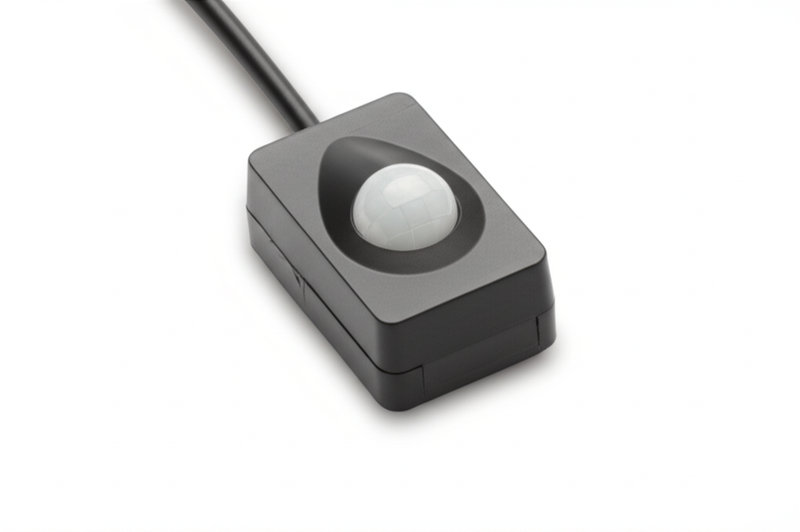
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for motion detector for led strip
The integration of motion detectors with LED strip lighting represents a transformative advancement in energy-efficient illumination, crucial for diverse industries and commercial environments worldwide. For international B2B buyers, especially those operating in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of this technology is vital to optimizing operational costs, enhancing safety, and meeting sustainability goals.
Motion detector LED strips automatically activate lighting only when movement is detected, significantly reducing energy consumption and extending the lifespan of lighting systems. This intelligent functionality not only cuts down on unnecessary power usage but also improves workplace safety and convenience across various applications—from manufacturing floors and warehouses to retail spaces and smart building projects.
This comprehensive guide offers a detailed exploration of motion detector LED strips, covering:
- Types and technologies: including Passive Infrared (PIR), ultrasonic, and microwave sensors tailored to different environmental needs.
- Materials and manufacturing standards: ensuring durability and compliance with international quality certifications.
- Supplier evaluation: criteria for selecting reliable manufacturers and distributors across global markets.
- Cost analysis: insights into pricing structures, total cost of ownership, and ROI considerations.
- Market trends: regional demand patterns and emerging innovations.
- Frequently Asked Questions: addressing common concerns to facilitate confident procurement decisions.
By equipping buyers with actionable insights and clear evaluation frameworks, this guide empowers businesses to source motion detector LED strips that align perfectly with their operational requirements and regional market dynamics. Whether upgrading existing systems or launching new projects, informed sourcing is the key to unlocking efficiency, safety, and sustainability on a global scale.
Understanding motion detector for led strip Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Passive Infrared (PIR) | Detects heat signatures from human or animal movement | Warehouses, retail stores, office lighting | + Energy efficient, low cost; – Limited range, less effective through barriers |
| Ultrasonic Sensors | Emits sound waves and detects reflections from moving objects | Manufacturing floors, large indoor spaces | + High sensitivity, wide coverage; – Potential interference, higher power consumption |
| Microwave Sensors | Uses electromagnetic waves to detect motion | Outdoor lighting, complex layouts, security zones | + Penetrates obstacles, long range; – More expensive, possible false triggers |
| Hybrid Sensors | Combines PIR and microwave technologies | High-security facilities, smart buildings | + Reduced false alarms, versatile; – Higher cost, complex installation |
| Smart IoT-Enabled Sensors | Integrates wireless connectivity for remote control and analytics | Smart factories, commercial buildings | + Remote management, data insights; – Requires network infrastructure, higher initial investment |
Passive Infrared (PIR) Sensors
PIR sensors are the most common and cost-effective motion detectors for LED strips, detecting infrared radiation emitted by warm objects. Their simplicity and low power consumption make them ideal for applications like warehouses, retail, and office environments where straightforward motion detection suffices. For B2B buyers, PIR sensors offer a reliable, energy-efficient option but require clear line-of-sight and may not perform well through glass or walls. Consideration should be given to installation environment and coverage needs.
Ultrasonic Sensors
Ultrasonic motion detectors utilize sound waves to detect movement, providing higher sensitivity and broader coverage than PIR sensors. They are well-suited for manufacturing floors and large indoor spaces with complex layouts. However, ultrasonic sensors can be prone to interference from ambient noise and consume more power. B2B buyers should evaluate the operational environment and weigh increased sensitivity against potential false positives and energy use.
Microwave Sensors
Microwave sensors emit electromagnetic waves that penetrate non-metallic objects, enabling motion detection through walls or obstacles. This makes them valuable for outdoor lighting, security zones, and environments with obstructions. Their longer range and higher accuracy come with increased cost and occasional false triggers from moving objects like foliage. Buyers targeting high-security or outdoor applications should balance performance benefits with budget and false alarm management.
Hybrid Sensors
Combining PIR and microwave technologies, hybrid sensors reduce false alarms by requiring both heat and motion detection to trigger lighting. These are ideal for high-security facilities and smart buildings where reliability and accuracy are paramount. Although hybrid sensors involve higher upfront costs and more complex installation, they offer superior performance and energy savings over time. Buyers should assess their security needs and installation capabilities when considering hybrid solutions.
Smart IoT-Enabled Sensors
The latest variation integrates motion detection with IoT connectivity, allowing remote monitoring, control, and data analytics. These sensors are increasingly popular in smart factories and commercial buildings aiming for operational efficiency and predictive maintenance. While the initial investment and network requirements are higher, the long-term benefits include enhanced control, energy management, and integration with building management systems. B2B buyers focused on digital transformation and sustainability should prioritize IoT-enabled options.
Related Video: Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models | DDPM Explained
Key Industrial Applications of motion detector for led strip
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Motion Detector for LED Strip | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Automated task lighting on production lines and assembly stations | Enhances worker safety and productivity while reducing energy costs | Durability under industrial conditions, sensor sensitivity, integration with existing lighting systems |
| Warehousing & Logistics | Aisle and storage area illumination triggered by movement | Minimizes energy consumption in large storage spaces, improves visibility for inventory management | Wide detection range, compatibility with large LED strips, ease of installation and maintenance |
| Retail & Commercial | Dynamic display lighting and customer pathway illumination | Increases customer engagement and reduces operational energy expenses | Adjustable detection zones, aesthetic LED strip design, integration with store automation systems |
| Hospitality & Facilities Management | Corridor and restroom lighting activated by occupancy | Improves guest experience and reduces utility costs | Sensor reliability, seamless integration with existing infrastructure, compliance with local regulations |
| Smart Buildings & Offices | Energy-efficient corridor and workstation lighting | Supports sustainability goals and optimizes energy use | Scalability, compatibility with building management systems, ease of remote control and monitoring |
Manufacturing
In manufacturing environments, motion detectors paired with LED strips provide automated lighting that activates only when workers are present at specific production lines or assembly stations. This targeted illumination enhances precision and safety while significantly cutting down on energy waste, a critical factor for facilities operating around the clock. For international buyers, especially in regions like South Africa and the UK, sourcing durable, industrial-grade motion detectors that can withstand harsh factory conditions and integrate with existing lighting infrastructure is paramount.
Warehousing & Logistics
Large warehouse spaces benefit greatly from motion detector LED strips installed along aisles and storage zones. These systems ensure illumination is provided only in active areas, improving visibility for inventory management and reducing electricity costs. Buyers in South America and the Middle East should prioritize solutions offering wide detection ranges and compatibility with extended LED strip lengths to cover vast spaces efficiently, while also considering ease of installation and maintenance in environments with varying climate conditions.
Retail & Commercial
Retailers leverage motion detector LED strips to highlight product displays and guide customers along store pathways dynamically. This not only enhances the shopping experience but also optimizes energy use by illuminating areas only when customers are present. For B2B buyers in Europe and Africa, selecting LED strips with adjustable detection zones and appealing aesthetics that align with brand identity is essential, along with ensuring seamless integration into existing store automation and lighting control systems.
Hospitality & Facilities Management
Corridors, restrooms, and common areas in hotels and commercial buildings benefit from motion-activated LED strip lighting, which improves guest comfort while lowering operational costs through energy savings. International buyers should focus on sensor reliability and compliance with local electrical and safety standards. Additionally, choosing systems that integrate smoothly with existing infrastructure helps minimize installation downtime and maintenance challenges.
Smart Buildings & Offices
In modern office buildings, motion detector LED strips are used to control corridor and workstation lighting efficiently, supporting corporate sustainability initiatives. These solutions enable energy use optimization by activating lights only when spaces are occupied. Buyers, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, must consider scalability, compatibility with building management systems (BMS), and options for remote monitoring and control to align with smart building strategies and reduce energy footprints.
Related Video: PIR motion sensor and garden LED light wiring.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for motion detector for led strip
When selecting materials for motion detectors integrated with LED strips, B2B buyers must balance performance, durability, cost, and compliance with international standards. The choice of material directly influences the device’s reliability, environmental resistance, and suitability for different markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in housing and components of motion detectors for LED strips, focusing on their key properties, advantages, limitations, and regional considerations.
1. Polycarbonate (PC)
Key Properties:
Polycarbonate is a high-impact thermoplastic known for excellent optical clarity, high heat resistance (typically up to 115°C continuous use), and good dimensional stability. It offers strong resistance to UV radiation and moderate chemical resistance, making it suitable for indoor and some outdoor applications.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: High durability and impact resistance protect sensitive electronic components. Lightweight and easy to mold, which reduces manufacturing complexity and cost. Transparent grades allow for efficient sensor operation without additional windows.
– Cons: Susceptible to scratching and can degrade under prolonged exposure to harsh chemicals or extreme UV without additives. Moderate cost compared to cheaper plastics.
Impact on Application:
Polycarbonate is ideal for motion detectors in indoor environments or semi-protected outdoor settings where impact resistance is critical. Its transparency supports PIR sensor efficiency, crucial for accurate motion detection.
Regional Considerations:
European and Middle Eastern buyers often require compliance with EN 62262 (IK code) for impact resistance and RoHS directives for material safety. African and South American markets may prioritize cost-effectiveness and UV resistance due to intense sunlight exposure, making UV-stabilized grades essential.
2. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Key Properties:
ABS is a common thermoplastic with good mechanical strength, moderate heat resistance (up to 80-100°C), and excellent surface finish capabilities. It offers good electrical insulation and chemical resistance against acids and alkalis.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Cost-effective and widely available globally, ABS is easy to manufacture with injection molding, enabling complex shapes and detailed finishes. Good dimensional stability and electrical insulation properties.
– Cons: Lower heat resistance than polycarbonate, which may limit use in high-temperature environments. Less UV resistant unless specially treated, leading to brittleness and color fading outdoors.
Impact on Application:
ABS suits indoor motion detectors for LED strips where cost constraints exist and thermal loads are moderate. It is less ideal for outdoor or high-humidity environments without protective coatings.
Regional Considerations:
For buyers in South America and Africa, ABS is attractive due to its affordability and local availability. European buyers may require compliance with REACH and RoHS standards, and the Middle East market often demands flame-retardant grades (UL 94 V-0) for safety.
3. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum offers excellent thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance (especially when anodized), and mechanical strength. It withstands high temperatures and harsh environmental conditions, including moisture and dust.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Superior heat dissipation helps maintain sensor and LED strip longevity. High durability and corrosion resistance make it suitable for outdoor and industrial applications. Premium aesthetic and recyclable, aligning with sustainability goals.
– Cons: Higher material and manufacturing costs due to machining or extrusion processes. Heavier than plastics, potentially increasing shipping costs.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum housings are preferred for outdoor motion detectors or industrial settings in harsh climates, such as desert regions in the Middle East or coastal areas in Europe and South Africa. Its heat dissipation capability supports high-performance LED strips.
Regional Considerations:
European buyers often require compliance with EN 1090 for structural aluminum components. In the Middle East and Africa, anodized aluminum is favored for corrosion resistance against saline or sandy environments. South American buyers may weigh cost against durability for outdoor installations.
4. Silicone Rubber (for seals and flexible components)
Key Properties:
Silicone rubber is highly flexible, with excellent thermal stability (-60°C to 230°C), UV and ozone resistance, and outstanding sealing properties against moisture and dust ingress.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Provides effective IP-rated sealing (IP65 and above), crucial for protecting motion detectors and LED strips in outdoor or industrial environments. Maintains flexibility over a wide temperature range, enhancing durability.
– Cons: Not a structural material; used mainly for gaskets and seals. Higher cost than standard rubber materials.
Impact on Application:
Silicone rubber is essential for motion detector assemblies exposed to harsh weather or industrial contaminants. It ensures long-term reliability by preventing ingress of water and dust that could impair sensor function.
Regional Considerations:
Buyers in Africa and the Middle East benefit from silicone’s UV and heat resistance in extreme climates. European markets require compliance with RoHS and REACH for silicone components. South American buyers should consider local availability and supplier certifications.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for motion detector for led strip | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polycarbonate | Indoor and semi-outdoor housings requiring impact resistance | High impact resistance and optical clarity | Moderate UV degradation without additives | Medium |
| ABS | Cost-sensitive indoor applications with moderate thermal load | Cost-effective, easy to mold, good insulation | Lower heat and UV resistance | Low |
| Aluminum | Outdoor/industrial housings needing heat dissipation | Excellent thermal management and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and weight | High |
| Silicone Rubber | Seals and gaskets for weatherproofing | Superior flexibility and environmental sealing | Not structural, higher cost than standard rubber | Medium |
This material selection guide equips international B2B buyers with actionable insights to choose the right materials based on application environment, regulatory requirements, and cost considerations, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of motion detectors for LED strips across diverse global markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for motion detector for led strip
Manufacturing and quality assurance of motion detectors for LED strips are critical to delivering reliable, energy-efficient, and durable lighting solutions. For international B2B buyers—especially those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—understanding the typical production workflow and quality control measures helps ensure procurement of products that meet stringent performance and safety requirements. This overview details the core manufacturing stages, key quality checkpoints, relevant standards, and practical steps buyers can take to verify supplier quality.
Manufacturing Process Overview
The production of motion detectors integrated with LED strips involves several precise stages designed to ensure functionality, durability, and compliance with electrical safety standards:
1. Material Preparation
- Component Sourcing: High-quality sensors (PIR, microwave, ultrasonic), LED strips, circuit boards, microcontrollers (e.g., ESP8266 or similar), and housing materials (usually plastics or aluminum) are procured from certified suppliers.
- Raw Material Inspection: Incoming materials undergo Initial Quality Control (IQC) to verify specifications such as sensor sensitivity, LED brightness, and PCB quality.
- Pre-treatment: Plastic parts may be molded and metal parts cut or treated for corrosion resistance; circuit boards are prepared with solder masks and conductive tracks.
2. Forming and Fabrication
- Injection Molding and CNC Machining: Enclosures and mechanical parts are shaped using injection molding for plastics and CNC machining for metal components. Precision here affects fit and sensor alignment.
- PCB Assembly: Surface-mount technology (SMT) and through-hole soldering techniques are applied to mount sensors, microcontrollers, and LEDs onto printed circuit boards. Automated optical inspection (AOI) is often used to detect defects at this stage.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
3. Assembly
- Component Integration: Sensors, LED strips, PCBs, and power supply units are assembled into the housing. This step requires careful alignment to ensure sensor fields of view and LED light distribution are optimal.
- Wiring and Connectivity: Electrical connections are made and insulated, with connectors often tested for robustness and conductivity.
- Firmware Installation: Embedded software controlling sensor sensitivity, light activation timing, and power management is uploaded and configured.
4. Finishing and Packaging
- Surface Treatment: Housings may be coated or painted for aesthetics and environmental protection (e.g., UV resistance, water-proofing).
- Labeling: CE, RoHS, or other certification marks are applied based on compliance.
- Packaging: Products are packed in anti-static, moisture-proof materials with user manuals and warranty cards, designed to prevent damage during shipping.
Quality Assurance and Control (QA/QC)
Robust quality assurance systems ensure that motion detector LED strips meet performance benchmarks and international safety standards, which is essential for minimizing returns, avoiding liability, and maintaining brand reputation.
Key International and Industry Standards
- ISO 9001: The foundational quality management system standard that governs the overall manufacturing and QC processes to ensure consistent quality output.
- CE Marking: Mandatory for European markets, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): Ensures electronic components do not contain harmful materials like lead or mercury.
- API and Regional Certifications: Depending on the market, certifications such as SABS (South African Bureau of Standards), INMETRO (Brazil), or SASO (Saudi Arabia) may be required.
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): Testing to confirm the device does not emit or is not susceptible to electromagnetic interference, crucial for industrial environments.
QC Checkpoints
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Verification of all incoming raw materials and components against technical specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during assembly, including solder joint inspection, sensor calibration, and firmware validation.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of finished products covering functional, safety, and cosmetic aspects before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
- Functional Testing: Verifies motion detection accuracy, LED illumination response time, and automatic shutoff functionality under various conditions.
- Environmental Testing: Includes humidity, temperature cycling, and dust or water ingress (IP rating) tests to simulate real-world usage scenarios.
- Electrical Safety Testing: Checks for insulation resistance, leakage current, and short circuits to prevent hazards.
- Durability Testing: Mechanical stress tests on switches, connectors, and housing to ensure longevity.
- EMC Testing: Confirms compliance with electromagnetic interference regulations.
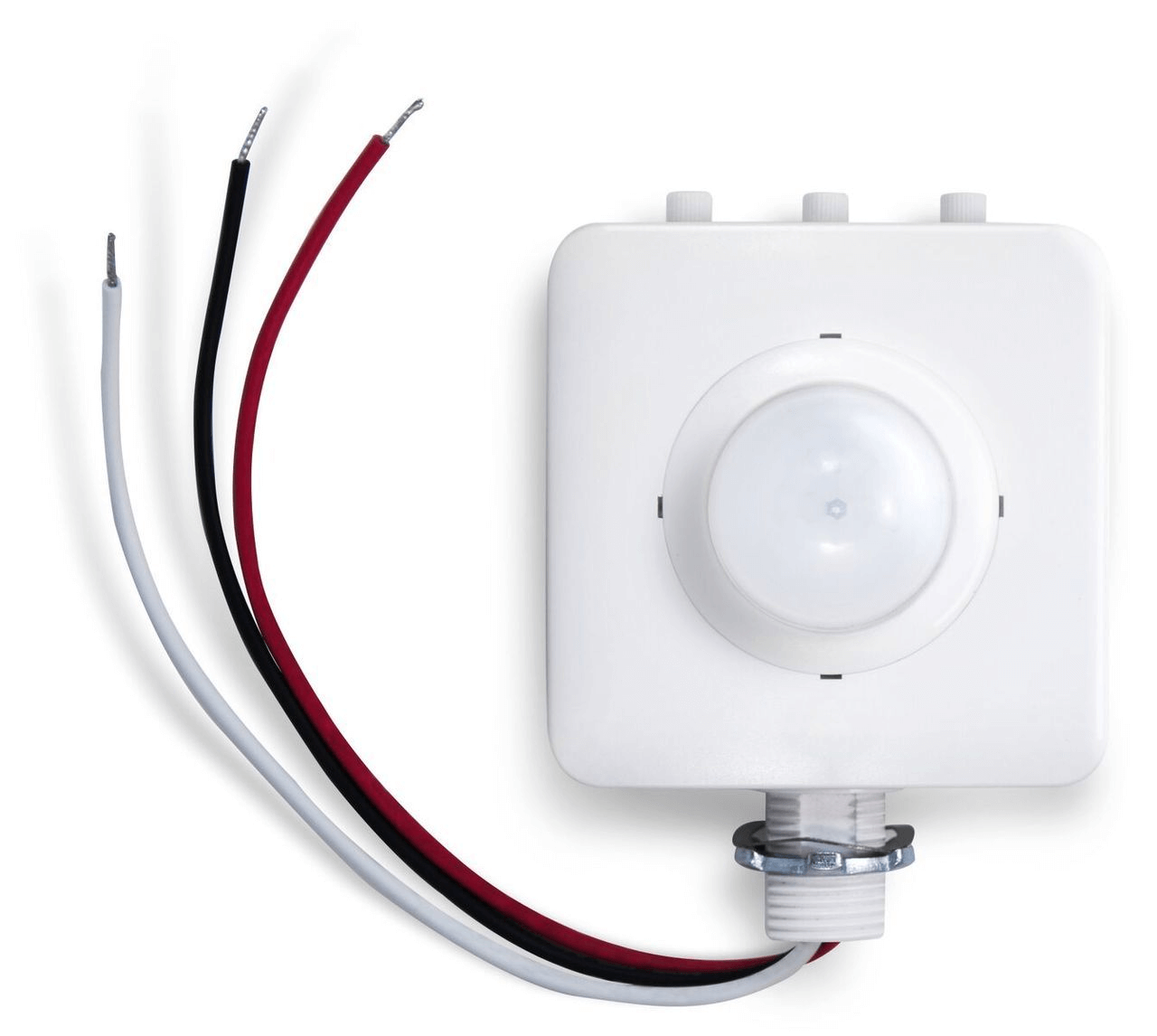
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
How B2B Buyers Can Verify Supplier Quality
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, ensuring that suppliers adhere to quality standards and manufacturing best practices is vital for reducing risk and ensuring smooth supply chains.
Verification Strategies
- Supplier Audits: Conduct on-site or third-party audits focusing on production capabilities, quality control systems, and compliance with ISO 9001 and local certifications. Audits help validate supplier claims and uncover hidden risks.
- Review of Quality Documentation: Request and review QC reports, test certificates, batch inspection records, and calibration certificates for sensors and components.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent inspection agencies to perform pre-shipment inspections, including random sampling and functional tests. This is especially important when dealing with new suppliers or bulk orders.
- Sample Testing: Obtain product samples for in-house or third-party laboratory testing to verify performance and compliance with local regulatory requirements.
- Certifications Verification: Confirm the authenticity of certification marks (CE, RoHS, SABS, INMETRO) through official registries or certification bodies.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
- Regional Adaptations: Products destined for African or Middle Eastern markets may require certifications aligned with local standards (e.g., SABS in South Africa or SASO in Saudi Arabia) in addition to global ones. Buyers should clarify these requirements upfront.
- Documentation Language and Clarity: Ensure that all technical documents, user manuals, and certificates are available in the buyer’s working language (English, Spanish, Arabic, or others) to avoid misinterpretations.
- Customs and Import Compliance: Understanding local import regulations related to electrical goods helps prevent delays and additional costs caused by non-compliance.
- Sustainability and Energy Efficiency: European buyers often prioritize products with energy efficiency labels and eco-certifications, which may not be mandatory but can provide competitive advantages.
Conclusion
For international B2B buyers sourcing motion detectors for LED strips, a clear grasp of manufacturing processes and rigorous quality assurance is indispensable. From meticulous material preparation and precision assembly to comprehensive functional and safety testing, the production lifecycle is designed to deliver reliable, energy-efficient lighting solutions. Buyers should leverage supplier audits, certification verification, and sample testing to ensure compliance with international and regional standards. This proactive approach not only mitigates supply chain risks but also guarantees that the lighting products will perform optimally in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Related Video: LED Light Making Process | How LED Lights Made Inside Factory | Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for motion detector for led strip Sourcing
Cost Components in Motion Detector for LED Strip Sourcing
When sourcing motion detectors for LED strips, understanding the detailed cost breakdown is essential for effective budget planning and supplier negotiation. Key cost components include:
-
Materials: This encompasses sensor modules (PIR, ultrasonic, microwave), LED strip components, microcontrollers (e.g., ESP8266), wiring, and casing materials. High-quality sensors and durable casing materials typically raise costs but enhance product reliability.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for assembly, sensor calibration, and quality control. Labor costs vary significantly by manufacturing location, impacting the final price.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: Includes factory utilities, machinery depreciation, and indirect labor. Efficient production lines and automation can reduce overhead costs.
-
Tooling and Equipment: Initial investments in molds, PCB fabrication tools, and sensor calibration equipment contribute to upfront costs, often amortized across production volumes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes, including sensor accuracy testing and durability assessments, add to the cost but ensure product performance and reduce returns.
-
Logistics: Freight charges, customs duties, and warehousing impact landed costs, particularly for international shipments.
-
Supplier Margin: Suppliers incorporate margins to cover profit, risks, and contingencies. Margins fluctuate with market demand and supplier positioning.
Key Price Influencers for International B2B Buyers
Several factors influence pricing dynamics in the motion detector for LED strip market:
-
Order Volume and Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ): Larger orders typically secure better unit pricing due to economies of scale. Buyers from regions like South America or Africa should explore consolidated shipments to meet MOQs and reduce per-unit costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized sensors with advanced features (e.g., adjustable sensitivity, multi-sensor integration) or bespoke LED strip configurations increase costs. Standardized products generally offer more competitive pricing.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Products with certifications such as CE, RoHS, or UL, which are often required for Europe and parts of the Middle East, command higher prices but ensure compliance and safety.
-
Supplier Location and Reputation: Manufacturers in Asia may offer lower base prices but consider the trade-offs in shipping time and after-sales support. European suppliers may charge premiums for quality and proximity.
-
Incoterms and Shipping Terms: Terms like FOB, CIF, or DDP affect logistics costs and buyer responsibilities. For buyers in South Africa or the UK, selecting favorable Incoterms can optimize total landed costs.
Practical Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing
-
Negotiate Beyond Price: Focus on total value including warranty terms, lead times, and after-sales service. Suppliers often offer flexibility on payment terms or bundled services which can reduce overall expenditure.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider energy savings from efficient motion detection, reduced maintenance due to LED longevity, and potential downtime costs. Lower upfront prices might lead to higher operational expenses.
-
Leverage Volume Aggregation: For buyers in markets with fragmented demand, pooling orders with other companies or using sourcing agents can unlock better pricing and logistics efficiencies.
-
Verify Compliance Early: Ensure that products meet local electrical and safety standards to avoid costly re-certifications or import delays.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances by Region: Import duties, VAT, and currency fluctuations can significantly affect final costs in Africa, South America, and the Middle East. Engaging with local customs experts and financial advisors is prudent.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Insist on transparent cost breakdowns to identify potential savings in materials, logistics, or packaging.
Indicative Pricing Disclaimer
Pricing for motion detectors integrated with LED strips varies widely depending on specifications, order size, and sourcing region. Typical unit prices may range from $5 to $25 per unit for standard configurations at medium volumes (hundreds to thousands of units). Custom or certified products can exceed this range. Buyers should treat all price indications as estimates and conduct direct supplier negotiations to obtain accurate, up-to-date quotations tailored to their requirements.
By dissecting the cost structure and understanding pricing drivers, international B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions that balance quality, compliance, and cost-efficiency across diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Spotlight on Potential motion detector for led strip Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘motion detector for led strip’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for motion detector for led strip
Key Technical Properties of Motion Detectors for LED Strips
Understanding the critical technical specifications of motion detectors integrated with LED strips is essential for making informed procurement decisions. These properties directly impact product performance, reliability, and suitability for specific applications in commercial or industrial environments across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Detection Range
This refers to the maximum distance at which the motion detector can sense movement, typically measured in meters. For LED strip applications, a detection range between 3 to 10 meters is common. Buyers should assess this based on the size of the installation area to ensure effective coverage without blind spots, optimizing energy savings and security.
2. Sensor Type
Common sensor technologies include Passive Infrared (PIR), Ultrasonic, and Microwave sensors. PIR sensors detect body heat and are energy-efficient, making them ideal for indoor use. Ultrasonic and microwave sensors detect motion through sound waves or electromagnetic signals, offering higher sensitivity and broader coverage, suitable for complex or large spaces. Selecting the right sensor type affects accuracy and false trigger rates.
3. Operating Voltage and Power Consumption
Motion detectors for LED strips often operate within low-voltage DC ranges (e.g., 5V to 24V). Power consumption should be minimal to maintain overall energy efficiency, especially in large-scale installations. Buyers must verify compatibility with existing LED strip power supplies and consider total system energy use to reduce operational costs.
4. Response Time and Delay Settings
Response time is the interval between motion detection and LED strip activation, usually within milliseconds to seconds. Delay settings allow the light to remain on for a preset duration after motion stops. These adjustable parameters help tailor lighting behavior to user needs, improving user experience and further conserving energy.
5. IP Rating (Ingress Protection)
This rating indicates the device’s resistance to dust and moisture. For indoor LED strip applications, an IP20 rating may suffice, but outdoor or harsh environment installations require higher ratings such as IP65 or above. Selecting the appropriate IP rating ensures durability and reduces maintenance costs, critical for buyers in diverse climates.
6. Material and Build Quality
High-grade plastics or metal casings improve durability and heat dissipation. Good material quality extends product lifespan, especially in industrial or outdoor settings. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who provide certifications or warranties confirming robust construction.
Common Trade Terminology for International B2B Buyers
Navigating the procurement process efficiently requires familiarity with key industry terms. Here are essential trade terms relevant to motion detector and LED strip sourcing:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce components or products that are branded and sold by another company. For buyers, OEM partnerships often mean access to customized or white-labeled motion detectors tailored to specific market requirements, enhancing brand differentiation.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell per order. Understanding MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory planning, especially for buyers in emerging markets who may require flexibility in order sizes to minimize upfront costs.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing, delivery, and terms for a specified quantity and product specifications. RFQs are standard in B2B procurement, enabling buyers to compare offers and negotiate better deals on motion detector LED strip solutions.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce defining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and customs clearance. Common Incoterms include FOB (Free on Board), CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), and DDP (Delivered Duty Paid). Clear understanding prevents disputes and ensures smooth cross-border transactions.
Lead Time
The time interval between placing an order and receiving the goods. Lead times vary based on supplier location, production capacity, and shipping method. Accurate lead time estimation helps buyers plan project timelines and avoid costly delays.
Certification and Compliance
Suppliers may provide certifications such as CE (Europe), RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), or UL (Underwriters Laboratories) that attest to product safety and regulatory compliance. Buyers should verify these certificates to meet local regulations and ensure quality standards.
By focusing on these critical technical properties and mastering key trade terminology, international B2B buyers can optimize their procurement strategies for motion detector LED strips, ensuring cost-effective, reliable, and compliant lighting solutions tailored to their regional market needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the motion detector for led strip Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for motion detectors integrated with LED strip lighting is expanding rapidly, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient and smart lighting solutions across diverse industries. Key growth sectors include commercial real estate, manufacturing, retail, hospitality, and residential smart home applications. For B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this market presents unique opportunities influenced by regional infrastructure development, urbanization, and energy conservation initiatives.
Global Drivers:
– Energy Efficiency Mandates: Governments in Europe and the Middle East are enforcing stricter energy consumption regulations, encouraging adoption of motion sensor LED technologies that reduce electricity usage.
– Automation & Smart Building Integration: The rise of IoT and smart building infrastructure, especially in developed markets like the UK and parts of Europe, is fostering demand for motion-activated LED strip lighting systems that integrate seamlessly with building management systems (BMS).
– Safety and Security Requirements: In manufacturing hubs and warehouses, particularly in South Africa and parts of South America, motion sensor LED strips improve workplace safety by providing instant illumination only when areas are occupied.
– Cost Optimization: Businesses worldwide seek to reduce operational costs; motion detector LED strips offer significant savings in energy and maintenance, making them attractive for large-scale commercial projects.
Emerging Sourcing and Technology Trends:
– Modular & Customizable Solutions: Suppliers increasingly offer customizable motion detector LED strips with adjustable sensor ranges, light intensity, and integration capabilities to suit diverse client needs.
– Wireless and Smart Connectivity: The integration of wireless protocols (Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Bluetooth) enables remote control and automation, a growing trend in B2B procurement especially in tech-forward European and Middle Eastern markets.
– Hybrid Sensor Technologies: Combining PIR, ultrasonic, and microwave sensors to enhance detection accuracy in complex environments is gaining traction. This hybrid approach is particularly relevant for large warehouses and manufacturing plants.
– Local Manufacturing & Assembly: To mitigate supply chain disruptions and reduce lead times, buyers in Africa and South America are favoring suppliers with local or regional assembly operations.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability considerations are now integral to procurement decisions in the motion detector LED strip sector. For international B2B buyers, especially in Europe and South Africa, aligning with environmental and ethical standards is not only a compliance issue but a strategic priority.
Environmental Impact:
Motion detector LED strips significantly reduce energy consumption by illuminating spaces only when occupied, which lowers carbon emissions. Additionally, LED technology’s long lifespan decreases waste and resource use compared to traditional lighting. However, the environmental footprint of manufacturing components—such as sensors, PCBs, and LED chips—remains a key factor. Selecting suppliers committed to minimizing hazardous substances and adopting circular economy principles (e.g., recyclability, reduced packaging) enhances sustainability.
Ethical Supply Chains:
Transparency and social responsibility in the supply chain are critical. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate fair labor practices, conflict-free sourcing of raw materials, and adherence to international labor standards. Certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management), ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety), and SA8000 (Social Accountability) provide assurance of ethical operations.
Green Certifications & Materials:
– RoHS Compliance: Restricts hazardous substances in electronic components.
– Energy Star or Equivalent: Certification of energy efficiency for lighting products.
– REACH Regulation Compliance: Ensures chemical safety in components.
– Use of Biodegradable or Recycled Materials: Some suppliers now offer LED strips with recyclable casings and reduced plastic usage, appealing to eco-conscious buyers.
By integrating sustainability criteria into sourcing decisions, B2B buyers can meet corporate social responsibility goals, comply with regional regulations, and appeal to environmentally aware end-users.
Evolution and Historical Context
Motion detector technology for LED strip lighting has evolved significantly over the past two decades. Initially, LED strips were manually controlled and lacked automation, limiting their energy efficiency. The integration of passive infrared (PIR) sensors marked the first major advancement, enabling lights to respond to human presence.
Over time, sensor technology diversified to include ultrasonic and microwave detection, improving sensitivity and reliability in various environments. The proliferation of IoT and wireless communication protocols in the 2010s further transformed motion detector LED strips into smart, connected devices capable of integration with building automation systems.
For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution highlights the importance of selecting motion detector LED strips that incorporate the latest sensor technologies and connectivity options to future-proof their investments and maximize operational benefits.
This comprehensive insight into market dynamics, sourcing trends, and sustainability considerations equips international B2B buyers—especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—to make informed decisions when procuring motion detector LED strip solutions.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of motion detector for led strip
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers of motion detectors for LED strips in international markets?
To vet suppliers, begin by verifying their business licenses, certifications (such as ISO 9001), and compliance with international quality standards. Request product samples and technical datasheets to assess quality and compatibility with your LED systems. Check references or reviews from other international clients, especially within your region (Africa, South America, Middle East, Europe). Use third-party inspection services for factory audits and quality control. Establish clear communication channels to evaluate responsiveness and technical support capabilities before finalizing partnerships. -
What customization options are typically available for motion detectors integrated with LED strips?
Many manufacturers offer customization including sensor type (PIR, ultrasonic, microwave), detection range, sensitivity, delay timer settings, and power input compatibility. You can also request tailored designs for specific environments—such as waterproof or dustproof casings for harsh industrial settings. Firmware customization for integration with smart building systems or IoT platforms is increasingly common. Discuss your application needs upfront to ensure suppliers can deliver bespoke solutions that align with your operational requirements and regional standards. -
What are common minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for motion detectors for LED strips in international B2B transactions?
MOQs vary widely depending on supplier scale and customization complexity but typically range from 100 to 500 units. Standard lead times are usually between 4 to 8 weeks, factoring in production, quality checks, and shipping. For custom orders, expect longer lead times. To optimize procurement, negotiate flexible MOQs or staggered shipments, especially when entering new markets or testing products. Early engagement with suppliers about production capacity and logistics helps avoid delays and ensures timely delivery. -
What payment terms are standard for international buyers of motion detectors for LED strips, and how can I mitigate financial risks?
Common payment terms include a 30-50% advance deposit with the balance paid upon shipment or after passing quality inspections. Letters of credit (LC) and escrow services offer greater security for large transactions. To mitigate risks, conduct due diligence on the supplier’s financial stability and reputation. Use trade finance instruments and consider insurance options like marine cargo insurance. Clear contractual agreements specifying payment milestones linked to delivery and quality benchmarks protect both parties. -
Which quality assurance certifications should I look for when sourcing motion detectors for LED strips internationally?
Key certifications include CE (for Europe), RoHS (restricting hazardous substances), FCC (for electromagnetic compatibility), and UL (for safety standards). ISO 9001 certification indicates robust quality management systems. For energy efficiency, look for ENERGY STAR or equivalent regional certifications. Ensure the products comply with your country’s import regulations and standards. Request supplier-provided test reports and factory inspection certificates to confirm consistent quality and regulatory adherence. -
What are the best logistics practices for importing motion detectors for LED strips from overseas suppliers?
Coordinate with freight forwarders experienced in electronics and fragile goods to ensure proper packaging and handling. Choose between air freight for speed or sea freight for cost-efficiency based on urgency and budget. Clarify Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) to understand risk and cost responsibilities. Track shipments actively and prepare customs documentation in advance to avoid clearance delays. Consider warehousing solutions near your distribution centers to streamline last-mile delivery within your region. -
How should I handle disputes or quality issues with overseas suppliers of motion detectors for LED strips?
Establish clear dispute resolution clauses in contracts, including arbitration venues and governing law. Document all communications and maintain records of quality inspections and shipment conditions. Use third-party inspection agencies to provide unbiased reports. Engage in prompt, professional dialogue to resolve issues amicably. If necessary, leverage trade associations or chambers of commerce for mediation. Building long-term relationships with trusted suppliers reduces dispute frequency and facilitates smoother conflict resolution. -
Are there specific considerations for sourcing motion detectors for LED strips tailored to markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe?
Yes, regional climate, electrical standards (voltage, frequency), and regulatory requirements vary significantly. For example, waterproof and dust-resistant designs are crucial in African and Middle Eastern environments. European buyers often require stringent energy efficiency and safety certifications. South American buyers should verify compliance with local import regulations and consider language support for technical documentation. Partnering with suppliers familiar with these markets ensures product suitability and smoother customs clearance.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for motion detector for led strip
Maximizing Value through Strategic Sourcing of Motion Detectors for LED Strips
For international B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, sourcing motion detectors for LED strips presents a unique opportunity to enhance energy efficiency, operational safety, and cost-effectiveness in diverse applications—from industrial facilities to commercial and residential projects. Key takeaways include prioritizing suppliers that offer advanced sensor technologies such as PIR, ultrasonic, or microwave detection, ensuring compatibility with LED strip systems, and verifying durability to withstand varied environmental conditions.
Strategic sourcing should emphasize suppliers with proven quality certifications, flexible customization options, and strong after-sales support to mitigate risks and optimize total cost of ownership. Additionally, partnering with manufacturers that integrate smart connectivity features can future-proof investments by enabling IoT-enabled lighting solutions tailored to evolving market demands.
Looking ahead, the growing global emphasis on sustainability and energy conservation will continue to drive demand for intelligent lighting controls. Buyers are encouraged to adopt a forward-thinking sourcing strategy that balances innovation with reliability. By doing so, businesses in regions like South Africa, Brazil, the Middle East, and the UK can secure competitive advantages, reduce operational expenses, and align with environmental goals—positioning themselves at the forefront of smart lighting transformation.

