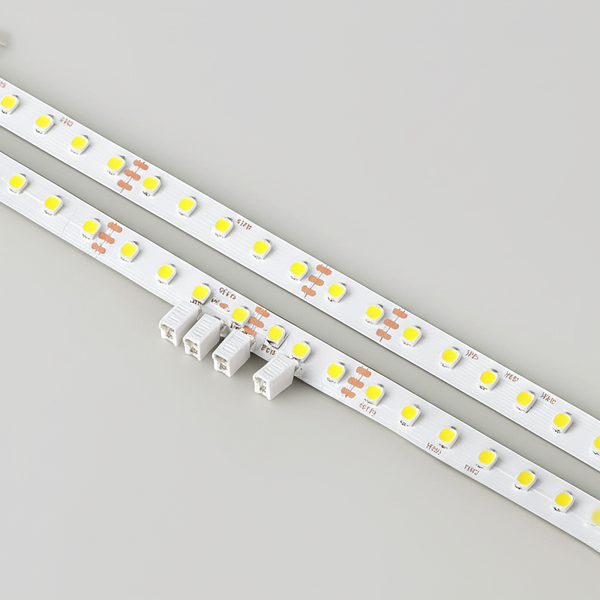
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for connecting led strips
Connecting LED strips is a pivotal element in modern lighting solutions, serving as the backbone for diverse applications ranging from architectural illumination to industrial installations. For international B2B buyers, especially those operating in dynamic markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of LED strip connectivity is essential for ensuring product reliability, energy efficiency, and scalability. The quality of connections directly influences system longevity, safety compliance, and maintenance costs—factors that significantly impact operational budgets and customer satisfaction.
This comprehensive guide offers an authoritative roadmap to mastering LED strip connections, covering essential topics such as the variety of LED strip types (single-color, RGB, tunable white, and addressable variants), critical wiring principles, and the selection of compatible materials and components. It also delves into manufacturing standards, quality control processes, and how to evaluate suppliers to mitigate risks associated with counterfeit or substandard products. Cost analysis and market trends provide buyers with a strategic perspective on pricing fluctuations and sourcing opportunities across different regions.
By integrating technical insights with practical sourcing strategies, this guide empowers international buyers to make well-informed decisions that align with their project requirements and regional market conditions. Whether sourcing for large-scale commercial projects in the UAE, infrastructure upgrades in Brazil, or innovative retail lighting in Europe, readers will gain actionable knowledge to optimize their procurement process, enhance system performance, and secure competitive advantages in their respective markets.
Understanding connecting led strips Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Color LED Strip | Two-wire connection, fixed color output, simple wiring | Retail, hospitality, office lighting | + Easy installation and control – Limited color flexibility |
| RGB and RGBW LED Strips | Multi-wire connections (4-5 wires), color mixing capability | Architectural, entertainment, branding lighting | + Dynamic colors and effects – Requires complex controllers |
| Tunable White (CCT) Strips | Three or more wires, adjustable color temperature (warm to cool) | Healthcare, museums, premium retail | + Enhances ambiance and visual comfort – Higher cost and wiring complexity |
| Addressable LED Strips | Individually controllable LEDs, requires data and power lines | Large-scale displays, advertising, interactive installations | + High customization and effects – Complex setup and higher investment |
| Parallel Connected Strips | Multiple strips powered independently from a central source | Long runs, commercial and industrial installations | + Reduces voltage drop and brightness inconsistency – More wiring and connectors needed |
Single-Color LED Strip
Single-color LED strips are the most straightforward type, featuring a simple two-wire connection and emitting a fixed color. Their simplicity makes them highly suitable for B2B projects requiring reliable, cost-effective lighting solutions such as retail shelves, office environments, and hospitality venues. Buyers should consider power supply capacity and wiring gauge carefully to avoid voltage drops, especially for longer runs. Their ease of installation and low maintenance are attractive for large-scale deployments in emerging markets across Africa and South America.
RGB and RGBW LED Strips
RGB and RGBW strips add color versatility by integrating multiple diodes that combine red, green, blue, and optionally white LEDs. These require multi-wire connections and dedicated controllers to manage color mixing and effects. They are ideal for architectural accents, event lighting, and branding projects in dynamic environments like the Middle East and Europe. B2B buyers must factor in the complexity of controllers, potential troubleshooting, and the need for skilled installation teams to maximize the visual impact and operational reliability.
Tunable White (CCT) LED Strips
Tunable white LED strips allow adjustment of color temperature between warm and cool white, enhancing visual comfort and ambiance. Featuring three or more wires, these strips are popular in healthcare facilities, museums, and upscale retail where lighting quality affects user experience. International buyers should evaluate the compatibility with dimming systems and ensure supplier expertise in delivering consistent color temperature control. Although more expensive, their adaptability offers significant value in premium projects requiring sophisticated lighting solutions.
Addressable LED Strips
Addressable LED strips provide the highest level of control by enabling individual LED pixel management through data lines, alongside power wiring. This complexity supports intricate lighting designs, including animations and interactive displays, commonly used in advertising, large-scale exhibitions, and entertainment installations. For B2B buyers in technologically advanced markets such as Europe and parts of Asia, considerations include the need for compatible controllers, software integration, and thorough technical support to ensure seamless deployment and maintenance.
Parallel Connected LED Strips
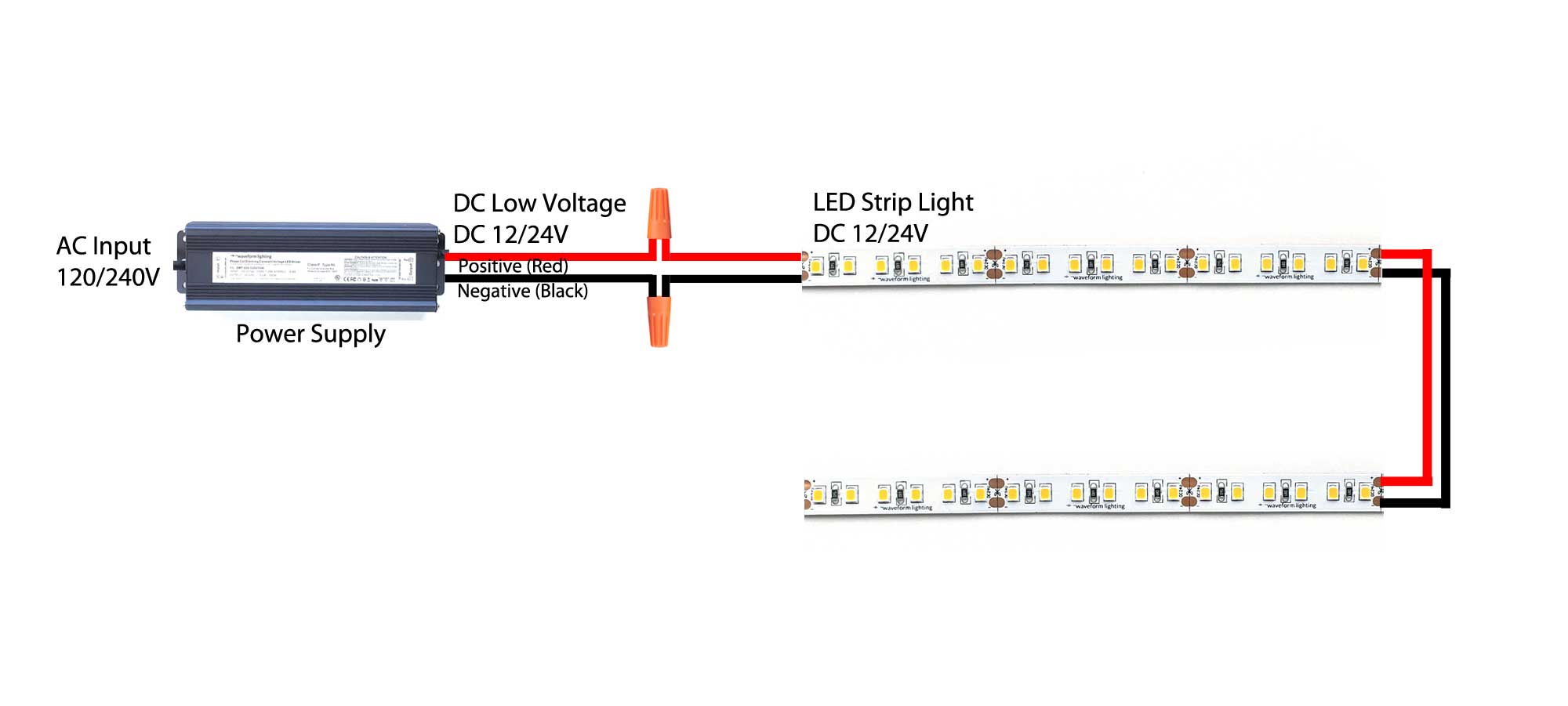
Parallel connection involves powering multiple LED strips independently from a centralized power source to mitigate voltage drop and maintain uniform brightness across long runs. This wiring approach is essential for commercial and industrial projects with extensive lighting layouts, such as warehouses and large retail stores. Buyers should prepare for increased wiring complexity and connector costs but benefit from improved system reliability and easier troubleshooting. This method is particularly advantageous in regions with challenging infrastructure, ensuring consistent lighting performance over time.
Related Video: How to Connect LED Strips – Soldering Connectors, Wires and More
Key Industrial Applications of connecting led strips
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of connecting led strips | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail & Commercial Spaces | Ambient and accent lighting in large retail outlets | Enhances customer experience, drives sales through appealing visuals, and reduces energy costs | Requires flexible, durable LED strips with consistent brightness and easy integration with existing lighting control systems; sourcing must consider voltage drop mitigation for long runs |
| Hospitality & Leisure | Mood and architectural lighting in hotels and resorts | Creates customizable atmospheres to improve guest satisfaction and brand differentiation | High IP-rated, dimmable LED strips with reliable connectors for humid or outdoor environments; compatibility with advanced control systems for dynamic lighting effects |
| Industrial & Manufacturing Facilities | Task and safety lighting along assembly lines and workstations | Improves worker productivity and safety compliance by providing uniform, bright illumination | Robust, long-lasting LED strips with high IP rating and resistance to dust/oil; wiring solutions that minimize voltage drop and allow modular expansion |
| Transportation & Infrastructure | Signage and pathway lighting in airports, metro stations, and highways | Enhances visibility, safety, and navigational clarity while reducing maintenance costs | LED strips with high brightness, energy efficiency, and long lifespan; connectors and wiring suitable for harsh environmental conditions and compliance with local standards |
| Agriculture & Controlled Environment | Growth lighting in greenhouses and vertical farms | Optimizes plant growth cycles, reduces energy consumption, and allows precision control of light spectrum | Specialized LED strips with specific wavelength outputs, waterproofing, and heat dissipation features; sourcing must prioritize reliability and ease of maintenance in humid conditions |
Retail & Commercial Spaces
In retail and commercial environments, connecting LED strips is widely used for ambient and accent lighting to create visually appealing spaces that attract customers and enhance brand perception. These installations often require long runs of LED strips connected in parallel to avoid voltage drop and maintain uniform brightness across large areas. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like the Middle East and Europe, sourcing LED strips with consistent color temperature and dimmability is crucial to integrate with sophisticated lighting control systems that adapt to different times of day or promotional events.
Hospitality & Leisure
Hotels and resorts leverage connected LED strips to craft dynamic, mood-enhancing lighting solutions that elevate guest experiences. Tunable white and RGB LED strips are often connected to centralized controllers, enabling customizable lighting scenes for lobbies, corridors, and outdoor terraces. Buyers from Africa and South America should prioritize LED strips with high ingress protection (IP65 or higher) due to humid climates and ensure compatibility with dimming protocols such as DALI or 0-10V for seamless integration into building management systems.
Industrial & Manufacturing Facilities
In manufacturing plants, connected LED strips provide focused task lighting along assembly lines and workstations, enhancing worker safety and efficiency. These applications demand LED strips that are rugged, dust and oil resistant, and capable of maintaining brightness over long distances without significant voltage drop. International buyers must carefully select wire gauge and connection methods to comply with local electrical standards and ensure easy scalability for future production expansions, particularly in fast-growing markets like the UAE and Brazil.
Transportation & Infrastructure
LED strips are extensively used in transportation hubs and infrastructure for signage, pathway illumination, and safety lighting. The value lies in their energy efficiency, long lifespan, and ability to deliver high brightness consistently, which reduces maintenance frequency and operational costs. B2B buyers from Europe and the Middle East should focus on sourcing LED strips with robust connectors and wiring solutions that withstand environmental stressors such as temperature fluctuations, dust, and moisture, while also meeting regional regulatory requirements.
Agriculture & Controlled Environment
Connected LED strips in agriculture are critical for growth lighting in greenhouses and vertical farms, where precise control over light spectrum and intensity directly impacts crop yields. These LED strips must be waterproof, have excellent heat dissipation, and deliver specific wavelengths tailored to plant species. Buyers from Africa and South America should prioritize suppliers offering reliable, easy-to-maintain LED strip systems designed for humid and nutrient-rich environments, ensuring long-term operational efficiency and crop quality.
Related Video: How to Connect LED Strips Using Various Connectors
Strategic Material Selection Guide for connecting led strips
When selecting materials for connecting LED strips in professional and commercial applications, understanding the properties and implications of each material is essential for ensuring durability, safety, and compliance. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in connectors, wiring, and terminals for LED strip connections, with a focus on their suitability for international B2B buyers, especially in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Copper
Key Properties:
Copper is the industry standard for electrical wiring due to its excellent electrical conductivity, high thermal resistance, and ductility. It performs well under varying temperatures and has good corrosion resistance when properly insulated or plated.
Pros & Cons:
Copper offers superior conductivity, resulting in minimal voltage drop and efficient power delivery for LED strips. It is relatively easy to work with during manufacturing and installation. However, pure copper can be expensive compared to alternatives and is prone to oxidation if exposed to moisture, which can impact long-term reliability without proper protective coatings.
Impact on Application:
Copper wiring and connectors are ideal for installations requiring stable, long-term performance, especially in commercial or industrial environments. For outdoor or humid climates common in parts of Africa and the Middle East, copper components should be plated (e.g., tin-plated) to prevent corrosion.
B2B Considerations:
Buyers from regions with high ambient temperatures (e.g., UAE, parts of South America) should specify copper with appropriate temperature ratings and protective coatings. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B170 (copper wire) and IEC 60228 (conductors) is critical for ensuring quality and interoperability.
2. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and has moderate electrical conductivity—approximately 61% that of copper. It is more susceptible to oxidation but forms a protective oxide layer that prevents further corrosion.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of aluminum is its lower cost and weight, making it attractive for large-scale installations with budget constraints. However, aluminum wiring requires larger gauge sizes to compensate for lower conductivity, and its mechanical properties make it less flexible and more prone to fatigue over time.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is less common for LED strip connections but may be used in power distribution wiring or busbars in large commercial projects where weight and cost savings are priorities. It is less suitable for flexible connectors or areas requiring frequent handling.
B2B Considerations:
In regions with high humidity or salt exposure, such as coastal areas in South America or the Middle East, aluminum connectors must be carefully sealed to prevent corrosion. Compliance with standards like DIN EN 573 (aluminum alloys) and regional electrical codes is essential.
3. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Insulation
Key Properties:
PVC is a widely used insulation material for wires and connectors due to its flame retardancy, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness. It can withstand temperatures up to around 70–105°C depending on formulation.
Pros & Cons:
PVC insulation offers good protection against moisture and mechanical abrasion, making it suitable for indoor and some outdoor applications. However, it is less flexible at low temperatures and can degrade under prolonged UV exposure, limiting its use in harsh outdoor environments.
Impact on Application:
PVC-insulated wires and connectors are common in commercial LED strip installations where moderate environmental protection is needed. For outdoor or high-temperature environments, alternatives like silicone or TPE insulation are preferred.
B2B Considerations:
Buyers in regions with strong sunlight or high ambient temperatures (e.g., UAE, Thailand) should verify UV and heat resistance ratings. Compliance with international flame retardancy standards (UL 94, IEC 60332) and RoHS directives is often required for export and local regulations.
4. Silicone Insulation
Key Properties:
Silicone insulation is highly flexible, resistant to extreme temperatures (from -60°C to +200°C), and offers excellent UV and chemical resistance. It maintains elasticity over time, making it ideal for dynamic or exposed installations.
Pros & Cons:
Silicone-insulated connectors and cables provide superior durability in harsh environments, including outdoor and industrial settings. The downside is a higher material and manufacturing cost compared to PVC, which may impact budget-sensitive projects.
Impact on Application:
Silicone insulation is preferred for LED strip connections in environments with wide temperature fluctuations, outdoor exposure, or where flexibility is critical (e.g., architectural lighting in Europe or outdoor installations in Africa).
B2B Considerations:
International buyers should ensure silicone components meet IEC 60502 and ASTM D2000 standards for insulation materials. In markets with stringent environmental regulations, silicone’s non-toxic and recyclable nature can be a selling point.
Summary Table of Materials for Connecting LED Strips
| Material | Typical Use Case for connecting led strips | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Primary conductor in wiring and connectors for indoor and outdoor LED strip installations | Excellent conductivity and durability | Higher cost and requires corrosion protection | High |
| Aluminum | Power distribution wiring and busbars in large-scale commercial LED projects | Lightweight and cost-effective for large runs | Lower conductivity and mechanical flexibility; prone to oxidation | Low |
| PVC | Insulation for wires and connectors in indoor and moderate outdoor environments | Cost-effective with good flame retardancy | Limited UV resistance and flexibility at low temps | Low |
| Silicone | Insulation for flexible, outdoor, and high-temperature LED strip connections | High flexibility and temperature/UV resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | Medium |
This material selection guide equips international B2B buyers with the knowledge to make informed decisions tailored to their specific regional and project requirements. Prioritizing compliance with local and international standards, environmental conditions, and budget constraints ensures optimal performance and longevity of LED strip installations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for connecting led strips
Manufacturing and quality assurance for connecting LED strips are critical to delivering reliable, high-performance lighting solutions suitable for diverse international markets. B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must understand these processes to select reputable suppliers and ensure compliance with local and global standards.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Typical Manufacturing Process for Connecting LED Strips
The production of connecting LED strips involves multiple precise stages designed to ensure electrical integrity, durability, and ease of installation.
1. Material Preparation
- Raw Materials: High-quality flexible PCB substrates, copper conductors, LED chips, resistors, connectors, and protective coatings are sourced.
- Quality Checks: Incoming materials undergo initial inspection for dimensions, conductivity, and chemical composition to ensure conformance with specifications.
- Pre-Treatment: PCBs may be cleaned and treated to enhance adhesion and solderability.
2. Forming and Circuit Patterning
- Copper Tracing: Copper is etched or printed on the flexible substrate to form precise circuit pathways. This process requires micron-level accuracy to prevent shorts or breaks.
- Solder Mask Application: Protective layers are applied over the circuit to prevent corrosion and electrical shorts, while exposing contact points for LED and connector attachment.
- Surface Finishing: Techniques such as gold plating or tinning are used on contact areas to improve solderability and electrical contact quality.
3. Assembly
- Component Placement: Automated pick-and-place machines position LED chips, resistors, and other components on the PCB.
- Soldering: Reflow soldering or selective soldering ensures secure electrical and mechanical connections. This step is crucial for long-term reliability under varying environmental conditions.
- Connector Integration: Connectors, terminals, or solder pads for connecting LED strips are affixed. This includes options for soldered joints or modular plug-in connectors, depending on the product design.
- Encapsulation: Protective silicone or epoxy coatings are applied to enhance waterproofing, flexibility, and mechanical protection.
4. Finishing
- Cutting and Shaping: LED strips are cut to standard lengths or customized sizes as per order requirements.
- Marking and Labeling: Product information, polarity markings, and certification logos are printed or etched.
- Packaging: LED strips are carefully wound or packed to avoid damage during transportation and storage.
Key Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) Practices
Robust QA/QC frameworks are essential to guarantee LED strips perform consistently and comply with international safety and performance standards.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This globally recognized standard ensures suppliers have structured quality management systems, enabling traceability, process control, and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: Mandatory for the European market, indicating compliance with EU safety, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), and environmental directives.
- RoHS Compliance: Restricts hazardous substances, critical for buyers in Europe and increasingly adopted worldwide.
- UL Certification: Important for North American markets but also recognized globally for electrical safety assurance.
- IEC Standards (e.g., IEC 60598): Cover luminaires and LED lighting safety and performance.
- Regional Certifications: Buyers from the Middle East and Africa should verify compliance with local standards such as SASO (Saudi Arabia) or SABS (South Africa), while South American buyers may require INMETRO certification (Brazil).
QC Checkpoints Throughout Production
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials and components before manufacturing starts to prevent defects from entering the production line.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing stages including solder joint inspection, component placement accuracy, and electrical testing. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) is common here.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of finished LED strips before shipment, including visual inspection, electrical performance, and functional testing under simulated real-world conditions.
Common Testing Methods
- Electrical Testing: Verification of voltage, current draw, and resistance to ensure circuit integrity and proper functioning.
- Voltage Drop Measurement: Ensures minimal brightness variation across the strip, vital for commercial-grade installations.
- Environmental Testing: Exposure to humidity, temperature cycles, and UV radiation to simulate conditions in regions such as the Middle East or tropical climates in Africa and South America.
- Mechanical Testing: Flexibility and tensile strength tests to confirm durability during installation and use.
- Safety Testing: Checks for insulation resistance, short circuits, and fire hazard potential.
How B2B Buyers Can Verify Supplier Quality Assurance
Due diligence is paramount when sourcing LED strip connectors internationally, particularly for buyers requiring products that meet stringent local regulations and performance expectations.
Supplier Audits
- Factory Audits: Arrange on-site inspections or remote audits to evaluate manufacturing capabilities, process controls, and quality management systems.
- Process Capability Review: Assess supplier’s ability to consistently produce within tolerance and meet delivery schedules.
- Certification Verification: Request valid certificates (ISO 9001, CE, RoHS, UL) and confirm authenticity through issuing bodies.
Quality Documentation and Reporting
- Inspection Reports: Demand detailed IQC, IPQC, and FQC reports, including test data and photographic evidence.
- Test Certificates: Obtain third-party lab test reports for electrical safety, EMC, and environmental resilience.
- Batch Traceability: Ensure suppliers provide batch numbers and production logs to facilitate recall or warranty claims if necessary.
Third-Party Inspection Services
- Independent quality inspection companies can conduct pre-shipment inspections, functional testing, and compliance verification on behalf of the buyer, providing an unbiased assessment.
QC and Certification Nuances for Buyers by Region
- Africa: Infrastructure variability means buyers should emphasize product robustness, environmental testing, and certifications like SABS. Local customs may require additional documentation; partnering with suppliers familiar with African regulatory frameworks is advantageous.
- South America: Certifications like INMETRO are crucial. Buyers should confirm that suppliers understand local import regulations and ensure compliance with power supply standards prevalent in South American markets.
- Middle East (e.g., UAE): The region’s harsh climate necessitates rigorous environmental testing. Certifications such as SASO and conformity to Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) standards are essential. Buyers should prioritize suppliers experienced with heat-resistant and UV-stabilized products.
- Europe: Strict adherence to CE, RoHS, and REACH regulations is mandatory. Buyers should seek suppliers with transparent quality management and environmental compliance to mitigate regulatory risks and meet sustainability goals.
Conclusion
For international B2B buyers, understanding the manufacturing and quality assurance processes behind connecting LED strips is vital for selecting dependable suppliers and ensuring product longevity. Evaluating suppliers’ adherence to international and regional standards, verifying robust QC checkpoints, and leveraging audits and third-party inspections will help buyers mitigate risks and secure high-quality LED lighting solutions tailored to their markets’ unique demands.
Related Video: LED Light Making Process | How LED Lights Made Inside Factory | Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for connecting led strips Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of sourcing connections for LED strips is critical for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize investment and ensure product reliability. The following analysis breaks down key cost components, price influencers, and strategic buyer tips tailored for markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Key Cost Components in LED Strip Connection Solutions
-
Materials
The primary materials include copper wiring, connectors (such as soldered joints, terminal blocks, or plug-in connectors), insulating materials, and protective casings. Higher-grade copper and advanced connector materials (e.g., gold-plated contacts) increase costs but significantly improve conductivity and durability. Material costs fluctuate with metal prices and regional availability, directly impacting supplier quotes. -
Labor
Skilled labor is required for precise wiring, soldering, and assembly, especially for complex parallel configurations or custom wiring harnesses. Labor costs vary widely by region; sourcing from countries with competitive labor markets can reduce expenses but may affect lead times and quality control. -
Manufacturing Overhead
Overhead includes factory utilities, equipment depreciation, quality assurance processes, and administrative expenses. Efficient factories with automated soldering or connector assembly lines tend to have lower overhead per unit, benefiting bulk buyers. -
Tooling and Setup Costs
Custom tooling for specialized connectors or wiring harnesses introduces upfront costs, often amortized over production volume. Buyers requesting bespoke specifications or small MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) runs should expect higher per-unit tooling costs. -
Quality Control (QC)
QC processes such as electrical testing, insulation resistance checks, and durability assessments add to the overall cost but are essential for compliance with international safety and performance standards (e.g., CE, RoHS, UL certifications). -
Logistics and Import Duties
Shipping, customs clearance, and local taxes vary by destination. Bulk shipments benefit from economies of scale, but buyers must factor in additional costs for expedited or insured shipping, especially for fragile or high-value components. -
Supplier Margin
Margins depend on supplier positioning, brand reputation, and market demand. Established manufacturers offering certified and tested products typically command higher margins but deliver greater reliability.
Price Influencers Affecting LED Strip Connection Sourcing
-
Order Volume and MOQ
Larger orders reduce unit costs by spreading fixed costs and increasing supplier willingness to offer discounts. However, international buyers should balance MOQ with inventory carrying costs and market demand. -
Product Specifications and Customization
Customized wiring lengths, connector types, or special certifications increase costs. Standardized components typically have more competitive pricing. -
Material Quality and Certification Requirements
Products certified to meet stringent international standards (e.g., IP ratings, fire resistance) incur higher costs but reduce risk and liability. -
Supplier Location and Capabilities
Suppliers with local presence or warehouses in target markets (e.g., UAE for Middle East, Germany for Europe) can reduce lead times and logistics costs. -
Incoterms and Payment Terms
The choice of Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP) affects who bears shipping and customs costs, impacting landed price. Favorable payment terms (letters of credit, deferred payment) can improve cash flow for buyers.
Strategic Tips for International B2B Buyers
-
Negotiate Beyond Unit Price
Engage suppliers on tooling fees, shipping arrangements, and warranty terms. Request volume discounts and bundled pricing for connectors plus wiring. -
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Evaluate long-term costs including installation labor, maintenance, failure rates, and warranty claims. Investing slightly more upfront for quality wiring and connectors reduces downtime and rework costs. -
Prioritize Certified and Tested Products
In regions with variable power quality and environmental conditions (high heat in Middle East, humidity in South America), certified components ensure safety and durability. -
Leverage Local Sourcing or Regional Distributors
To mitigate customs delays and reduce shipping costs, explore suppliers or distributors with regional warehouses. -
Understand Pricing Nuances by Region
For example, African markets may face higher logistics costs and import duties; European buyers should focus on compliance with EU regulations; Middle Eastern buyers often prefer suppliers familiar with GCC standards. -
Monitor Currency Fluctuations and Tariffs
Exchange rate volatility and changing trade policies can affect landed costs. Forward contracts or multi-currency payment options can hedge risks.
Indicative Pricing Disclaimer
Due to market variability in raw material costs, labor rates, and logistics, pricing for LED strip connection components can range significantly. Buyers should request detailed quotations based on their specific order size, customization needs, and delivery terms to obtain accurate cost assessments.
By understanding these cost drivers and market-specific factors, international B2B buyers can strategically source LED strip connecting components that optimize performance, compliance, and cost-effectiveness across diverse global markets.
Spotlight on Potential connecting led strips Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘connecting led strips’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for connecting led strips
Critical Technical Properties for Connecting LED Strips
1. Voltage Rating (12V vs. 24V)
LED strips commonly operate at 12V or 24V DC. Selecting the correct voltage rating is essential for compatibility with power supplies and controllers. Higher voltage (24V) systems allow longer runs with less voltage drop, improving brightness consistency in commercial projects. For international buyers, understanding voltage standards ensures the LED strips will integrate seamlessly with local power infrastructure and reduce installation complexities.
2. Wire Gauge and Current Capacity
Wire gauge (thickness) must match the current load and run length to prevent voltage drop, overheating, and fire hazards. Undersized wiring leads to brightness inconsistency and reliability issues. B2B buyers should specify wire gauge based on total wattage and distance, considering environmental factors such as ambient temperature. This technical detail directly impacts safety compliance and long-term system performance.
3. Connection Method and Material Quality
Connections can be soldered, clip-on connectors, or terminal blocks. High-quality connectors with corrosion-resistant materials (e.g., tin-plated copper) ensure stable electrical contact and reduce maintenance. For professional applications, choosing robust connection methods minimizes downtime and supports ease of servicing, which is critical for facility managers and contractors operating in diverse climates.
4. IP Rating (Ingress Protection)
The IP rating defines the LED strip’s resistance to dust and moisture. For indoor installations, IP20 is common, but outdoor or industrial environments require IP65 or higher. International buyers must assess environmental exposure to select appropriate IP ratings, ensuring durability and compliance with local safety standards.
5. Tolerance and Color Consistency
Tolerance relates to the allowable variation in electrical and optical performance, including voltage, current, and color temperature. Tight tolerance ensures uniform light output and color consistency across multiple strips, which is vital for aesthetic and branding purposes in commercial environments. Buyers should request datasheets specifying tolerance levels to guarantee product consistency.
6. Thermal Management Capabilities
LED strips generate heat that must be dissipated to maintain longevity and performance. Features like built-in heat sinks or compatibility with aluminum profiles improve thermal management. B2B buyers should prioritize LED strips designed for effective heat dissipation, especially for high-brightness or long-run installations, to reduce failure rates and maintenance costs.
Key Trade Terms for International LED Strip Buyers
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce LED strips or components which other businesses brand and sell. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers seeking customized products or exclusive designs tailored to their market needs. It impacts lead times, pricing, and quality assurance.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell. MOQs affect inventory planning and budgeting, especially for buyers in emerging markets. Negotiating MOQs can improve cash flow management and reduce storage costs for distributors and retailers.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal inquiry sent to suppliers to obtain pricing, lead times, and terms for specific LED strip configurations. RFQs streamline the sourcing process and enable buyers to compare offers transparently. Well-prepared RFQs should include technical specs and volume requirements to receive accurate quotes.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms defining responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs between buyer and seller. Common Incoterms include FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight). Understanding Incoterms helps buyers manage logistics risks, control costs, and ensure compliance with import regulations.
Voltage Drop
A technical term describing the reduction in voltage along the length of the LED strip due to resistance in wiring. Excessive voltage drop causes uneven brightness and can damage LEDs. Buyers should specify wiring and connection practices to minimize voltage drop, ensuring consistent lighting performance.
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) Dimming
A method for controlling LED brightness by rapidly switching the power on and off. PWM dimming is widely used in commercial lighting for energy efficiency and extended LED lifespan. Buyers should verify compatibility between LED strips and dimming controllers to enable smooth dimming functionality.
By mastering these essential technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that optimize installation quality, operational efficiency, and total cost of ownership for LED strip lighting projects across diverse markets.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the connecting led strips Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for connecting LED strips is expanding rapidly, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient, flexible lighting solutions across commercial, industrial, and architectural sectors. Key growth regions include Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where urbanization, infrastructure development, and smart city initiatives are fueling adoption. In markets such as the UAE and Thailand, investments in modernizing commercial buildings and hospitality venues are notable drivers.
Technological advancements are shaping the landscape, with 24V systems gaining preference due to lower voltage drop and enhanced brightness consistency over longer runs. Parallel wiring configurations are becoming the industry standard for commercial projects, offering improved reliability and ease of maintenance. Additionally, integration with smart controls—such as DMX512 decoders and PWM amplifiers—enables dynamic lighting schemes, appealing to high-end architectural and retail applications.
From a sourcing perspective, international B2B buyers are increasingly focusing on supplier reliability and product quality, prioritizing vendors who provide comprehensive technical support, certifications, and customization capabilities. The rise of modular LED strips with plug-and-play connectors reduces installation complexity and labor costs, which is especially relevant for large-scale projects in emerging markets. Furthermore, buyers are leveraging regional trade agreements and logistics hubs—like those in the Middle East—to optimize supply chains and reduce lead times.
Market dynamics also reflect heightened competition among manufacturers to innovate with flexible substrates, enhanced IP ratings for outdoor use, and improved thermal management solutions. These trends support diverse applications from industrial facility lighting to premium retail displays. B2B buyers are advised to assess suppliers’ capacity for technical customization and adherence to international electrical standards to ensure compliance and longevity in their projects.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a critical factor for B2B buyers in the connecting LED strip sector, with growing emphasis on minimizing environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle. LED strips inherently offer energy savings compared to traditional lighting, but the sourcing of raw materials, manufacturing processes, and end-of-life recyclability also significantly influence a product’s ecological footprint.
Ethical sourcing is gaining traction, especially in regions where supply chain transparency is mandated or incentivized by government policies. Buyers from Africa, South America, and Europe are prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate responsible sourcing of components such as copper wiring, semiconductors, and phosphor coatings. Certifications like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals), and Energy Star compliance are becoming baseline requirements in procurement contracts.
In addition, manufacturers are increasingly adopting eco-friendly materials, such as halogen-free coatings and recyclable substrates, to reduce toxic waste and facilitate circular economy initiatives. The use of LED drivers with high power factors and low harmonic distortion further supports energy efficiency goals. B2B buyers should seek suppliers who provide detailed environmental product declarations (EPDs) and engage in third-party sustainability audits, ensuring alignment with corporate social responsibility (CSR) policies.
For regions like the Middle East and Europe, where environmental regulations are stringent, integrating sustainability into product selection not only reduces operational costs but also enhances brand reputation and compliance. Buyers are encouraged to collaborate with suppliers offering lifecycle management services, including take-back programs and component recycling, to close the loop on LED strip installations.
Evolution and Historical Context
Connecting LED strips have evolved from simple, low-voltage decorative lights into sophisticated modular systems integral to modern lighting design. Initially popularized in residential and small-scale retail environments, the technology has rapidly matured due to advances in semiconductor efficiency, flexible PCB manufacturing, and control electronics.
Historically, the shift from 12V to 24V systems marked a significant milestone, enabling longer runs and reducing voltage drop challenges that plagued early installations. Parallel wiring architectures replaced daisy-chaining methods, improving system reliability and simplifying maintenance for commercial deployments.
The integration of digital control protocols such as DMX512 and the development of addressable LED strips have further expanded functionality, allowing dynamic color tuning, scene setting, and integration with building automation systems. This evolution positions connecting LED strips as a critical component in smart infrastructure projects worldwide, meeting the complex demands of international B2B buyers seeking scalable, energy-efficient, and customizable lighting solutions.
Related Video: International Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of connecting led strips
-
How can I effectively vet LED strip suppliers for international B2B purchases?
When sourcing LED strip suppliers internationally, prioritize those with verified certifications such as CE, RoHS, UL, and ISO to ensure product quality and compliance with safety standards. Request detailed technical datasheets and sample products to verify performance and durability. Check the supplier’s track record with previous B2B clients, especially in your region, and review their ability to support after-sales service and warranty claims. Additionally, assess their production capacity and communication responsiveness to avoid delays and misunderstandings. -
What customization options are typically available for connecting LED strips, and how do they impact pricing?
Most professional LED strip manufacturers offer customization including length, voltage (12V/24V), color temperature, waterproof rating (IP65, IP67), connectors, and control options like dimming or RGB control. Custom packaging and private labeling are also common for branding purposes. Customization usually increases lead time and cost, so clarify your specifications upfront and negotiate MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) accordingly. Understanding these factors helps you balance product uniqueness with budget and delivery timelines. -
What are typical MOQ and lead times for international LED strip orders, especially for buyers in Africa, South America, Middle East, and Europe?
MOQ often ranges from 500 to 1,000 meters depending on the supplier and customization level. Lead times for standard products generally span 2-4 weeks, but customized orders may require 4-8 weeks or more. For regions like Africa or South America, factor in additional shipping and customs clearance times, which can add 1-3 weeks. To optimize supply chain efficiency, establish clear lead times in contracts and consider buffer stock for critical projects. -
Which payment terms are standard in international B2B LED strip transactions, and how can buyers protect themselves?
Common payment terms include 30%-50% upfront deposit with the balance paid before shipment or upon delivery. Letters of Credit (LC) and escrow services offer enhanced security for large transactions. Buyers should insist on clear contractual terms covering product specifications, delivery schedules, and penalties for non-compliance. Using reputable freight forwarders and third-party inspection services before shipment can further mitigate risks. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from reliable LED strip manufacturers?
Reliable manufacturers implement strict quality control processes including in-line testing for voltage, current, and brightness consistency, as well as final product inspection for defects and waterproofing integrity. Certifications such as ISO 9001 confirm systematic quality management. Requesting factory audit reports and third-party lab test results can provide additional assurance. A robust warranty policy (typically 2-3 years) is a strong indicator of manufacturer confidence in product durability. -
Which certifications are critical for importing LED strips into markets like the UAE, Europe, and South America?
Key certifications include CE (European conformity), RoHS (restriction of hazardous substances), UL (safety standard mainly for US but respected globally), and FCC for electromagnetic compatibility. The UAE and Middle East markets often require SASO certification or local conformity assessments. For South America, INMETRO (Brazil) and SEC (Chile) are relevant. Ensuring your supplier provides these certifications helps smooth customs clearance and market acceptance. -
What are the best practices for managing logistics and shipping of LED strips internationally?
Choose suppliers experienced with international freight, offering options like FOB, CIF, or DDP terms depending on your logistics capabilities. LED strips are lightweight but delicate; packaging should prevent physical damage and moisture ingress. Air freight suits urgent orders but is costlier; sea freight is economical for bulk shipments but slower. Collaborate closely with freight forwarders familiar with your region’s customs regulations to avoid delays and unexpected fees. -
How should disputes regarding product quality or delivery be handled in international LED strip transactions?
Establish dispute resolution mechanisms in your contract, such as arbitration clauses or jurisdiction agreements. Maintain detailed documentation of communications, purchase orders, and product inspections. If quality issues arise, conduct joint inspections and use third-party testing labs to objectively assess claims. Engage suppliers proactively to negotiate remedies like replacement shipments or refunds. Building strong supplier relationships and clear contracts upfront reduces the likelihood and impact of disputes.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for connecting led strips
Connecting LED strips in commercial and industrial contexts demands precision, technical insight, and strategic sourcing to ensure optimal system performance and longevity. Key takeaways for international B2B buyers include prioritizing parallel wiring configurations to minimize voltage drop, selecting appropriate wire gauges based on current draw and run length, and utilizing professional-grade connection methods to guarantee reliability and ease of maintenance. Understanding these technical fundamentals mitigates common pitfalls such as uneven brightness, system failures, and costly troubleshooting.
From a sourcing perspective, partnering with experienced suppliers who offer high-quality components—power supplies, connectors, and controllers tailored to your regional requirements—is essential. This is particularly critical in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where environmental factors and infrastructure variations influence installation choices. Leveraging suppliers with robust technical support and localized logistics enhances project success and accelerates deployment timelines.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Looking ahead, the LED lighting industry continues to innovate with smarter control systems, energy-efficient drivers, and modular designs that simplify integration. International buyers are encouraged to adopt a strategic sourcing approach that balances cost, quality, and technological advancement to future-proof their lighting projects. Engaging with trusted partners and investing in education on wiring best practices will unlock superior outcomes and competitive advantages in a rapidly evolving market.

