Guide to Thin Led Light Strips
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for thin led light strips
- Understanding thin led light strips Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of thin led light strips
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for thin led light strips
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for thin led light strips
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for thin led light strips Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential thin led light strips Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for thin led light strips
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the thin led light strips Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of thin led light strips
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for thin led light strips
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for thin led light strips
Thin LED light strips have emerged as a pivotal lighting solution across diverse industries, combining cutting-edge technology with sleek, space-saving design. For international B2B buyers, especially those operating in dynamic markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Turkey and Spain—understanding the nuances of thin LED strip sourcing is essential for competitive advantage. These versatile lighting components not only enhance aesthetic appeal but also deliver superior energy efficiency and adaptability in commercial, residential, and industrial projects.
This guide offers a comprehensive roadmap tailored to the needs of global buyers seeking to optimize procurement strategies. It covers the full spectrum of critical topics: from the various types and technical specifications of thin LED strips, through insights into material quality and manufacturing processes, to rigorous quality control standards that ensure product reliability. Buyers will gain clarity on evaluating suppliers, navigating cost structures, and leveraging market trends to secure the best value.
Moreover, the guide addresses region-specific considerations, such as compliance with international certifications and logistical factors impacting import and distribution. A dedicated FAQ section further equips buyers to make informed, confident decisions amid a rapidly evolving marketplace.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
By consolidating expert knowledge and actionable insights, this resource empowers businesses to identify trusted partners, mitigate risks, and harness the full potential of thin LED light strips for scalable, innovative lighting solutions worldwide.
Understanding thin led light strips Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ultra-Thin Flexible LED Strips | Extremely slim profile (often <5mm wide), flexible PCB for curved surfaces | Architectural lighting, retail displays, automotive interiors | Pros: Highly adaptable, easy installation in tight spaces; Cons: Lower heat dissipation, may require careful handling |
| Waterproof Thin LED Strips | Thin strips with silicone or epoxy coating for water resistance | Outdoor signage, marine applications, hospitality venues | Pros: Durable in humid/wet environments; Cons: Slightly higher cost, reduced flexibility due to coating |
| High-Density Thin LED Strips | High LED count per meter on a narrow strip for intense brightness | Commercial lighting, film and photography, task lighting | Pros: Superior brightness and uniformity; Cons: Increased power consumption, higher purchase price |
| RGB & Addressable Thin LED Strips | Thin strips with color-changing LEDs and programmable controls | Event production, advertising, entertainment venues | Pros: Customizable colors and effects, enhances customer engagement; Cons: Requires controllers and technical know-how |
| Rigid Thin LED Bars | Slim, rigid structure with LEDs mounted on solid PCB | Under-cabinet lighting, display cases, industrial workstations | Pros: Stable mounting, consistent light output; Cons: Less flexible, installation limited to flat surfaces |
Ultra-Thin Flexible LED Strips
Ultra-thin flexible LED strips are prized for their minimal profile and adaptability, often measuring less than 5mm in width. Their flexible PCB allows installation on curved or irregular surfaces, making them ideal for architectural accents, retail fixtures, and automotive interiors. B2B buyers should assess project requirements carefully, as these strips have limited heat dissipation and may be more fragile during handling and installation. Sourcing from reputable suppliers ensures quality adhesives and durable components, critical for long-term performance in demanding environments.
Waterproof Thin LED Strips
Designed with protective silicone or epoxy coatings, waterproof thin LED strips are essential for outdoor or moisture-prone environments. Their slim form factor combined with water resistance makes them suitable for outdoor signage, hospitality settings, and marine applications. When procuring these strips, B2B buyers must verify the IP rating (commonly IP65 or higher) and ensure compatibility with local environmental standards. Though slightly more expensive than non-waterproof variants, the durability and reduced maintenance costs often justify the investment.
High-Density Thin LED Strips
High-density thin LED strips feature a greater number of LEDs per meter on a narrow PCB, offering intense, uniform brightness critical for commercial and task lighting applications. These strips are excellent for environments requiring high illumination levels, such as film sets, retail displays, and precision workstations. Buyers should consider the increased power requirements and ensure their electrical infrastructure supports the load. Bulk purchasing from suppliers offering consistent quality and warranty coverage is advisable to maintain performance across large-scale installations.
RGB & Addressable Thin LED Strips
RGB and addressable thin LED strips provide dynamic, programmable lighting effects through integrated controllers. Their thin design enables seamless integration into event production, advertising, and entertainment venues where visual impact drives customer engagement. For B2B buyers, it is crucial to source complete systems including compatible controllers and software, as well as technical support for installation and programming. The complexity of these strips demands careful planning but offers a significant competitive edge in experiential lighting solutions.
Rigid Thin LED Bars
Rigid thin LED bars combine a slim profile with a solid PCB, offering stable mounting and consistent light output. These are preferred for under-cabinet lighting, retail display cases, and industrial workstations where durability and precise illumination are priorities. While less flexible than strip variants, their robustness suits applications requiring fixed, flat installations. Buyers should evaluate mounting options and ensure the bars meet local electrical safety certifications. Sourcing from manufacturers with proven quality control processes reduces the risk of premature failure and supports long-term project success.
Related Video: Beginner’s Guide to Using LED Strips with Arduino
Key Industrial Applications of thin led light strips
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of thin led light strips | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail & Visual Merchandising | Accent lighting for product displays and shelves | Enhances product visibility and attractiveness, driving sales | Customizable length/color, dimmable options, consistent color rendering |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Interior ambient lighting in vehicle cabins | Improves user experience and modernizes vehicle interiors | High durability, temperature resistance, compliance with automotive standards |
| Architecture & Interior Design | Cove lighting and intricate architectural details | Provides sleek, energy-efficient illumination with minimal space | Flexible PCB quality, adhesive strength for varied surfaces, waterproof options |
| Electronics & Device Manufacturing | Backlighting for control panels and indicators | Enables compact design and clear visibility in tight spaces | Ultra-thin profile, high brightness, low heat emission |
| Hospitality & Event Management | Dynamic mood lighting for hotels, restaurants, and venues | Creates customizable atmospheres, enhancing customer experience | RGB capabilities, easy installation, compatibility with control systems |
Retail & Visual Merchandising
Thin LED light strips are widely used in retail environments to provide subtle yet effective accent lighting on shelves and display cases. Their slim profile allows installation in tight spaces without obstructing product visibility. For international B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets like Africa and South America, sourcing strips with consistent color rendering and dimmability is crucial to maintain a premium presentation that appeals to diverse consumer bases. Custom lengths and easy installation reduce labor costs and improve scalability for large retail chains.
Automotive Manufacturing
In automotive production, thin LED strips serve as ambient lighting within vehicle interiors, creating a modern and luxurious feel. These strips must withstand temperature fluctuations and vibrations common in vehicles, making durability and compliance with automotive quality standards essential. Buyers in regions such as the Middle East and Europe should prioritize suppliers offering automotive-grade certifications and robust testing to ensure long-term reliability and safety compliance.
Architecture & Interior Design
Architectural projects benefit from the flexibility of thin LED strips to illuminate coves, recesses, and other intricate design elements without bulky fixtures. Their low-profile design enables seamless integration into ceilings and walls. For international architects and contractors in countries like Turkey and Spain, sourcing options with strong adhesive backing and waterproof ratings is important to accommodate different environmental conditions, including humid or outdoor settings.
Electronics & Device Manufacturing
Thin LED strips are integral to backlighting control panels, instrument clusters, and electronic devices where space is limited. Their ultra-thin form factor allows manufacturers to design compact products without sacrificing visibility or brightness. B2B buyers should seek strips with low heat output to protect sensitive electronics, and high luminous efficacy to ensure clear, uniform illumination in various industrial applications.
Hospitality & Event Management
Hotels, restaurants, and event venues leverage thin LED strips for dynamic mood lighting that can be customized for different occasions. RGB and color-changing capabilities allow businesses to create immersive atmospheres that enhance guest experience. International buyers should focus on suppliers providing compatibility with popular lighting control systems, ease of installation, and durable materials to withstand frequent use and varied environmental conditions. This is particularly relevant for expanding hospitality markets in Africa and South America.
Related Video: LED – Light Emitting Diode | Basics, Characteristics, Working & Applications | LED Vs PN Diode
Strategic Material Selection Guide for thin led light strips
When selecting materials for thin LED light strips, international B2B buyers must consider factors such as durability, thermal management, flexibility, environmental resistance, and compliance with regional standards. The choice of materials directly influences the product’s performance, lifespan, and suitability for specific applications, especially in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Below is an analysis of four common materials integral to thin LED strip construction: the PCB substrate, LED chip encapsulant, adhesive backing, and protective coating.
1. Flexible PCB Substrate (Polyimide vs. PET)
Key Properties:
Flexible PCBs used in thin LED strips are typically made from polyimide or polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyimide offers excellent heat resistance (up to ~260°C), high tensile strength, and chemical stability, making it ideal for high-performance strips. PET substrates are more cost-effective but have lower thermal tolerance (~130°C) and mechanical strength.
Pros & Cons:
– Polyimide: Superior thermal stability ensures longer LED lifespan by efficiently dissipating heat. It supports complex bending and installation in tight spaces. However, it is more expensive and may increase manufacturing complexity.
– PET: Lower cost and easier to handle in mass production, but less durable under high temperatures and prone to deformation over time.
Impact on Application:
Polyimide-based PCBs are preferred for commercial and industrial lighting applications requiring long-term reliability and heat resistance, such as architectural lighting in warm climates (Middle East, Africa). PET substrates suit decorative or short-term installations where cost is a priority, common in retail or residential projects in South America and parts of Europe.
B2B Considerations:
Buyers in regions with high ambient temperatures should prioritize polyimide substrates to avoid premature failure. Compliance with international standards like IPC-4101 (for flexible PCBs) and local certifications (CE in Europe, INMETRO in Brazil) is essential. Suppliers offering certifications and traceability for PCB materials can facilitate smoother customs clearance and quality assurance.
2. LED Chip Encapsulant (Silicone vs. Epoxy)
Key Properties:
Encapsulants protect LED chips from moisture, dust, and mechanical damage. Silicone encapsulants provide excellent UV resistance, flexibility, and operate well across a wide temperature range (-40°C to 200°C). Epoxy resins are rigid, less expensive, but more susceptible to yellowing and cracking under UV exposure.
Pros & Cons:
– Silicone: Enhances LED longevity and color stability, especially in outdoor or high-UV environments. Higher material cost and more complex curing process.
– Epoxy: Cost-effective and easier to process, but limited outdoor durability and potential for reduced light output over time due to yellowing.
Impact on Application:
Silicone encapsulants are ideal for outdoor or industrial LED strips exposed to harsh environments, such as street lighting or signage in Middle Eastern deserts or African coastal areas. Epoxy encapsulants are suitable for indoor applications with controlled environments, such as office or retail lighting in Europe and South America.
B2B Considerations:
Buyers should verify encapsulant type to match environmental conditions and ensure compliance with RoHS and REACH regulations prevalent in European markets. For regions with high UV exposure, silicone encapsulated LEDs reduce maintenance costs and enhance customer satisfaction.
3. Adhesive Backing (Acrylic vs. Rubber-Based)
Key Properties:
Adhesives secure LED strips during installation and must maintain adhesion under temperature fluctuations and humidity. Acrylic adhesives offer strong bonding, UV resistance, and durability. Rubber-based adhesives provide good initial tack but degrade faster under heat and UV exposure.
Pros & Cons:
– Acrylic: Long-lasting adhesion, suitable for outdoor and industrial applications. Slightly higher cost and may require more careful surface preparation.
– Rubber-Based: Lower cost and easier repositioning during installation but prone to peeling and residue build-up over time.
Impact on Application:
Acrylic adhesives are preferred for permanent installations in environments with temperature extremes or outdoor exposure, common in Middle Eastern and African markets. Rubber-based adhesives are often used for temporary or indoor applications, such as event lighting or retail displays in Europe and South America.
B2B Considerations:
International buyers should assess adhesive performance relative to local climate conditions. Certifications like UL 969 (for adhesives) and compliance with ASTM D3330 (adhesion testing) can guide quality assurance. Suppliers offering customized adhesive solutions can add value for specialized projects.
4. Protective Coating (Silicone, Polyurethane, or None)
Key Properties:
Protective coatings shield LED strips from moisture, dust, and mechanical wear. Silicone coatings provide excellent flexibility and weather resistance. Polyurethane coatings offer superior abrasion resistance but are less flexible. Some LED strips are sold without coatings for indoor use only.
Pros & Cons:
– Silicone Coating: Ideal for outdoor and humid environments, maintains flexibility and transparency. Higher cost and slightly thicker profile.
– Polyurethane Coating: Robust against physical damage but can crack if bent repeatedly.
– No Coating: Lowest cost and simplest manufacturing but vulnerable to damage and environmental factors.
Impact on Application:
Silicone-coated strips are favored for outdoor architectural lighting and signage in regions with high humidity or dust, such as coastal South America and Middle East. Polyurethane coatings suit industrial indoor environments requiring abrasion resistance. Uncoated strips are best for dry, controlled indoor settings.
B2B Considerations:
Buyers must consider IP ratings (e.g., IP65 or higher) when selecting coated strips for outdoor use. Compliance with IEC 60529 standards and local environmental regulations is critical. Offering product variants with different coatings allows suppliers to cater to diverse market needs.
| Material | Typical Use Case for thin led light strips | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flexible PCB (Polyimide) | High-performance, heat-resistant indoor/outdoor lighting | Excellent heat dissipation and flexibility | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Flexible PCB (PET) | Cost-sensitive indoor decorative lighting | Low cost and easy processing | Lower heat tolerance and mechanical durability | Low |
| LED Chip Encapsulant (Silicone) | Outdoor, high-UV, and industrial applications | UV resistant, flexible, long lifespan | More expensive and complex curing process | High |
| LED Chip Encapsulant (Epoxy) | Indoor, controlled environment applications | Cost-effective |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for thin led light strips
Manufacturing Processes for Thin LED Light Strips
The production of thin LED light strips involves a series of precise and interrelated steps designed to ensure flexibility, durability, and optimal lighting performance. For B2B buyers targeting diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these manufacturing stages is crucial for selecting reliable suppliers and ensuring product consistency.
1. Material Preparation
The foundation of any thin LED strip is the selection and preparation of high-quality raw materials:
- LED Chips: Premium semiconductor chips sourced from reputable manufacturers determine brightness, energy efficiency, and lifespan. Buyers should confirm chip brands and specifications to match project requirements.
- Printed Circuit Board (PCB): Thin LED strips typically use flexible PCBs made from polyimide or PET substrates, offering bendability without compromising electrical integrity. The PCB thickness is often less than 1 mm for thin profiles.
- Adhesive Backing: High-grade, heat-resistant adhesive tapes (usually 3M or equivalent) are prepared to ensure strong adhesion on various surfaces while resisting peeling or degradation over time.
- Protective Coatings: Depending on application, materials such as silicone or epoxy resin may be prepared for waterproofing and mechanical protection.
2. PCB Fabrication and Forming
- Circuit Patterning: The flexible PCB undergoes photolithography or screen-printing to create copper circuit paths tailored for thin strip dimensions.
- Surface Treatment: Copper traces receive surface finishing (e.g., ENIG or HASL) to improve solderability and corrosion resistance.
- Cutting and Shaping: PCBs are cut to narrow widths, sometimes as slim as 5-8 mm, using precision laser or die-cutting techniques to maintain uniformity and prevent damage.
3. LED Mounting and Assembly
- Soldering LED Chips: Automated Surface Mount Technology (SMT) machines place and solder tiny LED chips onto the PCB pads with micron-level accuracy. This stage demands strict control to avoid heat damage to thin substrates.
- Component Placement: Additional components such as resistors, capacitors, or IC controllers (for RGB or dimmable strips) are mounted simultaneously.
- Adhesive Application: The prepared adhesive backing is laminated onto the PCB, ensuring even pressure and alignment to maintain strip flexibility.
- Encapsulation (Optional): For waterproof or dustproof models, a thin silicone or epoxy layer is applied over the LED assembly, cured under controlled conditions to preserve thinness.
4. Finishing and Packaging
- Cut-to-Length and Connector Attachment: Strips are cut into standard or customized lengths with precision scoring. Connectors or solder pads are attached for easy integration.
- Labeling and Branding: Quality manufacturers print batch codes, voltage ratings, and branding directly on the strip or packaging.
- Protective Packaging: Thin LED strips are carefully coiled and packaged in anti-static bags with cushioning to avoid bending stress during transit.
Quality Assurance: Standards and Testing for Thin LED Light Strips
Robust quality assurance (QA) frameworks are vital for B2B buyers to ensure the LED strips meet international safety, performance, and durability standards. This is especially critical when supplying markets with diverse regulatory requirements like the EU, Middle East, and emerging economies in Africa and South America.
Relevant International and Industry Standards
- ISO 9001: This global standard for quality management systems ensures manufacturers maintain consistent production processes and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: Mandatory for products sold within the European Economic Area, CE certification verifies conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- RoHS Compliance: Restricts hazardous substances (like lead and mercury) in electrical products, essential for Europe and increasingly adopted worldwide.
- UL Certification: Recognized mainly in North America but valued globally, UL tests electrical safety and fire hazards.
- IEC Standards: Cover performance and safety for LED lighting products, often referenced in Middle Eastern and South American markets.
- API or Local Certifications: Certain countries may require additional certifications or approvals for electrical goods, which buyers should verify with suppliers.
Key Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control in LED strip manufacturing is typically segmented into three critical inspection stages:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials including LED chips, PCBs, adhesives, and coatings undergo inspection for specifications, supplier documentation, and defect rates before entering production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during assembly, including solder joint integrity, LED placement accuracy, and adhesive application uniformity. Automated optical inspection (AOI) systems are common at this stage.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Completed strips are tested for electrical performance (voltage, current, luminous intensity), color consistency, physical durability (bend and peel tests), and waterproofing integrity if applicable.
Common Testing Methods
- Electrical Testing: Verifies correct voltage, current draw, and absence of short circuits.
- Luminous Efficacy and Color Rendering: Spectrophotometers measure brightness and color temperature to ensure lighting uniformity.
- Thermal Testing: Checks heat dissipation efficiency to prevent premature LED failure, especially crucial for thin strips with limited PCB mass.
- Mechanical Stress Tests: Simulates bending, twisting, and adhesive peel strength to confirm installation durability.
- Environmental Tests: Includes humidity, salt spray, and UV exposure tests for outdoor-rated strips.
How B2B Buyers Can Verify Supplier Quality Control
For international buyers, especially those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality assurance practices is paramount to mitigate risks related to product failure, compliance issues, and shipment delays.
Supplier Audits and Factory Inspections
- On-Site Audits: Visiting manufacturing facilities to observe production lines, QC processes, and inventory management provides firsthand insight into operational standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Independent quality inspection firms can perform pre-shipment inspections, random sampling, and testing to verify conformity with agreed specifications.
- Certification Verification: Request and validate supplier certificates (ISO 9001, CE, RoHS, UL) through official registries or certification bodies to ensure authenticity.
Quality Reports and Documentation
- Test Reports: Obtain detailed lab test results for electrical, mechanical, and environmental performance.
- Process Control Records: Review IQC, IPQC, and FQC logs to understand defect rates and corrective actions.
- Traceability: Ensure suppliers provide batch and lot numbers for components and finished products to facilitate accountability and recall management if necessary.
Quality Assurance Nuances for Different International Markets
- Africa & South America: Buyers should prioritize suppliers offering robust packaging and adhesive quality to withstand challenging shipping conditions and diverse installation environments. Local electrical regulations may be less stringent, but buyers should advocate for compliance with international standards to ensure long-term reliability.
- Middle East: Given the region’s extreme temperatures and dust exposure, waterproofing (IP65 or higher) and heat-resistant materials are critical. Certifications like IEC and CE are often required for import clearance.
- Europe (Turkey, Spain, etc.): European buyers demand strict adherence to CE marking, RoHS, and eco-design directives. Emphasis on energy efficiency, recyclability, and full documentation is expected.
Summary for B2B Buyers
- Select suppliers with transparent, documented manufacturing processes focusing on high-quality LED chips, flexible PCBs, and durable adhesives tailored for thin strip profiles.
- Verify adherence to international standards including ISO 9001, CE, RoHS, and applicable local certifications relevant to your market.
- Insist on comprehensive quality control protocols covering IQC, IPQC, and FQC with evidence from test reports and third-party inspections.
- Customize QC expectations based on destination market conditions, such as environmental resilience for Middle East or packaging robustness for Africa and South America.
- Engage in supplier audits or use trusted inspection agencies to reduce risks associated with bulk orders and ensure consistent product quality.
By integrating these manufacturing and quality assurance insights into your sourcing strategy, B2B buyers can confidently procure thin LED light strips that meet stringent performance criteria and regulatory demands across diverse international markets.
Related Video: LED Light Making Process | How LED Lights Made Inside Factory | Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for thin led light strips Sourcing
Understanding the Cost Components of Thin LED Light Strips
When sourcing thin LED light strips for international B2B projects, it is essential to break down the key cost elements that collectively define the final price. These components include:
- Materials: The quality and type of LED chips, flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs), adhesive backing, and protective coatings are the primary cost drivers. Premium LED chips and high-grade PCBs increase durability and luminous efficacy but come at a higher cost.
- Labor: Skilled labor for precise assembly, soldering, and quality checks adds to production expenses, especially for customized or complex designs.
- Manufacturing Overhead: This includes factory utilities, equipment depreciation, and indirect labor costs that support production.
- Tooling: Initial setup costs for molds, cutting dies, or custom packaging can be significant, especially for small or highly customized orders.
- Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing for electrical performance, heat resistance, and compliance with international standards (e.g., CE, RoHS) ensures product reliability but also raises production costs.
- Logistics: Shipping fees, customs duties, insurance, and warehousing costs vary widely depending on the supplier’s location and chosen Incoterms.
- Supplier Margin: Profit margins vary by supplier and market conditions, often influenced by volume commitments and relationship strength.
Key Pricing Influencers for International Buyers
Several factors critically influence the pricing of thin LED light strips, particularly for buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe:
- Order Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically unlock better unit prices due to economies of scale. However, MOQ thresholds vary by supplier and product type, so balancing order size with inventory capacity is vital.
- Product Specifications and Customization: Customized lengths, color temperatures, waterproofing, or smart control features increase complexity and cost. Buyers should carefully assess which features are essential to avoid unnecessary expenses.
- Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-grade materials and certifications such as CE, RoHS, or UL ensure compliance with regional regulations and reduce risk but add to cost. Buyers in Europe and Turkey, for example, often require strict certifications.
- Supplier Location and Reputation: Established suppliers with robust quality systems may charge premium prices but reduce risks of defects and shipment delays.
- Incoterms and Shipping Method: Terms such as FOB, CIF, or DDP impact who bears shipping, customs, and insurance costs. Selecting appropriate Incoterms aligned with the buyer’s logistics capabilities can optimize total landed cost.
Practical Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing and Negotiation
- Negotiate on Volume and Payment Terms: Use order volume as leverage to negotiate discounts or favorable payment terms, especially if you plan repeat purchases.
- Request Samples Before Bulk Orders: Testing samples helps verify product quality and compatibility, reducing costly returns or replacements.
- Calculate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond unit price, consider installation ease, energy efficiency, lifespan, and warranty support to evaluate true value.
- Consolidate Shipments: Combine orders to lower per-unit shipping costs and reduce customs clearance complexity.
- Leverage Local Regulations Knowledge: Understanding import duties, VAT, and certification requirements specific to your region (e.g., Middle East’s GCC standards or EU directives) can prevent unexpected costs.
- Evaluate Supplier Certifications: Prioritize suppliers with recognized certifications to avoid delays in customs and ensure product reliability.
- Factor in Currency Fluctuations: For buyers in volatile currency regions, negotiate prices or contracts in stable currencies or include currency adjustment clauses.
Indicative Pricing Considerations
Prices for thin LED light strips vary widely depending on specifications and sourcing strategies. As a guideline, wholesale prices can range from $1 to $5 per meter for standard quality strips, with premium or customized options commanding higher rates. Shipping and customs duties can add 10–20% or more to the landed cost depending on origin and destination.
This comprehensive understanding of cost components, pricing influencers, and negotiation strategies empowers international B2B buyers to optimize procurement decisions for thin LED light strips, ensuring cost-efficiency without compromising quality or compliance.
Spotlight on Potential thin led light strips Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section offers a look at a few manufacturers active in the ‘thin led light strips’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct their own extensive due diligence before any engagement. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for thin led light strips
Key Technical Properties of Thin LED Light Strips
Understanding the critical technical specifications of thin LED light strips is essential for B2B buyers aiming to source products that meet performance, durability, and application requirements. Here are the most important properties to consider:
-
LED Chip Quality and Type
The LED chips are the core light sources on the strip. High-quality chips from reputable manufacturers ensure superior brightness (luminous efficacy), longer lifespan, and consistent color rendering. For buyers, investing in premium chips means reduced maintenance costs and better customer satisfaction. -
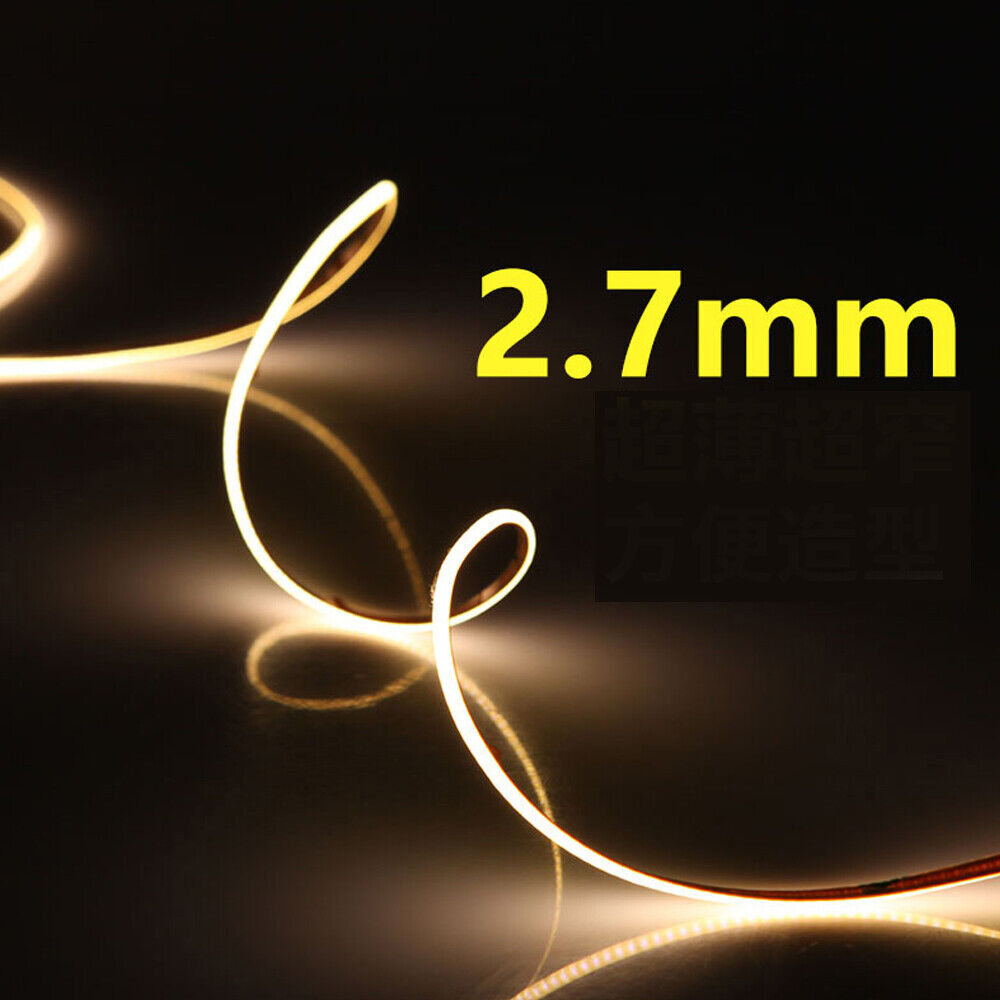
Strip Thickness and Flexibility
Thin LED strips typically range from 1mm to 3mm in thickness. Thinner strips are advantageous for installations in tight or curved spaces, such as architectural features or decorative accents. Flexibility also depends on the PCB substrate material, with flexible PCBs enabling bending without damage. This property directly impacts installation versatility and design possibilities. -
Power Consumption and Voltage
LED strips usually operate on low-voltage DC power (commonly 12V or 24V). Power consumption, measured in watts per meter (W/m), determines energy efficiency and heat generation. For large-scale projects, selecting strips with optimized power specs minimizes electricity costs and reduces cooling requirements. -
IP Rating (Ingress Protection)
The IP rating indicates the strip’s resistance to dust and moisture, critical for outdoor or humid environments. For example, IP65 strips are dust-tight and protected against water jets, while IP20 is suitable only for indoor, dry conditions. Buyers must match IP ratings to installation environments to ensure durability and safety compliance. -
Color Temperature and CRI (Color Rendering Index)
Color temperature, measured in Kelvins (K), defines the light’s warmth or coolness (e.g., 2700K warm white, 6000K daylight). CRI indicates the accuracy of color representation under the light source, with higher values (above 80) preferred for retail or hospitality settings. These properties affect ambiance and visual appeal, influencing customer experience. -
Adhesive Quality and Backing Material
The adhesive backing secures the strip in place during installation. High-quality adhesives ensure strong, long-lasting adhesion on various surfaces without residue or peeling. This reduces installation failures and maintenance costs, especially in challenging environments like outdoor facades or industrial sites.
Common Trade Terms and Industry Jargon for LED Strip Procurement
Navigating international B2B transactions requires familiarity with standard trade terms and industry-specific jargon. Here are key terms buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to manufacturers who produce LED strips that other companies rebrand and sell under their own names. OEM partnerships often allow customization options and cost advantages, enabling buyers to create private-label products tailored to their markets. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. MOQs vary widely depending on manufacturer capabilities and product type. Understanding MOQ helps buyers plan inventory, negotiate pricing, and avoid overstocking, especially critical for emerging markets with variable demand. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal inquiry sent to suppliers asking for price, lead time, and terms for specified products. RFQs are essential in comparing multiple vendors, clarifying specifications, and securing competitive pricing before committing to bulk purchases. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that define responsibilities between buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and customs duties. Common terms include FOB (Free On Board), CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), and DDP (Delivered Duty Paid). Clear understanding of Incoterms prevents disputes and unexpected costs in cross-border transactions. -
Color Binning
The process by which LED chips are sorted based on color consistency and brightness levels. Buyers should request information on binning standards to ensure uniform light quality across batches, which is crucial for aesthetic consistency in commercial installations. -
Dimmable and Smart LED Strips
These terms refer to strips that support brightness adjustment (dimmable) or integration with smart control systems via apps or voice assistants. Offering these advanced features can differentiate your product offerings in competitive markets.
By focusing on these technical properties and mastering essential trade terminology, international B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions, optimize procurement processes, and secure high-quality thin LED light strips tailored to their market needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the thin led light strips Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for thin LED light strips is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient, flexible, and customizable lighting solutions across commercial, industrial, and residential sectors. For international B2B buyers—especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—this sector presents significant opportunities fueled by urbanization, infrastructure development, and rising awareness of smart lighting technologies.
Key Drivers:
– Energy Efficiency & Cost Savings: Thin LED strips consume significantly less power than traditional lighting, appealing to markets where energy costs are high or power supply is inconsistent. This factor resonates strongly in regions like Africa and the Middle East.
– Versatility & Customization: Their flexible design allows installation in unconventional spaces, supporting diverse applications from retail displays in Spain to architectural lighting in Turkey. The availability of RGB, waterproof, and dimmable options enables tailored solutions.
– Smart Lighting Integration: Increasing adoption of IoT-enabled lighting systems, especially in Europe and South America, is pushing demand for LED strips compatible with app control, automation, and energy management systems.
Sourcing Trends:
– Direct Manufacturer Engagement: Buyers are increasingly sourcing directly from manufacturers to reduce costs, ensure product customization, and secure supply chain transparency. This trend is notable in emerging markets where procurement efficiency is critical.
– Emphasis on Quality & Compliance: With product longevity and safety paramount, international buyers prioritize suppliers who adhere to CE, RoHS, and UL certifications. This is especially crucial for European buyers who face stringent regulatory requirements.
– Bulk Purchasing & Scalability: Large-scale projects such as commercial developments, hospitality venues, and infrastructure upgrades are driving bulk orders. Consolidating suppliers for consistent product specs and delivery timelines is a growing procurement strategy.
Market Dynamics:
Geopolitical factors, shipping logistics, and tariff policies impact sourcing decisions. For instance, Middle Eastern buyers benefit from proximate manufacturing hubs in Asia, while European buyers leverage established import frameworks. African and South American markets are increasingly served by regional distributors who provide localized support and faster turnaround times.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a critical consideration in the thin LED light strips sector, with B2B buyers seeking products that minimize environmental impact throughout their lifecycle. Energy-efficient LED strips contribute to reduced carbon footprints, but sustainable sourcing extends beyond operational energy savings.
Environmental Impact:
– Material Selection: High-quality LED chips and PCBs made with environmentally responsible materials reduce toxic waste and facilitate recycling. Suppliers utilizing lead-free solder and halogen-free components help meet global environmental standards.
– Manufacturing Practices: Buyers increasingly favor manufacturers that implement waste reduction, energy conservation, and water-saving measures during production. Transparent reporting on environmental management enhances supplier credibility.
– Packaging & Logistics: Eco-friendly packaging materials and optimized shipping routes reduce the carbon footprint associated with distribution, a factor especially relevant for long-distance international shipments.
Ethical Supply Chains:
– Labor Standards: Ethical sourcing requires adherence to fair labor practices, ensuring workers involved in manufacturing LED strips operate under safe, equitable conditions. Certifications like SA8000 or WRAP provide assurance to buyers.
– Conflict-Free Materials: Responsible sourcing of raw materials, particularly rare earth elements in LED chips, is essential to avoid financing conflict zones and to comply with international regulations.
Green Certifications & Buyer Benefits:
– Certifications such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), Energy Star, and TUV SUD validate environmental and safety claims, helping buyers align procurement with corporate sustainability goals.
– Partnering with suppliers who prioritize sustainability enhances brand reputation and meets growing consumer and regulatory demands for environmentally conscious products.
For international B2B buyers, integrating sustainability criteria into procurement strategies not only mitigates risks but also opens access to emerging markets and government incentives focused on green technologies.
Evolution of Thin LED Light Strips in the B2B Context
Thin LED light strips have evolved substantially over the past two decades, transitioning from simple decorative lighting to sophisticated, multifunctional tools integral to modern lighting design. Early versions were limited by rigid designs, low brightness, and narrow color options. Advances in LED chip technology and flexible PCB fabrication have enabled ultra-thin, highly adaptable strips with improved luminous efficacy and extended lifespans.
This evolution has been driven by the demand for energy-efficient, customizable lighting in commercial and industrial applications worldwide. The integration of smart controls and IoT compatibility has further expanded their role, allowing B2B buyers to implement dynamic lighting schemes that improve ambiance, safety, and energy management.
Today, thin LED strips serve a wide range of sectors—from retail and hospitality to infrastructure and automotive—making them a cornerstone in contemporary lighting procurement strategies for buyers aiming to combine innovation, efficiency, and sustainability.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of thin led light strips
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers of thin LED light strips to ensure product quality and reliability?
Thorough supplier vetting is essential to mitigate risks in international B2B trade. Start by verifying the supplier’s business credentials, including company registration and export licenses. Request product samples and check for certifications like CE, RoHS, and UL that confirm compliance with international safety and environmental standards. Review customer feedback and industry reputation through platforms like Alibaba or Global Sources. Additionally, inquire about their quality control processes and production capabilities to ensure they can consistently meet your volume and technical requirements. -
What customization options are typically available for thin LED light strips, and how do they affect pricing and lead times?
Customizations often include specific strip lengths, LED color temperatures, brightness levels, adhesive backing types, and packaging tailored to your brand. Some suppliers also offer custom circuitry or smart control features. While customization can add value and better fit your project needs, it usually increases both unit cost and lead time due to design adjustments and tooling. To optimize costs and timelines, clearly define your technical requirements upfront and discuss batch sizes that can justify the customization without excessive overhead. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for thin LED light strips when sourcing internationally, especially for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe?
MOQs vary widely but generally range from 500 to 5,000 meters per order, depending on supplier scale and customization. Lead times can span from 3 to 8 weeks, factoring in production, quality inspections, and international shipping. For buyers in regions with complex logistics such as Africa or South America, allow additional buffer time for customs clearance and inland transport. Negotiate MOQs with suppliers, as some may offer lower thresholds for sample orders or repeat customers, which can help you test the market before committing to large volumes. -
What payment terms and methods are recommended for international B2B transactions involving thin LED light strips?
Secure payment terms balance supplier trust and buyer protection. Common methods include wire transfers (T/T), letters of credit (L/C), and escrow services. Typically, suppliers request 30% upfront and 70% upon shipment or receipt of inspection reports. Letters of credit offer added security by involving banks but may increase transaction complexity and fees. For new suppliers, consider using third-party escrow platforms or trade assurance services to minimize risk. Always clearly specify payment milestones in contracts and maintain transparent communication to avoid disputes. -
How can I ensure the quality assurance and certifications of thin LED light strips meet my country’s import regulations and industry standards?
Request detailed documentation including product test reports, certificates of conformity (CE, RoHS, UL), and factory audit summaries. Verify that the LEDs comply with your local electrical and safety standards, which can differ across regions like the EU, Middle East, or South America. Engage third-party inspection agencies to conduct pre-shipment quality checks and factory audits. This proactive approach reduces the risk of non-compliance, costly returns, or customs rejections, helping maintain your supply chain integrity and customer satisfaction. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing thin LED light strips to regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe?
Understand the import regulations, tariffs, and customs procedures specific to your destination country. Choose suppliers who offer flexible shipping options—air freight for urgent orders, sea freight for cost efficiency on large volumes. Factor in packaging that protects the delicate LED strips during transit and handling. Collaborate with experienced freight forwarders familiar with your target markets to optimize delivery times and reduce risks of damage or delays. Tracking shipments and maintaining clear documentation are crucial for smooth customs clearance. -
How should I handle disputes or quality issues with suppliers of thin LED light strips in international trade?
Establish clear contractual terms that specify product specifications, delivery timelines, quality standards, and dispute resolution mechanisms before ordering. If issues arise, document all communication and product evidence (photos, test reports). Attempt amicable negotiation or mediation to resolve concerns quickly. If unresolved, leverage trade protection mechanisms such as arbitration clauses, trade insurance, or recourse through platforms like Alibaba Trade Assurance. Building strong relationships and maintaining transparent communication with suppliers can also prevent disputes from escalating.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Are there benefits to consolidating orders of thin LED light strips across multiple projects or regions, and how can this impact procurement?
Consolidating orders can leverage economies of scale, reduce per-unit costs, and lower shipping expenses through bulk freight discounts. It simplifies supplier management by reducing the number of purchase orders and streamlining quality control. However, it requires robust inventory management and forecasting to avoid overstocking or obsolescence. For international buyers, consolidated shipments may optimize customs clearance and reduce logistical complexity. Collaborate closely with your supplier to coordinate production schedules and negotiate favorable terms that support your broader procurement strategy.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for thin led light strips
Strategic sourcing of thin LED light strips offers international B2B buyers a competitive edge through cost efficiency, product customization, and access to cutting-edge lighting technologies. Prioritizing reliable suppliers with strong quality control, transparent warranties, and compliance certifications ensures consistent performance and durability—critical factors for large-scale and diverse applications. Bulk purchasing not only reduces per-unit costs but also streamlines supply chain management, enabling seamless project execution across sectors from retail and hospitality to industrial installations.
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional market needs and supplier capabilities is essential. Tailoring orders to specific environmental conditions—such as humidity or temperature variations—and installation requirements enhances product longevity and customer satisfaction. Leveraging supplier partnerships for customization and timely delivery will further optimize procurement strategies.
Looking ahead, the LED lighting industry is poised for continued innovation, with smart and energy-efficient solutions gaining prominence. Forward-thinking buyers who integrate strategic sourcing with market insights and technological trends will unlock new growth opportunities. Now is the time to deepen supplier relationships, invest in quality assurance, and embrace flexible ordering options to illuminate your projects with thin LED light strips that meet tomorrow’s standards today.
