Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for arduino led strip
The global demand for Arduino LED strips is rapidly expanding, driven by their versatility in industrial automation, smart lighting, advertising, and creative electronics projects. For international B2B buyers, especially in dynamic markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of sourcing high-quality Arduino LED strips is essential to remain competitive and innovative. These regions present unique opportunities and challenges, including varying supply chain infrastructures, regulatory environments, and application requirements.
This comprehensive guide delves into every critical aspect of the Arduino LED strip market to empower buyers with actionable insights. It covers the diverse types of LED strips—from single-color to addressable RGBW models—highlighting their technical specifications and ideal use cases. Buyers will gain clarity on materials and manufacturing quality control processes, ensuring product reliability and longevity. The guide also provides an in-depth overview of trusted suppliers and manufacturers, with a focus on sourcing from regions that align with buyers’ logistical and cost-efficiency goals.
Cost considerations, including volume pricing, import duties, and total landed cost, are analyzed to help procurement teams optimize budgets without compromising quality. Additionally, the guide addresses market trends and regulatory compliance relevant to regions like Germany and Kenya, facilitating smoother cross-border transactions. A dedicated FAQ section resolves common queries, enabling confident decision-making.
By synthesizing technical knowledge and market intelligence, this guide equips B2B buyers to navigate complexities and secure the best Arduino LED strip solutions tailored to their regional needs and business objectives.
Understanding arduino led strip Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Color LED Strips | Emit one fixed color; simple control (on/off, dimming) | Basic lighting, signage, industrial indicators | Pros: Low cost, easy integration; Cons: Limited visual effects |
| RGB LED Strips | Combine red, green, blue LEDs for color mixing | Dynamic lighting, architectural accents | Pros: Versatile color options; Cons: More complex control and wiring |
| RGBW LED Strips | RGB plus dedicated white LED for enhanced color range | Retail displays, mood lighting, hospitality | Pros: Better white light quality; Cons: Higher cost, power consumption |
| Addressable LED Strips | Individually controllable LEDs using digital protocols | Large-scale displays, custom animations | Pros: High flexibility, complex effects; Cons: Requires advanced programming and power management |
| High Voltage LED Strips | Operate at 12V or 24V for longer runs without voltage drop | Outdoor lighting, industrial installations | Pros: Longer strip lengths, efficient power; Cons: Requires compatible power supplies and drivers |
Single Color LED Strips are the most straightforward option, emitting a single hue with basic on/off or dimming controls. Ideal for B2B buyers targeting simple applications like signage or industrial indicators, these strips offer cost-effective solutions with easy integration. However, their limited visual appeal restricts use in projects requiring dynamic lighting.
RGB LED Strips provide enhanced flexibility by mixing red, green, and blue LEDs to create a broad spectrum of colors. They are well-suited for architectural accents and dynamic lighting solutions in commercial and retail environments. Buyers should consider the increased complexity in wiring and control, which may necessitate additional components like resistors and PWM-capable microcontroller pins.
RGBW LED Strips add a dedicated white LED, improving the quality and range of white and pastel colors. This makes them attractive for hospitality, retail, and mood lighting applications where authentic white light is critical. The trade-off includes higher costs and increased power consumption, factors that B2B buyers must weigh against project requirements.
Addressable LED Strips, such as those using WS2812 or Neopixel protocols, allow individual LED control for sophisticated animations and effects. These strips are favored in large-scale displays, entertainment venues, and custom signage projects. While offering unparalleled versatility, they require advanced programming skills and careful power management, making them suitable for buyers with technical expertise or access to specialized development resources.
High Voltage LED Strips, typically operating at 12V or 24V, enable longer continuous runs without significant voltage drop, ideal for outdoor or industrial lighting installations. These strips reduce the need for frequent power injections, simplifying installation in large projects. Buyers must ensure compatibility with appropriate power supplies and may need additional drivers or transistors to manage higher currents safely.
Related Video: Addressable LED Strip + Arduino (Tutorial)
Key Industrial Applications of arduino led strip
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of arduino led strip | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing & Automation | Visual status indicators on production lines | Enhances real-time monitoring, reduces downtime, improves workflow efficiency | Durable, high-brightness strips; compatibility with industrial controllers; power efficiency; supply chain reliability |
| Retail & Commercial Spaces | Dynamic ambient and display lighting for product showcases | Attracts customer attention, improves brand experience, enables flexible lighting schemes | High color fidelity, programmable RGB or addressable strips; ease of installation; energy efficiency; local compliance with electrical standards |
| Smart Building & Infrastructure | Intelligent lighting control for energy management and safety | Reduces energy costs, improves occupant comfort, enhances safety through adaptive lighting | Integration capability with building management systems; scalability; long lifespan; robust environmental ratings |
| Automotive & Transportation | Customizable interior and exterior lighting for vehicles | Enhances aesthetic appeal, improves visibility and safety, supports branding | Vibration-resistant, weatherproof LED strips; automotive-grade certifications; low power consumption; sourcing from reliable suppliers |
| Entertainment & Events | Stage and architectural lighting effects | Creates immersive environments, supports complex lighting sequences, increases event impact | High precision color control; fast response times; modular design for scalability; availability of technical support |
Manufacturing & Automation
In manufacturing environments across regions like Germany and Kenya, arduino LED strips serve as critical visual indicators on assembly lines and machinery. They provide instant status updates through color-coded signals, enabling operators to quickly identify issues or production phases. This reduces downtime and streamlines workflow management. For B2B buyers, sourcing LED strips with industrial-grade durability, high brightness, and compatibility with existing automation systems is essential, especially considering varying power standards and environmental conditions in different markets.
Retail & Commercial Spaces
Retailers in South America and the Middle East leverage arduino LED strips to create dynamic, programmable lighting that highlights products and enhances store ambiance. These LED strips allow flexible color schemes and animations that can be customized for promotions or branding events. Businesses benefit from increased foot traffic and enhanced customer engagement. Buyers should prioritize LED strips with excellent color accuracy, ease of integration with control systems, and compliance with local electrical safety standards to ensure seamless installation and operation.
Smart Building & Infrastructure
Smart buildings in Europe and Africa increasingly incorporate arduino-controlled LED strips for adaptive lighting solutions that optimize energy use and occupant comfort. These strips integrate with sensors and building management systems to adjust lighting based on occupancy or daylight levels, contributing to sustainability goals and operational cost savings. When sourcing for such applications, buyers must assess the scalability of solutions, environmental protection ratings (IP ratings), and compatibility with existing infrastructure to guarantee long-term performance.
Automotive & Transportation
In the automotive sector, especially in markets like Germany and the Middle East, arduino LED strips are used for customizable interior mood lighting and exterior accent lights that improve vehicle aesthetics and safety. These applications demand LED strips that can withstand vibrations, temperature extremes, and moisture exposure. B2B buyers should focus on automotive-grade certifications, robust build quality, and low power consumption to meet stringent industry requirements and ensure reliability in diverse climatic conditions.
Entertainment & Events
Event organizers and architectural firms in regions such as Europe and South America utilize arduino LED strips to deliver captivating stage effects and architectural lighting. These strips enable intricate lighting sequences and rapid color changes, enhancing audience experience and venue appeal. Key sourcing factors include precision in color control, fast response times, modularity for scalable installations, and access to technical support to manage complex lighting setups efficiently.
Related Video: How to use WS2812B RGB LED strip with Arduino | ws2811 ws2812 ws2813 ws2815 sk6812 sk9822 neopixel
Strategic Material Selection Guide for arduino led strip
When selecting materials for Arduino LED strips, B2B buyers must consider performance characteristics, manufacturing feasibility, and regional compliance standards. The choice of materials directly affects durability, cost-efficiency, and suitability for specific applications, especially in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Flexible PCB Substrate (Polyimide and PET)
Key Properties: Flexible PCBs for LED strips are commonly made from polyimide or polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyimide offers excellent thermal stability (up to 260°C), high flexibility, and good chemical resistance, while PET is less heat resistant (up to ~120°C) but more cost-effective and widely used for less demanding applications.
Pros & Cons: Polyimide substrates provide superior durability and flexibility, making them ideal for curved or dynamic installations. However, they come at a higher cost and require more advanced manufacturing processes. PET substrates are cheaper and easier to process but have lower temperature tolerance and mechanical strength.
Impact on Application: Polyimide-based strips are preferred for industrial or outdoor environments where temperature fluctuations and mechanical stress are common. PET is suitable for indoor decorative lighting where cost sensitivity is higher and environmental stress is minimal.
International Considerations: European buyers, especially in Germany, often require compliance with RoHS and REACH regulations, favoring polyimide for its reliability and environmental safety. African and South American markets may prioritize cost and availability, making PET an attractive option. Middle Eastern buyers should consider UV resistance and flame retardancy, often better met by polyimide substrates.
Silicone or PVC Coating (Encapsulation)
Key Properties: Silicone coatings provide excellent UV resistance, flexibility, and high-temperature tolerance (up to 200°C), while PVC coatings are more rigid, less UV resistant, and have a lower temperature threshold (~105°C).
Pros & Cons: Silicone encapsulation enhances water and dust resistance (IP65 and above), ideal for outdoor or humid environments, but increases cost and complexity. PVC coatings are economical and sufficient for indoor use but degrade faster under sunlight and heat.
Impact on Application: Silicone-coated strips are suitable for outdoor signage, architectural lighting, and harsh environments common in Middle Eastern deserts or tropical African climates. PVC-coated strips are best for indoor retail or residential applications in Europe and South America.
International Considerations: Buyers in regions with stringent fire safety standards (e.g., Europe’s DIN EN 13501) prefer flame-retardant silicone coatings. In contrast, markets in Africa and South America may focus on price and availability, often accepting PVC coatings with basic IP ratings.
Copper Traces (Conductive Material)
Key Properties: Copper is the standard conductive material in LED strips due to its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal management. Thickness varies (commonly 1 oz to 2 oz per square foot), impacting current capacity and heat dissipation.
Pros & Cons: Thicker copper traces improve durability and allow longer strips without voltage drop but increase material cost and weight. Thin copper traces reduce cost but limit strip length and increase risk of overheating.
Impact on Application: For large-scale installations like commercial lighting in Europe or South America, thicker copper traces ensure reliability and safety. In smaller or cost-sensitive projects typical in parts of Africa, thinner copper traces may be acceptable but require careful power management.
International Considerations: Compliance with ASTM B170 (standard for copper) and IPC standards is critical for European buyers. African and Middle Eastern buyers should verify copper purity and plating quality to avoid corrosion in humid or saline environments.
Adhesive Backing (Acrylic vs. Silicone Adhesives)
Key Properties: Adhesive backing secures LED strips to surfaces. Acrylic adhesives offer strong bonding and temperature resistance (-40°C to 150°C), while silicone adhesives provide superior flexibility and UV resistance but at higher cost.
Pros & Cons: Acrylic adhesives are cost-effective and widely used for indoor applications but may fail in high-UV or oily environments. Silicone adhesives excel outdoors and in industrial settings but increase product cost and complexity.
Impact on Application: Acrylic adhesives suit indoor retail or office environments common in Europe and South America. Silicone adhesives are preferred for outdoor installations in harsh climates like the Middle East or tropical Africa, where UV exposure and temperature extremes are concerns.
International Considerations: Buyers in Europe often require adhesives compliant with ISO 9001 quality management standards. African and South American buyers may prioritize ease of installation and cost, favoring acrylic adhesives unless specific environmental factors dictate otherwise.
| Material | Typical Use Case for arduino led strip | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyimide / PET PCB | Flexible circuit substrate for LED mounting | High thermal stability and flexibility (polyimide) | PET has lower heat resistance; polyimide is costly | PET: Low, Polyimide: High |
| Silicone / PVC Coating | Protective encapsulation for outdoor/indoor use | Silicone offers superior UV and water resistance | PVC less durable under UV and heat | PVC: Low, Silicone: High |
| Copper Traces | Electrical conduction and heat dissipation | Excellent conductivity and thermal management | Thicker copper increases cost and weight | Medium |
| Acrylic / Silicone Adhesive | Surface mounting of LED strips | Acrylic is cost-effective; Silicone offers UV resistance | Acrylic less durable outdoors; Silicone costly | Acrylic: Low, Silicone: Medium |
This guide assists international B2B buyers in balancing cost, durability, and compliance when sourcing Arduino LED strips, ensuring optimal material selection aligned with regional market demands and application environments.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for arduino led strip
Manufacturing Processes for Arduino LED Strips
The production of Arduino-compatible LED strips involves several critical stages designed to ensure functionality, durability, and compatibility with Arduino microcontrollers. Understanding these stages enables B2B buyers to assess supplier capabilities and product quality more effectively.
- Material Preparation
- PCB Substrate Selection: The manufacturing starts with selecting a flexible or rigid PCB substrate, commonly made from materials like polyimide or fiberglass. This substrate must support the electrical pathways and withstand environmental conditions.
- LED and Component Sourcing: High-quality LEDs (single-color, RGB, or addressable types like WS2812) and electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, and controllers are sourced, prioritizing suppliers with traceable certifications.
- Copper Foil Lamination: Copper layers are laminated onto the substrate to form conductive tracks, essential for powering and controlling the LEDs.
- Forming and Circuit Patterning
- Photolithography and Etching: Precise circuit patterns are created on the copper layer using photolithography, followed by chemical etching to remove excess copper, defining the electrical pathways.
- Solder Mask Application: A protective solder mask is applied to insulate the circuitry and prevent short circuits, while exposing pads for component placement.
- Silkscreen Printing: Identification marks and connection points are printed to aid assembly and future troubleshooting.
- Component Assembly
- Surface Mount Technology (SMT): Automated SMT machines place LEDs, resistors, and integrated circuits onto the PCB with high precision. This stage demands strict alignment to ensure proper function.
- Reflow Soldering: The assembled boards pass through reflow ovens where solder paste melts to create reliable electrical connections.
- Manual Inspection and Touch-Ups: In some cases, manual soldering or corrections are made, especially for complex or addressable LED strips.
- Finishing Processes
- Cutting and Shaping: LED strips are cut into standard lengths or custom sizes, ensuring clean edges and correct terminal placement.
- Encapsulation and Coating: To enhance durability and waterproofing, strips may be coated with silicone or epoxy resin, important for outdoor or industrial applications.
- Connector Attachment: Connectors compatible with Arduino systems, such as JST or screw terminals, are attached for easy integration.
Quality Assurance and Control (QA/QC) in Arduino LED Strip Manufacturing
B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers with robust QA/QC systems that comply with international and industry-specific standards to guarantee product reliability and safety.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This is the foundational quality management system standard, ensuring suppliers have consistent processes for product quality and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: Especially critical for buyers in Europe and those exporting there, CE compliance confirms conformity with EU safety, health, and environmental requirements.
- RoHS Compliance: Restricts hazardous substances in electronics, crucial for environmental and health safety, relevant globally.
- UL Certification: Though more common in North America, UL marks indicate rigorous electrical safety testing and are increasingly recognized worldwide.
- Industry-Specific Certifications: Depending on application, certifications such as API (for industrial automation) or IEC standards may apply.
Quality Control Checkpoints
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC):
- Verifying raw materials and components against specifications.
- Sampling LED batches for brightness, color consistency, and electrical parameters.
- Checking PCB substrate quality, copper thickness, and surface finish.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC):
- Monitoring solder paste application and component placement accuracy.
- Real-time inspection during reflow soldering to detect solder defects.
- Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) to identify misaligned or missing components.
- Functional testing of control ICs and circuitry during assembly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC):
- Electrical Testing: Verifying voltage, current draw, and signal integrity to ensure compatibility with Arduino control signals.
- Visual Inspection: Checking for physical defects, proper connector attachment, and adherence to design specifications.
- Environmental Testing: Including thermal cycling, humidity exposure, and vibration testing, especially for industrial or outdoor use cases.
- Functional Testing: Running programmed sequences to validate color accuracy, brightness, and response to control inputs.
Common Testing Methods for Arduino LED Strips
- Spectral Analysis: Measures color output and consistency across batches.
- Lumen Measurement: Ensures brightness meets specified levels.
- Electrical Safety Tests: Includes insulation resistance, dielectric strength, and grounding checks.
- Burn-in Testing: Operating strips continuously for extended periods to identify early-life failures.
- EMC Testing: Ensures electromagnetic compatibility, critical to avoid interference with other devices.
How B2B Buyers Can Verify Supplier Quality Control
- Factory Audits: Conduct on-site or third-party audits focusing on manufacturing processes, equipment, and quality management systems.
- Review of QC Documentation: Request and analyze inspection reports, material certificates, and test result summaries.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent agencies for random sampling and testing before shipment, providing unbiased quality assurance.
- Sample Evaluation: Obtain pre-production and final product samples for in-house testing aligned with buyer requirements.
- Supplier Certifications: Verify authenticity and currency of ISO, CE, RoHS, and other relevant certificates.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
-
Africa and South America: Buyers in these regions should ensure suppliers provide documentation aligned with local import regulations and standards, which may vary or lag behind international norms. Paying attention to environmental and safety certifications can ease customs clearance and market acceptance.
-
Middle East: Compliance with GCC standards and sometimes additional safety certifications is often required. Buyers should clarify these requirements upfront and verify supplier familiarity.
-
Europe (e.g., Germany): European buyers demand strict adherence to CE and RoHS directives. Germany, with its rigorous quality expectations, may require additional documentation such as TÜV certifications or compliance with REACH regulations. Traceability and supplier transparency are critical.
-
Cross-Regional Considerations: International B2B buyers should clarify warranty terms, post-sale support, and availability of technical documentation like datasheets and programming guides. Language and communication clarity are vital for smooth collaboration.
Summary for B2B Buyers
Selecting a supplier with a transparent, well-documented manufacturing and QC process is essential for sourcing Arduino LED strips that meet both functional and regulatory demands. Buyers should prioritize partners who:
- Employ automated and manual QC measures at multiple production stages.
- Hold internationally recognized certifications and comply with regional standards.
- Facilitate comprehensive supplier audits and third-party inspections.
- Provide detailed test reports and support traceability from raw materials to finished goods.
This strategic approach mitigates risks, ensures product reliability, and supports successful integration into diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Related Video: How to make a sound reactive RGB LED strip with Arduino
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for arduino led strip Sourcing
Cost Components in Arduino LED Strip Sourcing
When sourcing Arduino-compatible LED strips for B2B purposes, understanding the underlying cost structure is crucial to making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
- Materials: This covers the LED diodes (single color, RGB, or addressable types), flexible PCB substrates, resistors, MOSFETs/transistors for control, power connectors, and protective coatings. High-quality LEDs and PCBs significantly affect durability and brightness, impacting costs.
- Labor: Skilled labor is required for assembly, soldering, and testing. Labor costs vary greatly by country and factory sophistication, influencing final pricing.
- Manufacturing Overhead: Includes factory utilities, equipment depreciation, and indirect labor costs. Efficient factories with automated lines can reduce overhead per unit.
- Tooling: Custom tooling for PCB assembly and testing jigs adds upfront costs, especially for specialized or custom LED strip designs.
- Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes, including functional testing, burn-in testing, and certification checks, add to production costs but ensure reliability—vital for B2B buyers.
- Logistics: Shipping, customs duties, and insurance costs impact landed price. International freight modes (air vs. sea) and packaging standards also play a role.
- Supplier Margin: Manufacturers and distributors include a margin to cover profit and risk.
Key Price Influencers for Arduino LED Strips
Several factors influence the pricing of Arduino LED strips in the B2B supply chain:
- Order Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically attract volume discounts, reducing unit cost. However, MOQ requirements can be challenging for smaller buyers in emerging markets.
- Specifications and Customization: Custom lengths, specific LED densities (e.g., LEDs per meter), color configurations (RGB vs. RGBW), and special features (waterproofing, addressable chips) increase complexity and price.
- Material Quality and Certifications: LED strips with certified components (e.g., RoHS, CE, UL) command higher prices but offer better compliance and reliability, important for European and Middle Eastern markets.
- Supplier Reputation and Location: Established suppliers with proven quality records may charge premiums but reduce risks. Proximity to buyer markets (e.g., European suppliers for Germany) can reduce logistics costs.
- Incoterms and Payment Terms: Prices vary depending on shipping terms (FOB, CIF, DDP). Buyers must account for customs clearance and local taxes under certain terms.
Strategic Buyer Tips for International B2B Procurement
International buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should adopt strategic approaches to optimize costs and value:
- Negotiate Beyond Price: Leverage volume commitments or longer contract terms to negotiate better tooling amortization, improved payment terms, or bundled shipping discounts.
- Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not only the unit price but also shipping duration, customs fees, after-sales support, and warranty services. For example, Kenyan buyers may prefer suppliers with local distribution hubs to minimize delays and import costs.
- Request Samples and Certifications: Insist on product samples and relevant certifications to verify quality and compliance before bulk ordering.
- Assess Supplier Flexibility: Suppliers able to accommodate customization requests with minimal tooling charges add value, especially for projects requiring unique LED configurations.
- Understand Pricing Nuances: Recognize that low-cost suppliers may compromise on QC or material quality, leading to higher failure rates and replacement costs.
- Optimize Logistics: Collaborate with suppliers to choose cost-effective shipping routes and consolidated shipments to reduce freight expenses and customs complexities.
Indicative Pricing Disclaimer
Prices for Arduino LED strips vary widely based on type, quality, and order size. As a rough benchmark, basic single-color strips may start around $1–$3 per meter, while addressable RGB strips range from $5 to $15 per meter. Custom or certified products command higher prices. These figures are indicative and subject to market fluctuations, supplier policies, and geopolitical factors affecting supply chains.
By thoroughly analyzing cost components and pricing influencers while applying strategic procurement practices, international B2B buyers can secure Arduino LED strips that balance cost-efficiency with quality and reliability tailored to their regional market needs.
Spotlight on Potential arduino led strip Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘arduino led strip’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for arduino led strip
Critical Technical Properties for Arduino LED Strips
1. Voltage Rating
Arduino LED strips typically operate at 5V or 12V. This rating is crucial because it determines the compatibility with power supplies and Arduino boards. For international buyers, selecting the correct voltage ensures safety, energy efficiency, and reduces the risk of damage during installation.
2. Current Consumption and Power Rating
Current rating (measured in amperes) per LED or per meter impacts the overall power supply requirements. Higher current demands necessitate robust power sources and often external drivers or MOSFETs. Understanding current consumption helps buyers plan for reliable, scalable installations without overloading circuits.
3. LED Density (LEDs per Meter)
This refers to how many LEDs are embedded per meter of the strip, influencing brightness and visual effect. Higher density strips offer smoother lighting but require more power. Buyers must balance LED density with project needs, cost, and power infrastructure, especially for large-scale deployments.
4. Control Protocol and Compatibility
LED strips may be simple (single color or RGB controlled by PWM) or addressable (each LED individually controllable via protocols like WS2812 or Neopixel). For B2B clients, choosing the right control protocol affects software integration complexity, hardware compatibility, and end-user customization potential.
5. Material Quality and IP Rating
The substrate material and protective coating impact durability, flexibility, and environmental resistance. An IP (Ingress Protection) rating, such as IP65 or IP67, indicates water and dust resistance, vital for outdoor or industrial applications. Buyers targeting diverse markets like Africa or the Middle East should prioritize IP-rated strips for harsher environments.
6. Color Rendering Index (CRI) and Brightness (Lumens)
CRI measures the accuracy of color reproduction, while brightness in lumens indicates light intensity. High CRI strips are essential for applications requiring true color display, such as retail or art installations. Understanding these specs helps buyers meet client expectations in varied sectors.
Key Industry and Trade Terminology for Arduino LED Strip Procurement
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce LED strips or components which other brands repackage or customize. B2B buyers can leverage OEM partnerships for cost-effective, tailored products, ensuring exclusivity or branding advantages in local markets.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest amount a supplier is willing to sell. MOQs vary widely and impact inventory costs and cash flow. Buyers from emerging markets like Kenya or South America should negotiate MOQs carefully to avoid overstocking while ensuring supply continuity.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal document buyers send to suppliers to obtain price quotes and product details. RFQs help compare multiple vendors, clarify specifications, and secure competitive pricing. Properly structured RFQs reduce misunderstandings and speed up procurement cycles.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms defining responsibilities and risks between buyers and sellers in international shipping. Common Incoterms include FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight). Understanding these terms enables buyers to negotiate better delivery conditions and control logistics costs.
Lead Time
The period between placing an order and receiving the goods. Lead time influences project scheduling and inventory management. Buyers must factor in longer lead times due to customs, shipping routes, or supplier capacity, especially when importing to regions with complex logistics.
PCB (Printed Circuit Board)
The flexible or rigid board on which LEDs and electronic components are mounted. PCB quality affects strip flexibility, heat dissipation, and lifespan. Buyers should verify PCB material and thickness to ensure product reliability for their intended application.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms empowers international B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions, optimize supply chains, and tailor products to regional market demands effectively.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the arduino led strip Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The Arduino LED strip sector is experiencing robust growth driven by increasing demand for customizable, energy-efficient lighting solutions across diverse industries. Globally, the integration of Arduino microcontrollers with LED strips has unlocked new opportunities in smart lighting, architectural design, automotive, entertainment, and advertising sectors. For international B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets like Africa (e.g., Kenya), South America, and the Middle East, this represents a gateway to innovative, affordable technology that supports local manufacturing, prototyping, and IoT-enabled applications.
Key market dynamics include a growing preference for addressable LED strips, which allow individual control of LEDs for sophisticated lighting effects. This trend is particularly strong in Europe (Germany) and the Middle East, where demand for advanced control systems and integration with smart home or industrial automation solutions is rising. Voltage and power efficiency remain critical selection criteria, as buyers seek strips compatible with 5V, 12V, or 24V systems that balance brightness and energy consumption.
Sourcing trends emphasize modularity and scalability. Suppliers offering flexible quantities, custom lengths, and pre-programmed Arduino-compatible modules are gaining favor. African and South American buyers increasingly prioritize suppliers with regional warehouses or distribution centers to reduce lead times and shipping costs. Additionally, the rise of online B2B marketplaces facilitates direct sourcing from manufacturers, empowering buyers to negotiate for tailored solutions and technical support.
Technological advancements such as integration with wireless communication (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth) and compatibility with open-source software ecosystems are shaping procurement decisions. Buyers are also influenced by the growing availability of plug-and-play kits that simplify installation and programming, reducing technical barriers and accelerating time-to-market.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a decisive factor for B2B buyers in the Arduino LED strip sector. The environmental impact of electronic components, including LED strips, is a growing concern as global supply chains face scrutiny over resource extraction, manufacturing emissions, and end-of-life disposal. International buyers, particularly in Europe and progressive markets in Africa and the Middle East, are demanding eco-friendly products that comply with stringent environmental regulations such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive).
Ethical sourcing is equally critical. Buyers are seeking suppliers who demonstrate transparency in their supply chains, ensuring conflict-free sourcing of raw materials such as rare earth elements used in LEDs. Certifications like ISO 14001 (environmental management) and adherence to fair labor practices are increasingly viewed as prerequisites for long-term partnerships.
From a materials perspective, “green” LED strips incorporate recyclable substrates, low-toxicity solder, and energy-efficient LEDs that reduce power consumption without compromising performance. Some manufacturers now offer biodegradable packaging and promote take-back programs to facilitate recycling of used strips and electronic waste.
For buyers in regions with developing environmental policies, such as parts of South America and Africa, partnering with suppliers who prioritize sustainability can enhance corporate social responsibility profiles and align with international standards, improving access to global markets.
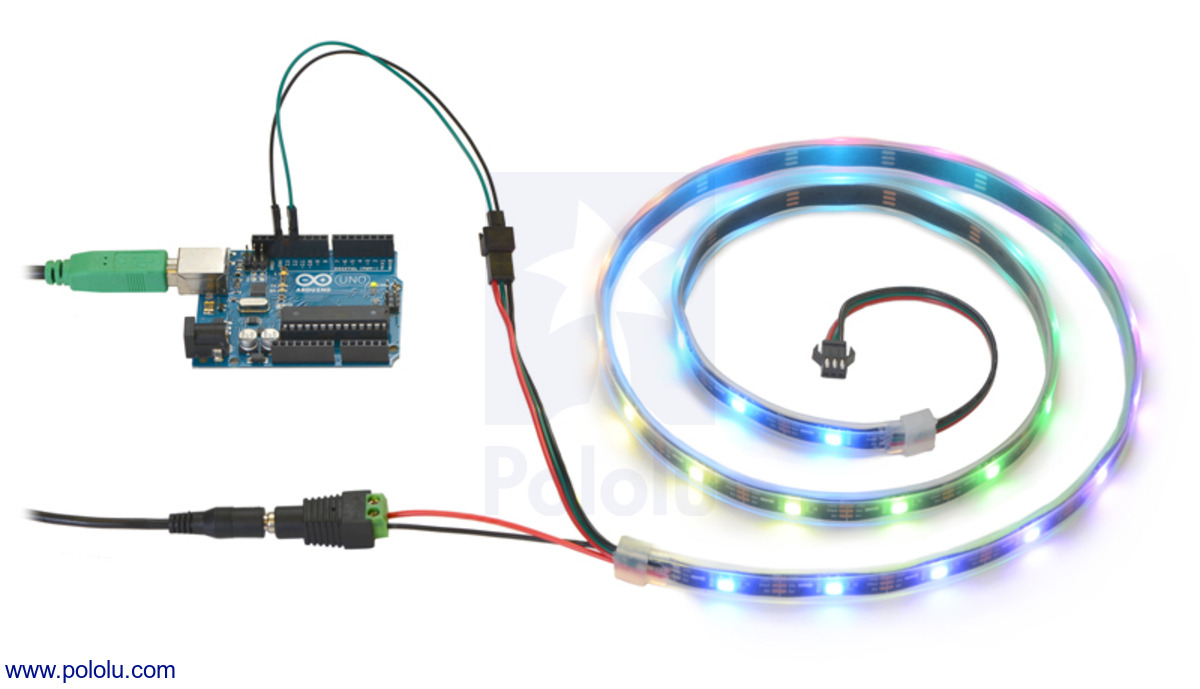
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Evolution and Historical Context
The Arduino LED strip sector has evolved significantly since the early 2010s, when LED strips were primarily simple, single-color lighting elements controlled by basic circuits. The introduction of Arduino microcontrollers revolutionized the market by enabling programmable, interactive lighting with relatively low technical complexity. This democratization of control technology opened doors for hobbyists and professionals alike to create dynamic lighting projects.
Over time, the sector has expanded from basic RGB strips to addressable LEDs like WS2812 and Neopixel, which allow individual LED control for complex animations and effects. This evolution has been fueled by advancements in microcontroller performance, software libraries, and open-source communities that provide extensive resources for customization.
For B2B buyers, understanding this progression is essential to selecting the right products that balance cost, functionality, and integration capabilities. It also highlights the importance of sourcing from suppliers who stay abreast of technological innovations and offer support for the latest Arduino-compatible LED strip solutions.
Related Video: Beginner’s Guide to Using LED Strips with Arduino
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of arduino led strip
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers of Arduino LED strips for international B2B transactions?
To vet suppliers, start by verifying their business licenses and certifications relevant to electronics manufacturing, such as ISO 9001 or CE marking. Request product samples to assess quality firsthand. Check for established export experience, especially in your region (Africa, South America, Middle East, Europe), and review references or client testimonials. Utilize platforms with verified supplier programs and conduct due diligence through third-party inspections or audits. Clear communication about technical specifications and after-sales support is critical to ensure the supplier aligns with your project and compliance needs. -
Is customization of Arduino LED strips feasible for bulk orders, and what should buyers consider?
Yes, customization is common and includes LED color configurations, strip length, voltage, and control protocols (e.g., addressable LEDs). When negotiating customization, clarify minimum order quantities (MOQs), lead times, and any tooling or design fees. Ensure the supplier can provide detailed technical drawings and prototype samples for approval. For international buyers, confirm that customized products meet local electrical and safety standards to avoid import issues. Early communication about firmware or control software customization can also optimize integration into your systems. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for Arduino LED strip orders?
MOQs vary widely based on customization, supplier capacity, and LED strip type. Standard off-the-shelf products may have low MOQs (e.g., 100-500 units), while customized orders often require larger commitments (1,000+ units). Lead times typically range from 3 to 8 weeks, influenced by order complexity, component availability, and shipping method. For buyers in Africa or South America, factor in additional time for customs clearance. Negotiate clear lead times and penalties for delays in contracts to safeguard your supply chain. -
What payment terms are standard when importing Arduino LED strips, and how can buyers minimize risks?
Common payment terms include 30% upfront deposit with balance paid upon shipment or delivery. Letters of Credit (LC) are preferred for large orders as they offer bank-backed payment security. For new suppliers, consider escrow services or smaller trial orders to reduce exposure. Always confirm payment methods accepted (T/T, PayPal, LC) and avoid full prepayments without verified supplier credibility. Use clear contracts stipulating quality standards and delivery timelines to support dispute resolution if needed.
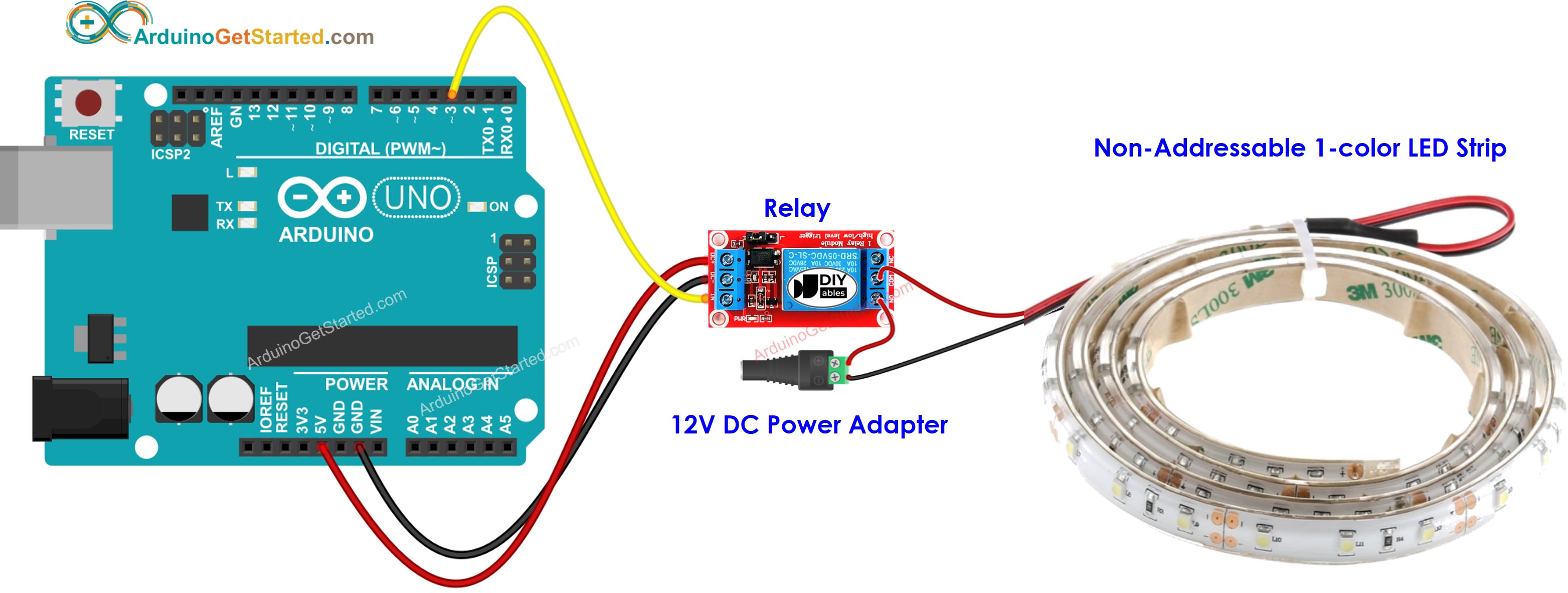
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Which quality assurance certifications should buyers look for in Arduino LED strip suppliers?
Key certifications include ISO 9001 for quality management, CE marking for European market compliance, RoHS for hazardous substances restriction, and FCC for electromagnetic compatibility. For buyers in Africa or the Middle East, check if suppliers meet local regulatory requirements or can provide test reports from accredited labs. Request batch-level quality inspection reports and inquire about in-line testing during production. Quality certifications not only ensure product safety but also facilitate smoother customs clearance and reduce liability risks. -
How should international buyers handle logistics and shipping for Arduino LED strips?
Choose logistics partners experienced in handling electronic components to minimize damage risks. For high-volume orders, sea freight is cost-effective but slower, typically 4-6 weeks transit. Air freight suits urgent deliveries but at a higher cost. Ensure proper packaging with anti-static materials and moisture barriers. Confirm Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) clearly in contracts to define responsibility for shipping costs and risks. For buyers in remote regions, plan for customs brokerage and local delivery delays. Tracking and insurance are essential to safeguard your shipment. -
What are common causes of disputes in Arduino LED strip B2B transactions, and how can buyers prevent them?
Disputes often arise from quality discrepancies, delayed shipments, unclear specifications, and payment disagreements. To prevent these, establish detailed contracts specifying technical requirements, inspection procedures, delivery schedules, and penalties for non-compliance. Maintain documented communication and confirm all customizations in writing. Employ third-party quality inspections before shipment and use secure payment methods. In case of disputes, a clear escalation path and arbitration clause can facilitate resolution without disrupting your supply chain. -
Are there specific considerations for buyers in regions like Germany or Kenya when sourcing Arduino LED strips?
Yes, buyers in Germany must comply with stringent EU regulations such as CE marking, RoHS, and WEEE directives, impacting product acceptance and disposal. Kenyan buyers should verify product certifications recognized by the Kenya Bureau of Standards (KEBS) and anticipate longer customs clearance times. Both markets benefit from suppliers who understand local voltage standards and provide clear documentation in English or local languages. Partnering with suppliers offering local after-sales support or regional warehouses can significantly improve service levels and reduce lead times.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for arduino led strip
Strategic sourcing of Arduino LED strips offers international B2B buyers a unique opportunity to leverage innovation, cost-efficiency, and customization in their product offerings. Key considerations include selecting suppliers who provide diverse LED strip types—such as RGB, RGBW, and addressable LEDs—with reliable power compatibility and quality assurance. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize partners with strong technical support and scalable manufacturing capabilities to accommodate evolving project demands.
Essential takeaways for effective sourcing:
- Supplier vetting: Assess manufacturers’ experience with Arduino-compatible LED strips and their adherence to international quality standards.
- Customization flexibility: Opt for suppliers offering tailored solutions that meet specific voltage, length, and control method requirements.
- Logistics and compliance: Ensure smooth import/export processes by understanding regional certifications and supply chain efficiency, especially for markets like Kenya and Germany.
- After-sales support: Partner with vendors providing comprehensive technical guidance and warranty services to mitigate risks.
Looking ahead, the integration of Arduino LED strips into smart lighting and IoT applications will continue to accelerate, creating new avenues for differentiation and value creation. International buyers are encouraged to adopt a strategic sourcing approach—balancing innovation, quality, and cost—to secure competitive advantage in dynamic markets. Establishing strong supplier relationships now will pave the way for future growth and technology adoption across diverse regions.

