long-term energy savings. -
Labor and Manufacturing Overhead
Labor costs vary significantly by manufacturing location. Automated assembly reduces labor expenses but requires substantial capital investment reflected in tooling costs. Overhead includes factory utilities, equipment depreciation, and quality control processes critical for maintaining consistent product standards. -
Tooling and Quality Control (QC)
Tooling expenses cover the design and setup of production lines, including custom molds or circuit designs. QC is essential to ensure product reliability, particularly for international shipments where failure rates can lead to costly returns or reputational damage. Certified quality checks (e.g., ISO, CE, RoHS) often add to costs but are indispensable for compliance in regulated markets. -
Logistics and Distribution
Shipping costs depend on volume, weight, and distance. For buyers in Nigeria, Poland, or the Middle East, selecting suppliers with proximity or established distribution networks can reduce lead times and freight costs. Additionally, customs duties, import taxes, and local regulations affect landed costs. -
Supplier Margin
Margins vary based on supplier scale, exclusivity, and service level. Bulk orders typically attract better pricing, but buyers must balance margin savings against inventory holding costs and market demand forecasts.
Influencers on Pricing
-
Order Volume and Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs): Larger volumes reduce unit costs through economies of scale. However, MOQs can be restrictive for smaller buyers or those testing new markets. Negotiate flexible MOQs or phased deliveries to optimize cash flow.
-
Product Specifications and Customization: Customized LED strips (e.g., specific color temperatures, IP ratings, lengths) command higher prices due to tooling adjustments and material variations. Standardized products offer better pricing but may not fully meet unique project requirements.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Certified products compliant with international safety and environmental standards often cost more but reduce risks associated with regulatory non-compliance, especially important in the EU and Middle Eastern markets.
-
Supplier Reliability and Location: Established suppliers with proven track records typically price higher but offer consistency and after-sales support. Conversely, emerging suppliers may offer aggressive pricing but pose risks in quality and delivery.
-
Incoterms and Payment Terms: The choice of Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP) directly impacts total landed cost and risk exposure. Negotiating favorable payment terms (e.g., letters of credit, escrow) can improve cash flow management, especially for buyers in regions with currency volatility.
Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing and Negotiation
-
Conduct Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Analysis: Beyond the purchase price, factor in electricity savings, maintenance, replacement frequency, and warranty terms. LED strips with higher upfront costs but superior energy efficiency often yield lower TCO.
-
Leverage Regional Trade Agreements: Buyers in Africa (e.g., Nigeria) and Europe (e.g., Poland) should explore sourcing within trade blocs (e.g., AfCFTA, EU) to benefit from reduced tariffs and streamlined customs procedures.
-
Negotiate Volume Discounts and Flexible MOQs: Even if initial requirements are small, discuss future scaling to secure tiered pricing that accommodates growth without renegotiation.
-
Request Detailed Product Specifications: Confirm voltage, current, power consumption per meter, and certifications to avoid hidden costs related to inefficiency or non-compliance.
-
Assess Supplier Support and After-Sales Service: Reliable technical support can reduce downtime and additional costs, which is particularly valuable when importing to regions with less developed local infrastructure.
-
Consider Logistics Optimization: Consolidate shipments, choose cost-effective freight modes, and clarify Incoterms to minimize unexpected logistics expenses.
Indicative Pricing Disclaimer
Prices for LED strip lights vary widely based on specifications, order size, and market conditions. This analysis provides a general framework rather than exact pricing figures. Buyers should engage multiple suppliers, request quotations, and perform due diligence tailored to their specific project needs and regional considerations.
By understanding these cost drivers and pricing influencers, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that balance initial investment with long-term operational efficiency and sustainability. Strategic sourcing aligned with energy-efficient LED technology not only lowers electricity consumption but also enhances competitive advantage in diverse global markets.
Spotlight on Potential do led strip lights use a lot of electricity Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘do led strip lights use a lot of electricity’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for do led strip lights use a lot of electricity
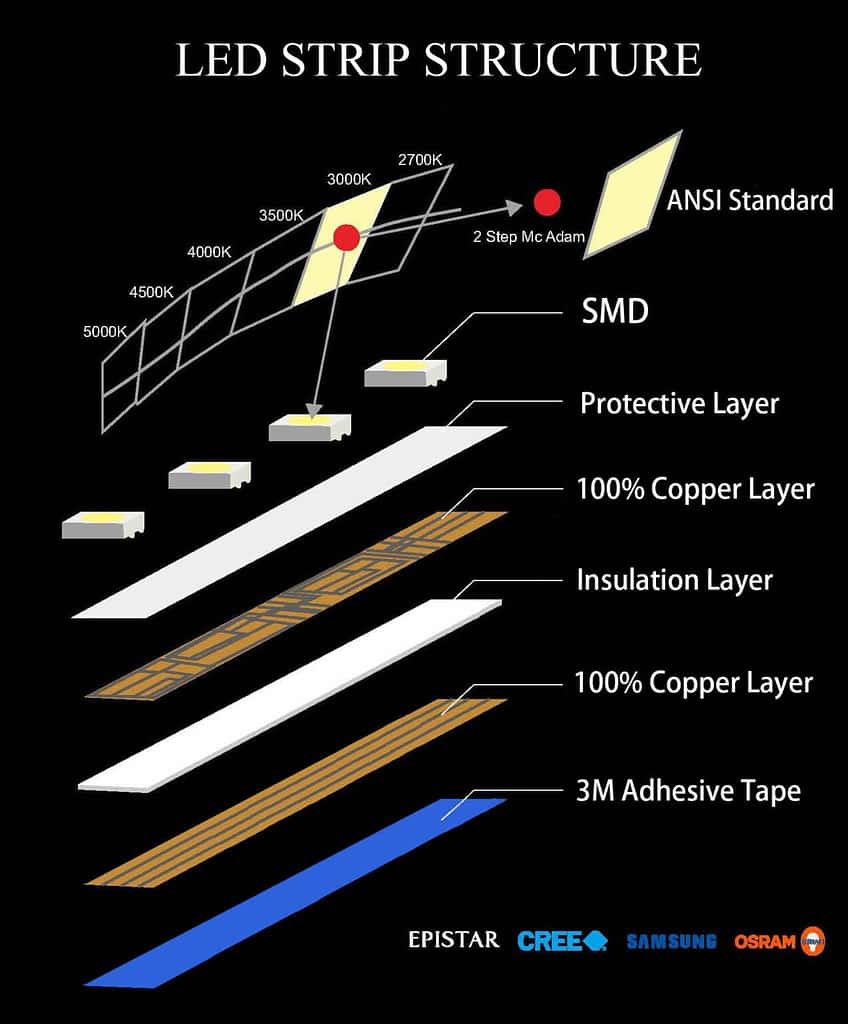
Critical Technical Properties of LED Strip Lights for Energy Consumption
Understanding key technical specifications is essential for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions regarding LED strip lights, especially in markets focused on energy efficiency and cost control such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
-
Power Consumption (Watts per Meter)
This measures the electrical power used by the LED strip per meter length, typically expressed in watts (W). Lower wattage means less electricity usage and reduced operating costs. For buyers, comparing wattage helps balance brightness requirements against energy budgets, critical for large-scale commercial installations. -
Voltage (V)
LED strips commonly operate at 12V or 24V DC. Voltage affects compatibility with power supplies and installation complexity. Higher voltage strips (24V) can run longer continuous lengths without voltage drop, reducing the need for additional power injection points—important for large projects. -
LED Density (LEDs per Meter)
This indicates how many individual LEDs are mounted per meter of strip. Higher density usually means brighter light but also increased power consumption. Buyers must align LED density with application needs—whether ambient lighting or accent illumination—to optimize energy use and cost. -
LED Chip Size and Type
Common chip sizes include 3528 (3.5mm x 2.8mm) and 5050 (5mm x 5mm). Larger chips generally emit more light but consume more power. Selecting the appropriate chip type influences energy efficiency and brightness, a crucial factor for buyers targeting energy-saving certifications or green building projects. -
Color Temperature and Color Rendering Index (CRI)
Color temperature (measured in Kelvins) affects the perceived warmth or coolness of the light. Higher CRI values indicate better color accuracy but may involve slight increases in power use. For retail or hospitality sectors, high CRI LED strips enhance product presentation and ambiance, justifying energy trade-offs. -
Lifespan and Thermal Management
A longer lifespan (often 30,000–50,000 hours) minimizes replacement frequency, reducing total cost of ownership. Effective thermal management built into the strip design prevents overheating, which can degrade efficiency and shorten lifespan. Buyers should verify product durability to ensure energy savings over time.
Common Industry and Trade Terms in LED Strip Lighting Procurement
Familiarity with trade terminology empowers international B2B buyers to negotiate effectively, manage supply chains, and understand contractual obligations.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to manufacturers who produce LED strips that can be rebranded by other companies. OEM partnerships allow buyers to customize product specifications, packaging, and branding, essential for market differentiation and meeting local regulatory standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. Understanding MOQ helps buyers plan inventory and budget, especially when entering new markets where demand may fluctuate. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal process where buyers request detailed pricing, specifications, and delivery terms from suppliers. RFQs facilitate transparent comparison of offers, enabling buyers to optimize costs and ensure suppliers meet technical and compliance requirements. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP) that define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs between buyers and sellers. Clarity on Incoterms reduces cross-border transaction risks, crucial for buyers importing LED strips into diverse regulatory environments. -
Voltage Drop
A reduction in voltage along the length of the LED strip due to resistance in the circuit. Excessive voltage drop causes uneven brightness and energy inefficiency. Buyers should consider this when specifying strip length and power supply to maintain consistent lighting performance. -
Dimmability
The capability of LED strips to adjust brightness through compatible controllers. Dimmability enables energy savings by reducing light output when full brightness is unnecessary, an attractive feature for energy-conscious projects and smart building integrations.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can strategically select LED strip lighting solutions that optimize energy consumption, reduce operational costs, and ensure compliance with international standards—key factors for successful procurement and long-term sustainability.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the do led strip lights use a lot of electricity Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global LED strip lighting market is witnessing robust growth driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient and versatile lighting solutions across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. For international B2B buyers in regions such as Africa (e.g., Nigeria), South America, the Middle East, and Europe (e.g., Poland), the appeal of LED strip lights lies in their low power consumption, flexibility, and superior lifespan compared to traditional lighting. These regions are actively adopting LED technology to address energy cost challenges and infrastructure modernization.
Key market drivers include advancements in LED technology that have improved energy efficiency by approximately 10% in recent years, making LED strips a cost-effective lighting solution. Additionally, the modular design of LED strips enables tailored installations, which is particularly attractive for large-scale projects such as retail spaces, hospitality venues, and architectural lighting. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing products with high LED density and customizable brightness levels, allowing them to balance illumination needs with energy budgets.
Sourcing trends show a growing preference for suppliers offering comprehensive technical specifications, including power consumption per meter, voltage requirements, and durability metrics. This transparency aids buyers in calculating total energy usage and operational costs accurately. Moreover, the rise of smart LED strips integrated with IoT and remote control features is reshaping procurement strategies, especially in technologically advanced markets in Europe and the Middle East. Buyers in emerging markets benefit from suppliers who provide scalable solutions and local support to navigate installation complexities.
The market is also influenced by regional energy policies and incentives promoting sustainable lighting solutions. For example, several African and South American countries are introducing subsidies or tax breaks for energy-efficient technologies, which encourages bulk purchasing of LED strips. European buyers, meanwhile, face stringent energy efficiency regulations, pushing suppliers to innovate with low-wattage, high-output LED strips that minimize electricity consumption without compromising performance.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a critical factor in B2B procurement decisions for LED strip lighting, especially as businesses strive to reduce their carbon footprints and comply with international environmental standards. LED strip lights inherently consume less electricity than traditional incandescent or fluorescent lighting, which significantly lowers greenhouse gas emissions associated with power generation. This energy efficiency not only reduces operational costs but also supports corporate sustainability goals.
Ethical sourcing in the LED sector involves ensuring that raw materials, such as semiconductor components and circuit boards, are procured responsibly. Suppliers adhering to conflict-free mineral sourcing, including tin, tungsten, tantalum, and gold, are increasingly favored to avoid contributing to social and environmental harm. For B2B buyers in Africa and South America, where mineral sourcing is a sensitive issue, partnering with certified suppliers ensures compliance with global ethical standards and mitigates reputational risks.
Green certifications such as ENERGY STAR, RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), and the EU’s EcoDesign Directive are essential benchmarks when selecting LED strip products. These certifications guarantee that the products meet strict environmental and safety criteria, including limits on hazardous materials and energy consumption thresholds. Buyers should also look for suppliers that utilize recyclable materials and offer product take-back or recycling programs to promote circular economy principles.
Incorporating sustainability into the supply chain extends beyond product specifications. It includes evaluating supplier practices related to energy use in manufacturing, waste management, and labor conditions. International buyers benefit from suppliers who provide transparent sustainability reports and third-party audits, facilitating informed purchasing decisions aligned with global ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) frameworks.
Brief Evolution of LED Strip Lighting for B2B Buyers
LED strip lighting has evolved from simple indicator lights in electronic devices to sophisticated, flexible lighting solutions widely used in architectural, decorative, and industrial applications. Early LED strips offered limited brightness and color options, primarily serving niche markets. However, advances in semiconductor technology and manufacturing processes have enabled the production of high-density, multi-color LED strips with enhanced brightness and energy efficiency.
For B2B buyers, this evolution means access to a broad spectrum of LED strip products—from basic models for cost-sensitive projects to advanced strips with smart controls and superior durability for premium installations. Understanding this progression helps buyers assess product maturity and future-proof their investments by selecting LED strips that incorporate the latest efficiency standards and technological features. This historical context also underlines the importance of continuous upgrades to leverage improvements in energy consumption and lighting quality.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of do led strip lights use a lot of electricity
-
How can I verify the reliability and energy efficiency claims of LED strip light suppliers?
When sourcing LED strip lights internationally, especially from regions like Asia or Eastern Europe, conduct thorough supplier vetting. Request detailed product specifications including wattage per meter and energy efficiency ratings. Ask for independent test reports or certifications such as CE, RoHS, or Energy Star, which assure compliance with international energy and safety standards. Additionally, seek references from other B2B buyers or industry partners in your region (e.g., Nigeria, Poland) to verify supplier credibility and product performance under local conditions. -
Is it possible to customize LED strip lights to balance brightness and electricity consumption for different markets?
Yes, customization is common and recommended. Suppliers can adjust LED density, diode size (e.g., 3528 vs. 5050), and color temperature to optimize energy use versus brightness based on your target market’s preferences and energy costs. For example, African and Middle Eastern markets may prioritize energy efficiency due to power costs, while European buyers might focus on brightness and quality certifications. Clarify your needs upfront, and confirm minimum order quantities (MOQs) for custom runs to ensure cost-effectiveness. -
What are typical MOQs and lead times when ordering energy-efficient LED strip lights from international manufacturers?
MOQs vary widely but generally start from 500 to 1000 meters for standard LED strips, with customized versions potentially requiring higher quantities. Lead times typically range from 3 to 8 weeks, depending on order size, customization, and supplier location. For buyers in South America or Africa, factor in additional shipping and customs clearance time. Negotiate with suppliers about partial shipments or samples to test energy consumption before committing to bulk orders. -
Which quality assurance and certifications should I require to ensure LED strips meet international energy standards?
Demand products certified with CE (Europe), RoHS (restriction of hazardous substances), UL (safety in the US), or equivalent regional marks. These certifications guarantee that LED strips meet safety, energy efficiency, and environmental standards. For Africa and Middle East buyers, confirm compliance with local electrical regulations and look for energy efficiency labels recognized by your country’s authorities. Insist on factory audits or third-party inspections to verify production quality and adherence to specifications. -
How do I calculate the expected electricity consumption of LED strip lights for budgeting in my region?
Calculate power usage by multiplying voltage (V) by current (A) to get watts (W), then multiply by usage hours to get kilowatt-hours (kWh). For example, a 24V LED strip drawing 0.1875A per meter uses 4.5W per meter. Multiply by strip length and daily usage hours to estimate energy consumption and cost. This method allows buyers in markets with varying electricity tariffs (e.g., Nigeria’s higher rates vs. Poland’s lower rates) to accurately budget operational costs and negotiate better pricing based on expected power efficiency. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing LED strip lights internationally?
LED strips are lightweight but sensitive to moisture and static, requiring proper packaging and handling. Choose suppliers offering moisture-proof reels and anti-static protection. Shipping by sea is cost-effective for large orders but slower, while air freight suits urgent needs but is pricier. Account for customs duties and import taxes specific to your country, and confirm that shipping documentation includes product specifications to avoid clearance delays. Working with experienced freight forwarders familiar with electronics shipments in your region ensures smoother logistics. -
How can I handle disputes related to discrepancies in electricity consumption or product quality after delivery?
Establish clear contracts specifying product specifications, energy consumption tolerances, and testing protocols before shipment. Include clauses for third-party inspection or sample testing upon arrival. If discrepancies arise, promptly document and communicate issues with the supplier, providing evidence such as energy meter readings or lab test reports. Many reputable suppliers offer warranty or replacement policies for defective batches. Engaging local trade chambers or arbitration bodies can help resolve disputes amicably while preserving long-term supplier relationships. -
Are there specific energy-saving features or advancements I should look for in the latest LED strip light technologies?
Yes, recent innovations have improved LED efficiency by approximately 10%. Look for LED strips featuring high-density but low-wattage diodes, advanced semiconductor materials, and integrated smart controllers that allow dimming and color adjustments to reduce power consumption. Some suppliers offer strips with adaptive brightness sensors or programmable modes tailored to usage patterns, ideal for commercial clients aiming to minimize energy costs. Prioritize suppliers who invest in R&D and provide detailed energy performance data, especially when sourcing for energy-conscious markets like Europe or progressive African cities.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for do led strip lights use a lot of electricity
LED strip lights represent a transformative lighting solution that balances aesthetic appeal with energy efficiency, making them a compelling choice for diverse commercial and industrial applications across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Their low power consumption—significantly less than traditional incandescent or fluorescent lighting—translates into tangible cost savings and reduced carbon footprints, essential factors for businesses prioritizing sustainability and operational efficiency.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
For B2B buyers, strategic sourcing of LED strip lighting requires careful evaluation of power specifications, LED density, and color output to optimize both energy use and lighting performance. Understanding the technical parameters and energy consumption formulas enables precise budgeting and helps avoid over-specification that can inflate electricity costs. Furthermore, sourcing from reputable manufacturers offering the latest energy-efficient models ensures long-term value and compliance with regional energy regulations.
Looking ahead, continuous advancements in LED technology promise even greater efficiency gains and smarter lighting solutions. International buyers are encouraged to leverage these innovations by integrating LED strip lights into their projects, aligning with global sustainability goals while enhancing competitive advantage. Proactive engagement with suppliers on product specifications and total cost of ownership will be key to unlocking the full benefits of LED lighting in an increasingly energy-conscious marketplace.
