Guide to E26 Vs E27
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for e26 vs e27
- Understanding e26 vs e27 Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of e26 vs e27
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for e26 vs e27
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for e26 vs e27
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for e26 vs e27 Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential e26 vs e27 Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for e26 vs e27
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the e26 vs e27 Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of e26 vs e27
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for e26 vs e27
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for e26 vs e27
Understanding the distinctions between E26 and E27 bulb bases is crucial for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize their lighting procurement strategies. These seemingly similar Edison screw bases differ in subtle but impactful ways—ranging from size and voltage compatibility to manufacturing standards—that directly influence product performance, safety, and regulatory compliance across diverse markets.
For businesses operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including industrial hubs in Indonesia and Germany, making the right choice between E26 and E27 is not merely a technical detail but a strategic decision. It affects operational efficiency, cost management, and long-term supplier relationships in regions where electrical standards and infrastructure vary significantly.
This guide delivers a comprehensive analysis tailored to the needs of wholesalers, distributors, manufacturers, and facility managers. It covers:
- Technical specifications including dimensions, voltage ratings, and thread design
- Material and build quality considerations impacting durability and safety
- Manufacturing and quality control protocols aligned with ANSI and IEC standards
- Key supplier profiles and sourcing strategies optimized for global markets
- Cost factors influenced by regional demand, tariffs, and logistics
- Market trends and regional preferences to align inventory with customer expectations
- Frequently Asked Questions addressing common challenges in cross-border procurement
By equipping buyers with actionable insights and clear comparisons, this resource empowers informed sourcing decisions that minimize risks, enhance compatibility, and maximize value in complex international supply chains. Whether upgrading facilities or launching new product lines, understanding the E26 vs E27 dynamic is essential for sustainable success in the global lighting market.
Understanding e26 vs e27 Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard E26 Bulbs | 26mm Edison screw base, designed for 110-120V systems | North American commercial/residential lighting | Pros: Widely available in Americas, cost-effective; Cons: Not suitable for 220-240V markets, risk of electrical mismatch |
| Standard E27 Bulbs | 27mm Edison screw base, designed for 220-240V systems | European, Asian, Middle Eastern commercial and industrial lighting | Pros: Compatible with higher voltage systems, compliant with IEC standards; Cons: Slightly larger size may cause fitting issues in E26 sockets |
| High-CRI E26/E27 LED | Enhanced color rendering index for accurate color representation | Art galleries, retail displays, photography studios | Pros: High color accuracy improves visual appeal; Cons: Typically higher cost, requires precise voltage matching |
| Dimmable E26/E27 Bulbs | Compatible with dimmer switches, available in both bases | Hospitality, office spaces, event venues | Pros: Flexible lighting control, energy savings; Cons: Compatibility with dimmers varies, may require specific drivers |
| Specialty Temperature Bulbs (e.g., 2700K, 5000K) | Available in both bases with various color temperatures for ambiance or task lighting | Hospitality, horticulture, healthcare | Pros: Tailored lighting improves environment; Cons: Needs accurate specification to match fixture and application |
Standard E26 Bulbs
E26 bulbs feature a 26mm Edison screw base designed for 110-120V electrical systems, predominantly used in North America and Japan. These bulbs are ideal for commercial and residential settings like offices, retail stores, and warehouses within these regions. For B2B buyers targeting markets in Africa or South America where North American voltage standards are common, E26 bulbs offer cost-effective sourcing and widespread compatibility. However, buyers should avoid deploying these bulbs in 220-240V markets to prevent safety risks and premature failures.
Standard E27 Bulbs
E27 bulbs have a 27mm Edison screw base and are engineered for 220-240V systems, common in Europe, the Middle East, Asia, and parts of Africa and South America. These bulbs are suitable for industrial facilities, public buildings, and outdoor lighting in these regions. For B2B buyers, sourcing E27 bulbs ensures compliance with IEC standards and compatibility with local electrical infrastructure. The slightly larger base size requires attention during procurement to avoid socket fitting issues in mixed-use or imported fixtures.
High-CRI E26/E27 LED Bulbs
High Color Rendering Index (CRI) bulbs are available in both E26 and E27 bases and are essential for applications demanding accurate color representation such as art galleries, jewelry stores, and photography studios. These bulbs enhance product presentation and visual clarity, which can drive sales and customer satisfaction. B2B buyers should consider voltage compatibility and source from manufacturers offering certifications to ensure consistent color quality and safety across international markets.
Dimmable E26/E27 Bulbs
Dimmable bulbs with E26 or E27 bases provide flexible lighting control, enabling energy savings and ambiance customization in hospitality, office, and event environments. These bulbs require compatible dimmer switches and sometimes specific driver electronics, which buyers must verify to avoid compatibility issues. For international B2B buyers, confirming dimmer compatibility and sourcing from reliable suppliers ensures optimal performance and reduces costly returns or replacements.
Specialty Temperature Bulbs (e.g., 2700K, 5000K)
Both E26 and E27 bulbs come in various color temperatures, from warm (2700K) to daylight (5000K+), catering to different lighting needs such as relaxation, productivity, or horticulture. Selecting the appropriate color temperature enhances the environment and user experience. B2B buyers should specify exact color temperature requirements and verify electrical standards to ensure the bulbs meet the intended application and regional regulations, thereby maximizing operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Related Video: All Machine Learning Models Clearly Explained!
Key Industrial Applications of e26 vs e27
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of e26 vs e27 | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial Lighting | Office and retail lighting fixtures in North America vs Europe | Ensures compatibility with local voltage standards, reduces maintenance costs due to fitting issues | Confirm voltage rating and socket compatibility; regional certifications (ANSI for E26, IEC for E27) |
| Hospitality & Hotels | Lighting installations in hotels and resorts across different regions | Enhances guest safety and comfort by using appropriate bulb bases for local electrical systems | Bulk sourcing with regional compliance; consider voltage tolerance and energy efficiency ratings |
| Industrial Facilities | Factory floor and warehouse lighting in high-voltage (Europe, Asia) vs low-voltage (North America) environments | Improves operational uptime by avoiding overheating and fixture damage | Evaluate voltage and durability specs; ensure bulbs meet industrial safety standards for the region |
| Film & Photography | Specialized LED bulbs with specific color temperatures and bases for studio lighting | Achieves precise color rendering and flicker-free operation, critical for professional imaging | Source bulbs with exact base type and color temperature; verify electrical compatibility for location |
| Horticulture | Grow lights with appropriate screw base for different regional electrical setups | Maximizes plant growth efficiency with correct voltage and secure fitting | Prioritize bulbs with tailored spectra and regional voltage ratings; check for warranty and support |
In commercial lighting, the choice between E26 and E27 bases is crucial due to regional voltage differences. For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, sourcing the correct bulb base ensures seamless integration into local fixtures operating at either 110-120V or 220-240V. Using the wrong base can cause flickering, loose fittings, or premature bulb failure, increasing maintenance costs. Buyers should prioritize bulbs certified under ANSI or IEC standards depending on their market to guarantee safety and reliability.
In the hospitality sector, hotels and resorts require lighting solutions that align with regional electrical standards to maintain guest safety and comfort. For example, a hotel chain operating across Europe and South America must source E27 bulbs for European locations and E26 bulbs for American-influenced markets. Bulk procurement should consider voltage compatibility, energy efficiency, and certification compliance to reduce risks of electrical faults and ensure consistent lighting quality.
Industrial facilities face high operational demands where lighting reliability directly impacts productivity. Factories and warehouses in Europe and Asia predominantly use E27 bulbs rated for 220-240V, while North American counterparts use E26 bulbs at 110-120V. Selecting the appropriate bulb base prevents overheating and fixture damage in harsh industrial environments. International buyers should verify durability, voltage tolerance, and safety certifications to minimize downtime and costly replacements.
For film and photography studios, precise lighting control is essential. LED bulbs with E26 or E27 bases must match local electrical standards and provide specific color temperatures for accurate color rendering. Studios in Germany or Indonesia, for example, need to source bulbs that not only fit their sockets but also deliver flicker-free performance at the correct voltage. Buyers should focus on bulbs with stable electrical drivers and regional compliance to maintain production quality.
In horticulture, grow lights with the correct screw base and voltage rating are critical to optimizing plant growth. International B2B buyers sourcing for farms in the Middle East or South America must ensure compatibility with local electrical infrastructure. Additionally, bulbs offering customized light spectra paired with the correct E26 or E27 base improve energy efficiency and crop yields. Warranty support and after-sales service are important considerations for these high-investment applications.
Related Video: What are all the Laboratory Apparatus and their uses?
Strategic Material Selection Guide for e26 vs e27
Material Selection Considerations for E26 vs E27 Bulb Bases
Selecting the right material for E26 and E27 bulb bases and fixtures is critical for ensuring safety, durability, and regulatory compliance in diverse international markets. The choice impacts not only manufacturing complexity and cost but also performance under different electrical and environmental conditions prevalent across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the production of E26 and E27 components, focusing on their key properties, advantages, limitations, and relevance to global B2B buyers.
1. Brass
Key Properties:
Brass is an alloy primarily composed of copper and zinc, known for excellent electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and moderate mechanical strength. It performs well in temperature ranges typical for lighting applications and resists oxidation, which is crucial for maintaining reliable electrical contact.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: High conductivity ensures efficient power transfer; corrosion resistance extends product life in humid or coastal environments; relatively easy to machine and form.
– Cons: Higher cost compared to steel or aluminum; heavier weight can increase shipping costs; potential for dezincification in highly corrosive environments if not properly alloyed.
Impact on Application:
Brass is ideal for bulb bases and sockets where electrical reliability and longevity are paramount. It is especially suitable for markets with high humidity or salt exposure, such as coastal regions in Africa and South America.
International B2B Considerations:
Brass components often comply with ASTM B16/B36 standards (USA) and DIN EN 12164/12165 (Europe). Buyers in Germany and Europe will value brass for its compliance with RoHS and REACH regulations. In the Middle East and Africa, brass’s corrosion resistance is a significant advantage, though cost sensitivity may require balancing with alternative materials.
2. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, has good thermal conductivity, and offers moderate corrosion resistance, especially when anodized. It is non-magnetic and easy to extrude or cast into complex shapes, making it popular for heat sinks and bulb housings.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Lightweight reduces shipping and handling costs; good heat dissipation improves LED bulb lifespan; corrosion resistance can be enhanced via surface treatments.
– Cons: Lower electrical conductivity than copper/brass; can be prone to galvanic corrosion if in contact with dissimilar metals; manufacturing complexity increases with anodizing or coating processes.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is frequently used in LED bulb housings and heat sinks rather than the screw base itself. Its thermal management properties are critical for high-wattage bulbs used in industrial or commercial settings, common in European and Middle Eastern markets.
International B2B Considerations:
Compliance with EN 755 (European aluminum standards) and JIS H 4000 (Japan) is often required. Buyers from Indonesia and South America should consider local availability of anodized aluminum to ensure consistent quality. Aluminum’s lightweight nature favors logistics in regions with higher freight costs.
3. Nickel-Plated Steel
Key Properties:
Steel offers high strength and durability but lower corrosion resistance. Nickel plating enhances corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, making it suitable for bulb bases exposed to mechanical stress and varying environmental conditions.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Cost-effective compared to brass; strong and durable under mechanical stress; nickel plating improves lifespan and electrical contact quality.
– Cons: Plating can wear off over time, especially in harsh environments; steel’s weight is higher than aluminum; susceptibility to rust if plating is compromised.
Impact on Application:
Nickel-plated steel is commonly used in mass-produced, cost-sensitive bulbs where mechanical robustness is necessary. It suits indoor commercial lighting in controlled environments, such as offices and retail spaces in Europe and South America.
International B2B Considerations:
Buyers should verify plating thickness and adherence to ASTM B689 or ISO 4527 standards. In humid or coastal regions of Africa and the Middle East, additional corrosion protection may be required to prevent premature failure.
4. Ceramic
Key Properties:
Ceramic materials exhibit excellent heat resistance, electrical insulation, and durability under high temperatures. They do not conduct electricity and are chemically inert, making them ideal for insulating parts of bulb bases and sockets.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Superior heat resistance extends bulb life in high-temperature applications; excellent electrical insulation prevents short circuits; chemically stable and corrosion-proof.
– Cons: Brittle and prone to cracking under mechanical shock; higher manufacturing costs; heavier than plastics or metals.
Impact on Application:
Ceramic is preferred in high-end or industrial lighting fixtures where heat dissipation and electrical safety are critical, such as in factories or outdoor lighting in Europe and parts of the Middle East.
International B2B Considerations:
Compliance with IEC 60672 (insulating materials) and local fire safety standards is essential. Buyers in regions with extreme temperature variations, like parts of Africa and the Middle East, benefit from ceramic’s stability despite the higher price point.
Summary Table of Material Selection for E26 vs E27
| Material | Typical Use Case for e26 vs e27 | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | Screw bases and sockets requiring high conductivity and corrosion resistance | Excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and heavier than alternatives | High |
| Aluminum | LED bulb housings and heat sinks requiring lightweight and thermal management | Lightweight with good heat dissipation | Lower electrical conductivity, prone to galvanic corrosion | Medium |
| Nickel-Plated Steel | Cost-sensitive bulb bases needing mechanical strength and moderate corrosion resistance | Durable and cost-effective with improved corrosion resistance due to plating | Plating can wear off, susceptible to rust if damaged | Low |
| Ceramic | High-temperature insulating parts in industrial or outdoor lighting | Superior heat resistance and electrical insulation | Brittle, higher manufacturing cost | High |
This material guide equips international B2B buyers with critical insights for selecting the optimal base and fixture materials for E26 and E27 bulbs. Understanding these factors helps ensure product reliability, compliance with regional standards, and cost-effective sourcing tailored to diverse market needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for e26 vs e27
Understanding the manufacturing and quality assurance processes behind E26 and E27 bulbs is critical for international B2B buyers aiming to ensure product reliability, safety, and regulatory compliance. The following detailed overview highlights key manufacturing stages, quality control protocols, and actionable insights for buyers sourcing lighting products across diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Manufacturing Process Overview for E26 and E27 Bulbs
The production of E26 and E27 bulbs involves several precise stages to guarantee compatibility with respective electrical standards (110-120V for E26, 220-240V for E27) and physical dimensions (26mm vs. 27mm base diameter). The main manufacturing phases include:
-
Material Preparation
– Raw Materials Sourcing: High-quality glass, metal alloys (usually brass or aluminum for the screw base), phosphor powders (for fluorescent/LED coatings), and electronic components (LED chips, drivers) are procured.
– Material Testing: Incoming raw materials undergo inspection to verify purity, composition, and conformity to specifications, reducing risks of defects downstream.
– Pre-Processing: Metals are cleaned and treated to ensure corrosion resistance; glass components are molded or cut to size. -
Forming and Component Fabrication
– Glass Bulb Formation: Automated glass blowing or molding machines shape the bulb envelope to precise dimensions, essential for fitting and light diffusion.
– Base Manufacturing: The Edison screw bases (E26 or E27) are formed via stamping and threading machines to maintain strict tolerances in diameter and thread pitch.
– Electronic Assembly: For LED bulbs, driver circuits and LED arrays are mounted on PCBs (printed circuit boards) using surface mount technology (SMT) or manual soldering for specialty bulbs. -
Assembly
– Sub-Assembly: Glass bulbs are fitted with internal components such as filaments, LEDs, or driver units.
– Base Attachment: The metal screw base is mechanically and electrically joined to the bulb housing, often by crimping or soldering.
– Sealing and Insulation: Bulbs are sealed under controlled atmospheres to prevent moisture ingress; insulation materials may be added to prevent short circuits. -
Finishing and Packaging
– Surface Treatments: Bulbs may receive coatings for anti-glare, UV protection, or aesthetic finishes.
– Marking: Compliance labels, voltage ratings, and brand information are printed or etched.
– Packaging: Bulbs are packed in protective materials designed to withstand shipping stresses, especially important for international logistics.
Key Quality Assurance and Control (QA/QC) Checkpoints
Robust quality control is paramount to ensure bulbs meet safety and performance standards, particularly for international buyers dealing with varied regulatory environments. The QC process typically includes:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials and components to prevent defective inputs.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing stages to detect deviations early, including dimensional checks of screw bases, solder joint inspections, and electronic testing.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of finished bulbs before shipment, verifying electrical performance, mechanical integrity, and visual quality.
International Standards and Certifications Relevant to E26 and E27 Bulbs
B2B buyers must ensure suppliers comply with applicable standards, which vary by region but often include:
- ISO 9001: A globally recognized quality management standard ensuring consistent production quality and continuous improvement practices.
- CE Marking: Mandatory for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating conformity with EU safety, health, and environmental requirements.
- UL/CSA: North American certifications ensuring electrical safety—critical if E26 bulbs are intended for export to markets like Canada or the U.S.
- IEC Standards: International Electrotechnical Commission standards govern bulb performance and safety, widely accepted in Europe, Asia, and parts of the Middle East.
- RoHS Compliance: Restriction of hazardous substances, important for environmental and health regulations globally.
Common Testing Methods in E26 and E27 Bulb Manufacturing
Testing ensures bulbs meet operational and safety criteria:
- Dimensional Inspection: Precision measurement of screw base diameter and thread pitch to ensure socket compatibility.
- Electrical Testing: Voltage withstand, insulation resistance, and leakage current tests verify electrical safety under rated conditions.
- Thermal Testing: Heat dissipation and temperature rise tests confirm bulbs operate safely without overheating.
- Light Performance: Lumen output, color temperature, and Color Rendering Index (CRI) are measured to meet lighting quality specifications.
- Mechanical Testing: Vibration, shock, and drop tests assess durability for transport and use in industrial environments.
- Life Cycle Testing: Accelerated aging simulates long-term use, identifying potential early failures.
How B2B Buyers Can Verify Supplier Quality Control
To mitigate risks and ensure product reliability, buyers should engage in proactive supplier quality verification:
- Factory Audits: Conduct or commission on-site audits to review manufacturing capabilities, process controls, and workforce training.
- Review of QC Documentation: Request inspection reports, test certificates, and compliance documentation (e.g., ISO 9001 certificates, CE declarations).
- Third-Party Inspections: Utilize independent inspection agencies to perform random sampling and testing before shipment.
- Sample Testing: Order product samples for in-house or third-party lab testing to validate performance and compliance claims.
- Supplier Quality Agreements: Establish contractual quality requirements, including penalties for non-compliance and defect rates.
Nuances in QC and Compliance for International Markets
B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe face specific considerations when sourcing E26 or E27 bulbs:
- Voltage and Compatibility Checks: Ensure bulbs match local electrical standards (e.g., 220-240V for Europe, Middle East; 110-120V for some South American regions) to prevent safety hazards.
- Certification Recognition: Some regions may require local certifications or approvals in addition to international marks; for example, GCC conformity in the Middle East or INMETRO certification in Brazil.
- Environmental and Safety Regulations: Awareness of regional regulations on hazardous substances and waste management (e.g., WEEE Directive in Europe) is essential.
- Logistics and Packaging: Packaging must withstand long-distance shipping conditions prevalent in African and South American markets, with clear labeling in local languages where necessary.
- Cultural and Market Preferences: Some markets prioritize energy efficiency and long lifespan (e.g., Germany, Indonesia), influencing QC focus areas like lumen maintenance and driver reliability.
Summary for B2B Buyers:
When evaluating E26 vs E27 bulb suppliers, prioritize manufacturers with transparent and rigorous quality management systems aligned with international standards such as ISO 9001 and CE. Insist on detailed QC documentation and independent verification to avoid costly compatibility and safety issues. Tailor sourcing decisions to local voltage requirements and certification expectations to secure reliable lighting solutions that meet your region’s operational and regulatory demands.
Related Video: Mercedes C-Class CAR FACTORY – HOW IT’S MADE Assembly Production Line Manufacturing Making of
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for e26 vs e27 Sourcing
Understanding the cost and pricing dynamics between E26 and E27 bulb sourcing is critical for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize procurement expenses while ensuring product quality and compliance. Both bulb types share similarities but differ in manufacturing requirements and market standards, influencing their cost structures and pricing models.
Key Cost Components in E26 vs E27 Bulb Manufacturing
-
Materials
The core materials—glass, metal bases, filaments or LED components—are largely similar. However, E27 bulbs often require components rated for higher voltages (220-240V), which may increase material costs slightly due to enhanced insulation and durability requirements. Buyers sourcing for markets like Europe or Indonesia should expect these specifications to affect pricing. -
Labor and Manufacturing Overhead
Labor costs vary significantly by region. Manufacturing in Asia (e.g., Indonesia) may offer cost advantages over Europe due to lower wages and overhead. However, stringent quality control (QC) and compliance with IEC standards for E27 bulbs can add to overhead costs, especially for suppliers targeting European or Middle Eastern markets. -
Tooling and Equipment
The 1mm difference in screw base diameter means tooling for E26 and E27 production lines is slightly different. Suppliers producing both variants may pass tooling costs into pricing. For custom or specialized bulbs (e.g., horticulture or high-CRI lighting), tooling costs rise further. -
Quality Control and Certification
Compliance with ANSI standards (E26) or IEC standards (E27) requires dedicated QC processes. For B2B buyers in regulated markets like Germany or the EU, certification costs are embedded in pricing. This assures safety and reliability but can increase unit costs by 5-15%. -
Logistics and Freight
Shipping costs vary by destination and Incoterms. Bulk shipments to Africa or South America might incur higher freight charges and import duties. Additionally, fragility and volume of bulbs necessitate careful packaging, raising logistics costs. Buyers should consider total landed cost, not just FOB prices. -
Supplier Margin
Margins depend on supplier scale, exclusivity, and market demand. High-volume buyers can negotiate better rates. Margins may be tighter in highly competitive markets like Europe but higher in emerging markets with fewer reliable suppliers.
Price Influencers and Negotiation Factors
- Order Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically reduce per-unit costs. Buyers from South America or the Middle East should leverage consolidated shipments to negotiate volume discounts.
- Customization and Technical Specifications: Customized color temperatures, wattages, or certification levels raise prices. Standard E26 bulbs for North America may be cheaper than specialized E27 bulbs with enhanced features.
- Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-grade LEDs or glass, plus certifications like RoHS or CE, increase pricing but improve product lifespan and compliance.
- Supplier Location and Reliability: Sourcing from local or regional suppliers can reduce logistics costs and lead times but may come with a price premium.
- Incoterms and Payment Terms: Clear agreement on shipping terms (FOB, CIF, DDP) affects overall cost exposure. Favorable payment terms can improve cash flow for buyers.
Practical Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing
- Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider bulb lifespan, energy efficiency, and replacement costs alongside unit price to avoid false savings.
- Verify Voltage and Standards Compatibility: Avoid costly returns or safety risks by confirming product specs match local electrical standards (110-120V for E26; 220-240V for E27).
- Leverage Regional Trade Agreements: Buyers in Africa, South America, or the Middle East should explore preferential tariffs or trade agreements to reduce import duties.
- Negotiate MOQ and Packaging: Request flexible MOQs or tailored packaging to reduce inventory costs and improve supply chain agility.
- Request Samples and QC Documentation: Ensure product quality before bulk purchase, especially when dealing with new suppliers or unfamiliar markets.
- Plan for Logistics Delays: Factor in extended shipping times and customs clearance in lead time calculations to avoid stockouts.
Indicative Pricing Disclaimer
Prices for E26 and E27 bulbs vary widely based on supplier, order size, customization, and market conditions. The analysis above provides a framework rather than exact figures. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and supplier audits to obtain precise quotes tailored to their specific needs.
By understanding these cost drivers and pricing influencers, international B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions that balance cost-efficiency, compliance, and product performance across diverse markets from Africa to Europe.
Spotlight on Potential e26 vs e27 Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section offers a look at a few manufacturers active in the ‘e26 vs e27’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct their own extensive due diligence before any engagement. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for e26 vs e27
Critical Technical Properties for E26 vs E27 Bulbs
1. Base Diameter and Thread Tolerance
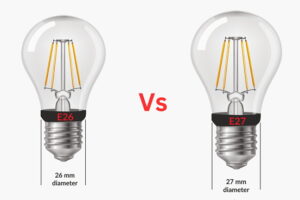
– Definition: E26 and E27 bulbs differ primarily in their screw base diameter—26mm vs. 27mm respectively. Thread tolerance refers to the acceptable manufacturing variation in these dimensions.
– B2B Importance: Even a 1mm difference impacts socket compatibility, affecting installation ease and operational reliability. For buyers supplying diverse markets, specifying precise base dimensions ensures bulbs fit correctly without causing loose connections or damage, reducing maintenance and returns.
2. Voltage Rating
– Definition: E26 bulbs are designed for 110-120V systems typical in North America and Japan, whereas E27 bulbs support 220-240V systems common in Europe, Africa, South America, and parts of Asia.
– B2B Importance: Voltage compatibility is critical for safety and longevity. Using a bulb rated for lower voltage in a higher voltage system can cause overheating or failure, risking downtime and liability in commercial settings. Proper voltage specification streamlines procurement for region-specific electrical standards.
3. Material Grade and Thermal Resistance
– Definition: This refers to the quality of metals and insulators used in the bulb base and the bulb’s ability to withstand heat generated during operation.
– B2B Importance: Higher-grade materials increase durability and safety, especially in industrial or high-use environments. Buyers targeting harsh climates or continuous-use applications should prioritize bulbs with certified material grades to reduce warranty claims and operational disruptions.
4. Electrical Contact Design
– Definition: The design and quality of the contact points between the bulb base and the socket, including plating materials and contact pressure.
– B2B Importance: Reliable electrical contacts prevent flickering and power loss, crucial in commercial installations where stable lighting impacts productivity and safety. Understanding contact design helps buyers select bulbs optimized for their fixture types and usage conditions.
5. Compliance with Regional Standards
– Definition: E26 bulbs typically comply with ANSI (American National Standards Institute) standards, while E27 bulbs adhere to IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) requirements.
– B2B Importance: Compliance ensures products meet safety, performance, and testing criteria required by local regulations. For international buyers, verifying certification prevents customs issues and supports market acceptance.
6. Wattage and Lumens Output
– Definition: Wattage indicates power consumption; lumens measure brightness. Both influence energy efficiency and lighting quality.
– B2B Importance: Selecting bulbs with appropriate wattage and lumen output tailored to application needs optimizes energy costs and user satisfaction. Buyers should align specifications with client requirements and local energy regulations.
Essential Industry and Trade Terminology for International Buyers
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Refers to a company that produces components or products to be branded and sold by another company. In lighting, OEM bulbs may be manufactured to buyer specifications, enabling private labeling and tailored solutions.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– The smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell in one order. Understanding MOQ helps buyers plan inventory and negotiate cost-effective deals, especially when entering new markets with uncertain demand.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– A formal inquiry sent by a buyer to suppliers asking for pricing, availability, and terms for specific products. RFQs are critical for comparing vendors and securing competitive pricing for bulk purchases.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Standardized trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs between buyers and sellers. Common terms include FOB (Free On Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight). Knowing Incoterms helps buyers manage logistics and control costs effectively.
Lead Time
– The period between placing an order and receiving the goods. For lighting products, lead time affects project schedules and inventory management, making it vital to confirm with suppliers before contract commitments.
Certification Marks
– Symbols on products indicating compliance with safety and quality standards (e.g., CE for Europe, UL for North America). Certifications assure buyers and end-users that products meet regulatory requirements, reducing risks in import and resale.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing E26 and E27 bulbs. This knowledge supports selecting the right products for target markets, ensuring safety, compatibility, and cost-efficiency across diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the e26 vs e27 Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global lighting market involving E26 and E27 bulbs is shaped by distinct regional preferences, voltage standards, and evolving technological demands. For B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including markets like Indonesia and Germany—understanding these nuances is critical for successful sourcing and deployment.
Regional Market Dynamics:
– Africa and South America are experiencing rapid urbanization and infrastructure development, driving demand for energy-efficient lighting solutions compatible with local voltage standards. Many countries in these regions lean towards 220-240V systems, making E27 bulbs prevalent. However, pockets of North American electrical influence, especially in industrial zones, necessitate occasional E26 sourcing.
– Middle East markets balance between commercial high-rise developments and traditional infrastructure, often requiring both E26 and E27 bulbs depending on the origin of electrical installations. The region’s growing hospitality and retail sectors fuel demand for specialty LED bulbs with high color rendering indexes (CRI) and tailored color temperatures.
– Europe and Indonesia predominantly use E27 bulbs due to the 220-240V standard, but strict regulatory frameworks and sustainability mandates push buyers to prioritize certified, energy-efficient LED lighting with longer lifespans.
Emerging B2B Trends:
– LED Adoption and Smart Lighting: The transition from incandescent and fluorescent to LED bulbs continues to accelerate, with a focus on smart lighting technologies compatible with E26/E27 fittings. Integration with IoT systems and human-centric lighting solutions is increasingly valued for commercial and industrial applications.
– Customization and Spectrum Control: B2B buyers are seeking bulbs with customizable color temperatures and spectral outputs to suit specific applications like horticulture, artwork display, and film production. This trend favors suppliers offering modular product lines with flexible specifications.
– Supply Chain Localization: Geopolitical uncertainties and logistics challenges have pushed buyers to diversify sourcing, favoring manufacturers with regional distribution centers or local assembly to reduce lead times and inventory risks.
Key Sourcing Considerations:
– Ensure voltage compatibility and socket fitment to avoid costly returns and operational disruptions.
– Verify compliance with regional electrical and safety standards (ANSI for E26, IEC for E27).
– Prioritize suppliers offering detailed technical specifications and support for high-performance LED options.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is increasingly a decisive factor in the procurement of E26 and E27 bulbs, especially among international buyers committed to reducing their environmental footprint and meeting regulatory demands.
Environmental Impact:
Traditional incandescent bulbs consume significantly more energy and have shorter lifespans compared to LEDs, contributing to higher carbon emissions and waste. Transitioning to LED bulbs with E26 or E27 bases reduces energy consumption by up to 80%, lowering greenhouse gas emissions across the product lifecycle. Additionally, LED bulbs generate less heat, enhancing energy efficiency in climate-controlled environments common in commercial buildings.
Ethical Supply Chains:
B2B buyers are urged to scrutinize the ethical credentials of their suppliers. This includes ensuring responsible sourcing of raw materials such as rare earth elements and conflict-free components. Transparency in labor practices and adherence to fair working conditions are vital, particularly when sourcing from regions with variable regulatory enforcement.
Green Certifications and Materials:
Look for bulbs certified by recognized environmental standards such as ENERGY STAR, RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), and CE marking. Certifications like these indicate compliance with energy efficiency, hazardous substance restrictions, and safety. Moreover, some manufacturers now offer bulbs with recyclable components and packaging, aligning with circular economy principles.
Actionable Recommendations:
– Partner with suppliers who provide full lifecycle assessments or environmental product declarations (EPDs).
– Prioritize LED bulbs with certifications relevant to your market’s regulatory environment.
– Request transparency reports covering supply chain ethics and sustainability practices.
– Explore opportunities to integrate smart lighting controls that further reduce energy usage.
Evolution and Historical Context
The Edison screw base, named after Thomas Edison, revolutionized lighting by standardizing bulb sockets for easy installation and replacement. The E26 and E27 bases emerged as regional adaptations of this design, differentiated primarily by their diameter and voltage compatibility to suit the North American (E26) and European/Asian (E27) electrical systems.
This seemingly minor 1mm difference in screw diameter reflects deeper electrical infrastructure distinctions—110-120V systems in North America versus 220-240V systems in Europe and much of Asia. Over the decades, these standards have shaped manufacturing, regulatory compliance, and market expectations for lighting products.
For B2B buyers today, appreciating this history underscores the importance of careful product specification and sourcing. It also highlights the ongoing global convergence toward LED technology, which maintains the Edison base form factor while delivering superior efficiency and versatility.
By navigating these market dynamics, sourcing trends, and sustainability imperatives, international B2B buyers can optimize their procurement strategies for E26 and E27 lighting products—ensuring compatibility, regulatory compliance, operational efficiency, and environmental responsibility across diverse global markets.
Related Video: Trade Wars & China’s Innovation Surge: Reshaping Global Supply Chains
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of e26 vs e27
-
How should I vet suppliers for E26 and E27 bulbs to ensure quality and compliance for my international market?
Thorough supplier vetting is essential when sourcing E26 or E27 bulbs internationally. Verify their manufacturing certifications such as ANSI (for E26) or IEC (for E27) compliance to ensure adherence to regional safety and performance standards. Request product samples and detailed technical datasheets to confirm specifications match your market needs, including voltage and base dimensions. Check references and reviews from other B2B buyers, and assess their quality assurance processes, such as in-house testing and third-party inspections. Suppliers with transparent supply chains and responsive communication reduce risks of product quality and regulatory issues. -
Can E26 and E27 bulbs be customized for specific voltage or design requirements in different regions?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for E26 and E27 bulbs to meet regional electrical standards and application needs. Customizations may include voltage tolerance (e.g., E26 bulbs rated for 250V for export), lumen output, color temperature, and dimmability features. When negotiating customization, clarify minimum order quantities (MOQs), lead times, and additional costs. Tailored products can improve compatibility and performance, especially in markets with unique electrical grids like Africa or South America. Ensure customized bulbs undergo proper certification testing to maintain compliance. -
What are typical MOQs and lead times when ordering E26 or E27 bulbs for international B2B distribution?
MOQs for E26 and E27 bulbs vary by supplier but typically range from 500 to 5,000 units depending on customization and packaging requirements. Lead times often span 4 to 12 weeks, influenced by production capacity, complexity of customization, and shipping logistics. To optimize inventory and reduce delays, negotiate clear production schedules upfront and consider suppliers with local warehouses or regional distributors. For emerging markets like parts of Africa or the Middle East, factor in customs clearance and potential shipping disruptions when planning order timing. -
Which quality assurance certifications should I require for E26 and E27 bulbs to ensure safe international trade?
Demand certificates that align with your target markets’ electrical and safety standards. For E26 bulbs, ANSI certification and UL listing are common in North America, while E27 bulbs should comply with IEC standards and carry CE marking for Europe. Additional certifications such as RoHS (restriction of hazardous substances) and FCC may be relevant depending on application and region. Insist on factory quality control reports, batch testing results, and third-party lab certifications to verify compliance. This minimizes risks related to product recalls, legal penalties, and safety incidents. -
How can I manage logistics and shipping challenges for E26 and E27 bulbs when sourcing internationally?
Bulbs are fragile and require careful packaging to prevent damage during transit. Work with suppliers who use reinforced packaging and palletization suitable for long-distance shipping. Choose reliable freight forwarders experienced in handling electronics or lighting products. Understand import regulations, tariffs, and documentation requirements for your country, especially in Africa and South America where customs may be complex. Consider Incoterms that clearly define responsibility for shipping costs and risks. Regular communication with logistics partners helps anticipate delays and optimize supply chain efficiency. -
What payment terms are common for international bulk purchases of E26 and E27 bulbs?
Common payment terms include 30% upfront deposit with balance paid upon shipment or delivery. Letters of credit (LC) are frequently used to secure transactions, offering protection for both buyer and supplier. For established relationships, suppliers may offer net 30 to 60-day terms. Always confirm payment methods accepted (wire transfer, PayPal, etc.) and consider currency exchange risks when dealing with suppliers in different regions. Negotiate clear contract terms addressing refunds or penalties in case of defects or shipment issues to safeguard your investment. -
How can I handle disputes or quality issues with suppliers of E26 and E27 bulbs after shipment?
Establish clear contractual terms covering product specifications, inspection protocols, and remedies for non-compliance before finalizing orders. Upon receipt, conduct immediate quality inspections or engage third-party inspection services to identify defects. Document all discrepancies with photos and detailed reports. Communicate promptly and professionally with suppliers to seek resolution, such as replacement shipments or refunds. In case of unresolved disputes, leverage trade dispute resolution mechanisms, including mediation or arbitration through trade chambers or international platforms. -
Are E26 and E27 bulbs interchangeable in all international markets, and what risks should B2B buyers consider?
While E26 and E27 bulbs have similar screw sizes (26mm vs. 27mm), they are not universally interchangeable due to electrical voltage differences and threading tolerances. E26 bulbs typically suit 110-120V systems (North America, Japan), while E27 bulbs are designed for 220-240V systems (Europe, Asia, Africa). Using the wrong bulb can cause overheating, fixture damage, or safety hazards. B2B buyers must match bulbs to local voltage and socket standards and verify supplier specifications carefully. For mixed or export markets, consider sourcing bulbs rated for dual voltage or confirm compatibility with local electrical codes.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for e26 vs e27
Choosing between E26 and E27 bulb bases is a critical decision for international B2B buyers, especially when operating across diverse electrical standards in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the subtle yet impactful differences in voltage compatibility (110-120V vs. 220-240V), socket sizing, and regional compliance standards is essential to ensure product safety, longevity, and optimal performance. These factors directly influence maintenance costs, operational efficiency, and regulatory adherence in large-scale commercial and industrial lighting projects.
Strategic sourcing in this context means more than just selecting a bulb; it involves partnering with suppliers who provide accurate product specifications, regional certifications, and tailored solutions that address local market requirements. Buyers should prioritize vendors with robust quality control, flexibility to supply both E26 and E27 variants, and technical support that mitigates risks associated with voltage mismatches or fitting incompatibilities.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Looking ahead, the global trend toward energy-efficient LED technology and smart lighting systems will further elevate the importance of precision in sourcing decisions. International buyers are encouraged to leverage this knowledge to negotiate better contracts, optimize inventory management, and future-proof their lighting infrastructure. By proactively aligning sourcing strategies with regional standards and emerging technologies, businesses in Indonesia, Germany, and beyond can secure competitive advantages and sustainable growth in evolving markets.

