Guide to Led Strip Light
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for LED Strip light
- Understanding LED Strip light Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of LED Strip light
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for LED Strip light
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for LED Strip light
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for LED Strip light Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential LED Strip light Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for LED Strip light
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the LED Strip light Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of LED Strip light
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for LED Strip light
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for LED Strip light
LED strip lights have rapidly become indispensable components across a diverse range of industries, from architectural lighting and retail displays to automotive and entertainment sectors. Their versatility, energy efficiency, and customizable features position them as critical assets for businesses aiming to enhance product offerings or infrastructure aesthetics. For international B2B buyers, especially those operating in emerging and established markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of sourcing LED strip lights is vital to maintaining competitive advantage and ensuring quality.
This guide delivers a comprehensive roadmap to mastering the global LED strip light market. It covers essential aspects including the various types of LED strips—ranging from single-color to RGB and smart-enabled variants—and the materials that influence durability and performance. The manufacturing and quality control processes are examined in detail, empowering buyers to assess supplier reliability and product consistency effectively. Additionally, the guide explores sourcing strategies, cost considerations, and market dynamics tailored to the unique challenges and opportunities faced by buyers in regions like Brazil, France, and beyond.
By navigating this guide, international buyers will gain actionable insights to optimize procurement decisions, mitigate risks related to quality and compliance, and leverage supplier networks globally. Whether upgrading supply chains or launching new product lines, this resource equips decision-makers with the knowledge to confidently engage with manufacturers and distributors, ensuring their investments in LED strip lighting deliver maximum value and innovation.
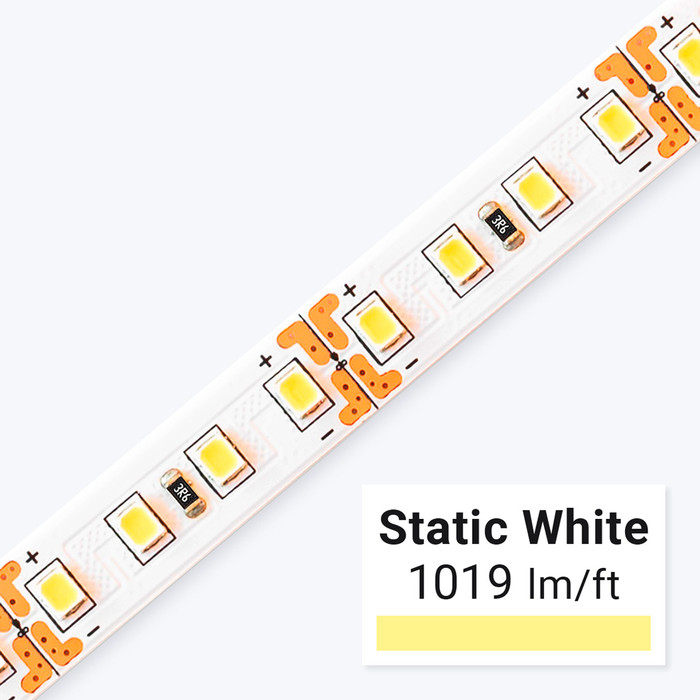
Understanding LED Strip light Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Color LED Strip | Emits a fixed color, typically white or primary colors | Retail displays, architectural lighting | Cost-effective and simple, but limited in customization |
| RGB LED Strip | Combines red, green, and blue LEDs for color mixing | Hospitality, event lighting, advertising | Versatile color options; requires controllers, higher cost |
| Addressable LED Strip | Individually controllable LEDs for dynamic effects | Digital signage, entertainment, smart lighting | Highly flexible and customizable; complex integration, premium price |
| Waterproof LED Strip | Encased in silicone or epoxy for moisture resistance | Outdoor lighting, marine applications | Durable in harsh environments; slightly higher price, less flexible |
| High-Density LED Strip | Higher LED count per meter for brighter, uniform light | Industrial lighting, high-end retail, studios | Superior brightness and uniformity; higher energy consumption |
Single Color LED Strip
Single color LED strips are the most straightforward type, emitting a constant color such as warm white, cool white, or a fixed primary color. They are ideal for applications requiring consistent illumination, like retail shelving or architectural accents. For B2B buyers, these strips offer a cost-effective solution with simplified installation and control. However, their lack of color variability limits their use in dynamic or mood-based lighting environments.
RGB LED Strip
RGB LED strips integrate red, green, and blue LEDs, allowing for a broad spectrum of colors through color mixing. This type is popular in hospitality, event venues, and advertising sectors that demand vibrant and customizable lighting. Buyers should consider the need for compatible controllers and power supplies, which add to the overall cost and complexity. The versatility in color output makes them a valuable investment for businesses targeting experiential lighting.
Addressable LED Strip
Addressable LED strips provide individual control over each LED, enabling complex lighting patterns and animations. This feature is essential for digital signage, entertainment venues, and smart building projects where dynamic lighting enhances user engagement. While they offer unparalleled customization, they require advanced controllers and programming expertise, impacting procurement and installation timelines. Buyers should assess their technical capacity to integrate these systems effectively.
Waterproof LED Strip
Encased in silicone or epoxy, waterproof LED strips are designed for outdoor or moisture-prone environments, such as marine settings, garden lighting, or industrial facilities. Their durability ensures longevity despite exposure to water, dust, or chemicals. B2B buyers must balance the higher upfront cost against reduced maintenance and replacement expenses. Waterproofing may also limit flexibility in bending and cutting during installation.
High-Density LED Strip
High-density LED strips feature a greater number of LEDs per meter, delivering intense and uniform illumination. These are suited for industrial environments, high-end retail displays, and photographic studios where light quality is paramount. Buyers should consider the increased power consumption and potential heat dissipation requirements. The enhanced brightness and smooth light output justify the investment for applications demanding premium lighting performance.
Related Video: THE SECRET OF GREAT LED STRIP LIGHT INSTALLS – COB
Key Industrial Applications of LED Strip light
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of LED Strip light | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail & Commercial | Accent lighting for product displays | Enhances product visibility, attracts customers, increases sales | Quality of light color rendering (CRI), energy efficiency, customization options |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Interior and exterior vehicle lighting | Improves aesthetic appeal, reduces energy consumption, enhances safety | Compliance with automotive standards, durability under vibration and temperature |
| Hospitality & Tourism | Ambient lighting in hotels and restaurants | Creates inviting atmosphere, reduces energy costs, flexible design | IP rating for moisture resistance, dimmability, color temperature options |
| Agriculture & Horticulture | Supplemental lighting for plant growth | Boosts crop yield, extends growing seasons, energy-efficient lighting | Spectrum control, waterproofing, lifespan under humid conditions |
| Industrial Facilities | Task and safety lighting in manufacturing plants | Enhances worker productivity and safety, lowers maintenance costs | Robustness, heat dissipation, certification for hazardous areas |
Retail & Commercial Applications
LED strip lights are widely used in retail environments to highlight merchandise and enhance visual appeal. For international buyers, especially in emerging markets like Africa and South America, sourcing LED strips with high Color Rendering Index (CRI) ensures products appear vibrant and true to color, which is crucial for luxury goods and fashion. Energy efficiency reduces operational costs, a significant factor in regions with high electricity prices. Customizable lengths and color options allow retailers to adapt lighting to various display designs and store layouts.
Automotive Manufacturing
In automotive production, LED strip lights serve as both interior accent lighting and exterior decorative or functional lighting. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East must prioritize compliance with regional automotive lighting standards and certifications. The strips need to withstand high temperatures and vibrations typical in vehicles, demanding durable materials and robust construction. Energy-efficient LED strips contribute to overall vehicle efficiency, aligning with global trends toward sustainability.
Hospitality & Tourism
Hotels and restaurants utilize LED strip lighting to create mood and ambiance that enhance guest experience. International B2B buyers should focus on LED strips with high IP ratings to resist moisture and humidity, especially in tropical climates of South America and the Middle East. Dimmable options and adjustable color temperatures allow venues to tailor lighting throughout the day and events. Energy savings and long lifespan reduce maintenance efforts and costs, important for large hospitality chains.
Agriculture & Horticulture
LED strip lights designed for horticulture provide specific light spectrums that promote photosynthesis and plant growth. Buyers in Africa and South America, where agriculture is a vital economic sector, benefit from LED solutions that extend growing seasons and improve yields in controlled environments. Waterproof and corrosion-resistant strips are essential for humid greenhouses. Energy efficiency helps reduce operational expenses, a critical factor in regions with limited power infrastructure.
Industrial Facilities
In manufacturing and industrial settings, LED strip lighting enhances task visibility and safety, contributing to higher productivity and fewer accidents. International buyers must consider strips with robust heat dissipation and certifications for use in hazardous or explosive environments, common in sectors like mining and chemical processing. Durable construction reduces downtime and maintenance costs, a key consideration for industries in Europe and the Middle East aiming to optimize operational efficiency.
Related Video: LED Strip Lighting Installs: Beginner, Intermediate and Expert Level
Strategic Material Selection Guide for LED Strip light
Analysis of Common Materials for LED Strip Light Manufacturing
When sourcing LED strip lights internationally, selecting the right material is critical for ensuring product durability, performance, and compliance with regional standards. The choice of materials impacts not only the manufacturing process but also the end-use environment, especially for buyers in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Flexible Printed Circuit Board (FPC) – Polyimide or PET Substrates
Key Properties:
FPCs used in LED strips typically employ polyimide or PET (polyethylene terephthalate) substrates, which offer excellent flexibility, thermal stability (polyimide up to 260°C), and good electrical insulation. Polyimide is more heat resistant and durable compared to PET, which is cheaper but less heat tolerant.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: High flexibility allows for curved or irregular installations; lightweight; good thermal resistance (especially polyimide); compatible with automated manufacturing.
– Cons: PET substrates have lower heat resistance and can degrade faster under high temperatures; polyimide is more expensive; both can be vulnerable to mechanical damage if not properly protected.
Impact on Application:
Flexible PCBs are ideal for indoor and some outdoor LED strip applications where bending and shaping around corners is required. For humid or outdoor environments, additional waterproof coatings or encapsulations are necessary to prevent moisture ingress.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions with high humidity or temperature fluctuations (e.g., Middle East, Brazil) should prioritize polyimide-based FPCs for enhanced durability. Compliance with IEC and RoHS standards is common in Europe and increasingly demanded globally. Understanding local electrical safety and fire retardancy standards (e.g., EN 60335 in Europe) is essential when specifying materials.
2. Silicone Rubber Encapsulation
Key Properties:
Silicone rubber is widely used as an encapsulant or coating for LED strips due to its excellent UV resistance, flexibility, and high temperature tolerance (typically -60°C to +200°C). It also provides outstanding waterproofing and chemical resistance.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Superior weatherproofing; flexible and durable; resistant to UV, ozone, and chemicals; suitable for harsh outdoor environments.
– Cons: Higher material and processing costs; more complex manufacturing steps; potential issues with adhesion if not properly applied.
Impact on Application:
Silicone-encapsulated LED strips are preferred for outdoor, marine, or industrial applications where exposure to sunlight, moisture, and chemicals is expected. This makes them highly suitable for markets in Africa and the Middle East with intense sunlight and dust conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify compliance with IP ratings (IP65, IP67, or IP68) for waterproofing. European buyers often require REACH compliance and adherence to EN standards for outdoor lighting. In South America, durability against tropical climates is a priority, making silicone a favored choice despite the higher cost.
3. Rigid Aluminum PCB
Key Properties:
Rigid aluminum PCBs provide excellent thermal conductivity, allowing efficient heat dissipation from LEDs. They are typically rated for operating temperatures up to 130°C and offer good mechanical strength and corrosion resistance when anodized.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Superior heat management improves LED lifespan and brightness; robust mechanical properties; corrosion-resistant with anodized finish; relatively cost-effective.
– Cons: Less flexible, limiting design options; heavier than FPC; may require additional waterproofing for outdoor use.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum PCBs are ideal for high-power LED strips used in commercial or industrial lighting where heat dissipation is critical. They are less suitable for applications requiring flexibility or complex shapes.
Considerations for International Buyers:
European and Middle Eastern buyers often demand compliance with DIN and IEC thermal management standards. Aluminum PCBs are favored in regions with high ambient temperatures to prevent LED overheating. Corrosion resistance is crucial for coastal areas in Africa and South America, necessitating quality anodization.
4. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Housing or Coating
Key Properties:
PVC is commonly used for the outer housing or coating of LED strips due to its low cost, ease of processing, and reasonable chemical resistance. It offers moderate temperature resistance (up to ~60°C) and basic mechanical protection.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Cost-effective; easy to mold and extrude; provides basic protection against dust and minor impacts; widely available.
– Cons: Limited temperature tolerance; can become brittle or yellow over time under UV exposure; less environmentally friendly; lower chemical resistance compared to silicone.
Impact on Application:
PVC-coated LED strips are generally suited for indoor applications with controlled environments. They are less appropriate for outdoor or high-temperature settings.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in Europe should consider environmental regulations restricting PVC use (e.g., RoHS, REACH). In Africa and South America, PVC remains popular due to cost sensitivity but may require additional UV stabilizers for durability. Compliance with ASTM or ISO standards for plastic materials is advisable.
Summary Table of Materials for LED Strip Light
| Material | Typical Use Case for LED Strip light | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flexible Printed Circuit Board (Polyimide/PET) | Flexible indoor/outdoor LED strips requiring bending | High flexibility and good thermal stability (polyimide) | PET has lower heat resistance; polyimide is costly | Medium |
| Silicone Rubber Encapsulation | Outdoor, marine, industrial LED strips requiring waterproofing | Excellent UV and chemical resistance; superior waterproofing | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Rigid Aluminum PCB | High-power commercial/industrial LED strips needing heat dissipation | Superior thermal management and mechanical strength | Limited flexibility; heavier; requires waterproofing | Medium |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Housing/Coating | Indoor LED strips with basic protection | Cost-effective and easy to process | Low temperature tolerance; UV degradation; environmental concerns | Low |
This guide equips international B2B buyers with critical insights to select materials that align with their regional environmental conditions, regulatory requirements, and application needs, ensuring optimal LED strip light performance and longevity.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for LED Strip light
Overview of Manufacturing Processes for LED Strip Lights
The manufacturing of LED strip lights involves a series of meticulously controlled stages designed to ensure product reliability, efficiency, and longevity. For B2B buyers, understanding these stages is critical to evaluating supplier capabilities and product quality.
1. Material Preparation
This initial phase involves sourcing high-quality raw materials including LED chips, flexible printed circuit boards (FPCBs), resistors, capacitors, and adhesives. The FPCBs are typically made from copper-clad laminates coated with a flexible polymer such as polyimide or polyester. Material quality here influences the strip’s durability and electrical performance. Suppliers often procure LED chips from certified manufacturers with proven luminous efficacy and lifespan.
2. Forming and Circuit Fabrication
In this stage, the FPCBs are precisely cut and etched to form the circuitry paths. Techniques such as photolithography and chemical etching define the copper traces that conduct electricity. Automated machinery places solder masks and protective coatings to prevent oxidation and electrical shorts. Accurate alignment and circuit integrity are crucial to ensure consistent electrical flow and heat dissipation.
3. Component Assembly and Soldering
Automated pick-and-place machines position LED chips and passive components onto the FPCBs. Surface mount technology (SMT) is the dominant method here, ensuring high precision and repeatability. Following placement, reflow soldering secures components, creating robust electrical and mechanical connections. The assembly process often includes the integration of resistors and connectors tailored to client specifications.
4. Encapsulation and Finishing
After assembly, LED strips undergo encapsulation to protect against environmental factors such as moisture and dust. This can involve silicone or epoxy coatings, which also contribute to flexibility and heat resistance. Additional finishing steps include printing product information, cutting to length, and attaching connectors or adhesive backing for installation ease.
Quality Assurance Framework in LED Strip Light Production
Robust quality control (QC) is non-negotiable in LED strip light manufacturing due to the product’s application in critical lighting solutions. International B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers with comprehensive QC processes aligned with global standards.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key International and Industry Standards
– ISO 9001: The foundation for quality management systems, ensuring consistent production processes and continuous improvement.
– CE Marking: Mandatory for European markets, confirming compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental requirements.
– RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): Ensures materials used are free from harmful substances like lead and mercury, crucial for Europe and increasingly for other regions.
– UL Certification: Important for North American markets but also recognized globally, focusing on electrical safety.
– IP Ratings: Indicate the ingress protection level against dust and water, essential for buyers sourcing LED strips for outdoor or industrial use.
Critical Quality Control Checkpoints
1. Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
IQC involves inspection and testing of raw materials and components before production. This includes verifying LED chip specifications, PCB integrity, and solder paste quality. For international buyers, requesting IQC documentation helps ensure that suppliers do not use substandard inputs.
2. In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
During manufacturing, IPQC monitors assembly accuracy, solder joint quality, and component placement using automated optical inspection (AOI) systems and manual checks. This stage minimizes defects early in the process, reducing waste and rework costs.
3. Final Quality Control (FQC)
The FQC stage tests finished LED strip lights for electrical performance (voltage, current, brightness), physical durability, and visual inspection for defects. Functional tests include:
- Lumen output and color temperature measurement to ensure light consistency.
- Electrical safety tests including insulation resistance and dielectric withstand voltage.
- Environmental tests such as thermal cycling and humidity exposure to simulate operational conditions.
- Flexibility and adhesion tests to verify mechanical robustness.
Testing Methods and Technology Utilized
- Spectroradiometers and Integrating Spheres: Measure luminous flux, color rendering index (CRI), and color temperature to verify lighting performance.
- X-ray Inspection: Detects hidden solder defects in multilayer PCBs.
- Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): Identifies component misplacements, solder bridges, and surface defects.
- Electrical Testing Stations: Conduct continuity and short circuit tests to ensure safety and functionality.
- Environmental Chambers: Subject samples to accelerated aging, temperature extremes, and moisture to assess product lifespan and reliability.
How B2B Buyers Can Verify Supplier Quality Controls
Supplier Audits: Conduct or commission on-site audits focusing on manufacturing capabilities, QC processes, and compliance with relevant standards. Audits help validate the supplier’s claims and identify potential risks.
Review of Quality Documentation: Request ISO certificates, CE declarations, test reports, and batch traceability documents. Comprehensive documentation reflects transparency and adherence to quality protocols.
Third-Party Inspection and Testing: Engage independent laboratories to perform random batch testing or pre-shipment inspections. This is particularly important for buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East where local regulatory oversight may be limited.
Sample Evaluation: Prior to bulk orders, assess samples under your own testing conditions or through trusted local partners. This step confirms that product specifications meet your operational and regulatory requirements.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Markets
-
Africa and South America: Regulatory frameworks may vary widely. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with internationally recognized certifications (ISO, CE, RoHS) and insist on third-party testing to mitigate risks associated with inconsistent local standards. Import regulations often require compliance documentation to clear customs smoothly.
-
Middle East: Many countries emphasize CE and RoHS compliance, especially for products imported from Europe or Asia. Heat resistance and IP ratings are critical due to harsh environmental conditions.
-
Europe (e.g., France): Strict adherence to CE marking, RoHS, and REACH regulations is mandatory. Buyers should verify that suppliers maintain updated certifications and conduct regular compliance audits. Energy efficiency and eco-friendly materials are increasingly important.
Final Recommendations for B2B Buyers
- Prioritize suppliers with end-to-end quality management systems certified by ISO 9001 or equivalent.
- Insist on transparent QC documentation and access to production data for traceability.
- Utilize third-party inspection services to independently verify supplier claims, especially for initial orders.
- Understand local regulatory requirements in your target markets and ensure suppliers comply accordingly.
- Establish long-term partnerships with manufacturers who demonstrate consistent quality and responsiveness to QC feedback.
By thoroughly understanding manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that reduce risks, optimize costs, and secure high-quality LED strip lighting solutions tailored to their markets.
Related Video: How are LED Chips and LED Encapsulation made – LED Strip Light Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for LED Strip light Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of LED strip lights is crucial for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize procurement strategies, especially in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis breaks down key cost components, pricing influencers, and practical tips to enhance negotiation and purchasing decisions.
Core Cost Components in LED Strip Light Manufacturing
-
Materials
The primary raw materials include LED chips, flexible PCB substrates, resistors, connectors, and protective coatings. High-quality LEDs with better brightness and longevity typically command higher costs. The choice between standard and premium materials significantly affects the base cost. -
Labor
Labor costs vary widely depending on the manufacturing country. Facilities in Asia often offer lower labor expenses compared to Europe or the Middle East. However, skilled labor for precise assembly and quality assurance can justify higher labor costs for premium products. -
Manufacturing Overhead
This includes factory utilities, equipment depreciation, and indirect labor. Efficient production lines and automation can reduce overhead, impacting final pricing. -
Tooling and Setup
Custom designs or specific tooling requirements increase upfront costs. Buyers requesting unique lengths, color temperatures, or features like waterproofing should anticipate higher tooling expenses. -
Quality Control (QC)
Rigorous QC processes, including photometric testing and durability checks, add to costs but ensure product reliability. Certifications such as CE, RoHS, or UL further increase QC expenses but are critical for compliance in many international markets. -
Logistics and Freight
Shipping costs vary based on origin, destination, and transport mode (air vs. sea freight). Buyers from remote or inland regions in Africa or South America may face higher logistics expenses, including customs duties and inland transportation. -
Supplier Margin
Manufacturers and distributors include profit margins that reflect market competition, brand positioning, and volume commitments.
Key Price Influencers for International Buyers
-
Order Volume / Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)
Larger orders typically attract volume discounts, lowering per-unit costs. Buyers should balance MOQ requirements against storage and cash flow constraints. -
Product Specifications and Customization
Customized lengths, color options, dimming capabilities, or advanced features like smart control increase costs. Standard models are usually more economical. -
Material Grade and Certification Level
Products with international certifications (e.g., CE for Europe, UL for the US market) cost more but facilitate smoother market entry and reduce compliance risks. -
Supplier Reputation and Location
Established suppliers with reliable delivery and after-sales support may charge premiums. Proximity to buyer markets can reduce logistics and lead times. -
Incoterms
The choice of Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP) significantly impacts total landed cost. For instance, buyers opting for FOB bear shipping and import duties, while DDP places these responsibilities on the supplier, often reflected in higher unit prices.
Strategic Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency and Negotiation
-
Leverage Volume for Better Pricing
Consolidate orders where possible or partner with other buyers to meet MOQ thresholds, unlocking discounts. -
Clarify Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Consider not just unit price but warranty terms, energy efficiency, expected lifespan, and maintenance costs. Cheaper LED strips may incur higher replacement or operational expenses. -
Negotiate on Multiple Fronts
Discuss payment terms, lead times, packaging, and after-sales support alongside unit price to create a comprehensive value proposition. -
Understand Regional Pricing Nuances
African and South American buyers should factor in higher import duties and potential delays, whereas European buyers may prioritize compliance and certification costs. -
Request Transparent Cost Breakdowns
Encouraging suppliers to share detailed cost components fosters trust and uncovers negotiation opportunities. -
Plan for Currency Fluctuations and Payment Methods
International transactions are subject to exchange rate risks; negotiating prices in stable currencies or using forward contracts can mitigate this.
Indicative Pricing Disclaimer
Prices for LED strip lights vary widely depending on product quality, specifications, order size, and sourcing location. Typical unit prices may range from $0.50 to $5.00 per meter for standard models, excluding shipping and taxes. Buyers should obtain multiple quotations and conduct due diligence to confirm current market rates.
By carefully analyzing these cost elements and pricing influencers, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that optimize procurement costs while ensuring product quality and compliance. Strategic negotiation and a holistic view of total cost will be particularly beneficial for buyers navigating diverse regional challenges in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Spotlight on Potential LED Strip light Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section offers a look at a few manufacturers active in the ‘LED Strip light’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct their own extensive due diligence before any engagement. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for LED Strip light
Key Technical Properties of LED Strip Lights for B2B Buyers
When sourcing LED strip lights internationally, understanding critical technical specifications ensures you select products that meet your quality, durability, and application needs. Here are the essential properties to evaluate:
-
Material Grade and PCB Quality
The base of an LED strip light is typically a flexible printed circuit board (PCB). High-grade PCBs use materials such as FR4 or aluminum, which affect heat dissipation and longevity. For B2B buyers, opting for premium material grades reduces failure rates, especially in demanding environments common in Africa and the Middle East where heat tolerance is crucial. -
Color Temperature (CCT) and Color Rendering Index (CRI)
Color temperature, measured in Kelvins (K), defines the light’s warmth or coolness (e.g., 2700K for warm white, 6500K for daylight). CRI, rated from 0 to 100, indicates how accurately colors appear under the LED light. For projects in retail or hospitality sectors in Europe and South America, high CRI (above 80) ensures vibrant, natural lighting, enhancing customer experience. -
LED Density and Brightness (Lumens per Meter)
LED density (number of LEDs per meter) directly impacts brightness and uniformity. A higher LED count usually means smoother light distribution but may increase power consumption. Understanding lumens per meter helps buyers balance energy efficiency with lighting performance, a key consideration in energy-conscious markets like France and Brazil. -
Power Consumption and Voltage Compatibility
LED strips commonly operate at 12V or 24V DC. Lower voltage strips are safer but may require thicker wiring for longer runs. Power consumption, measured in watts per meter, affects operational costs and driver selection. International buyers must confirm voltage compatibility with local electrical standards to avoid costly modifications. -
Ingress Protection (IP) Rating
The IP rating defines resistance to dust and water (e.g., IP20 for indoor use, IP65 or higher for outdoor or damp environments). For buyers in humid or outdoor markets like coastal regions of South America or the Middle East, selecting an appropriate IP rating ensures durability and compliance with safety regulations. -
Tolerance and Quality Control Standards
Tolerance indicates the allowable deviation in LED performance specs such as brightness or color temperature. Stricter tolerances mean more consistent product quality. Requesting suppliers’ quality control certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) helps minimize variability and maintain brand reputation across diverse markets.
Essential Trade Terminology for International LED Strip Light Buyers
Navigating B2B sourcing requires familiarity with key trade terms that impact procurement, negotiations, and logistics:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to manufacturers who produce LED strip lights that can be rebranded by buyers. OEM relationships allow customization in design, packaging, and specifications, enabling businesses to create unique product lines without investing in manufacturing infrastructure. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell in one order. MOQs vary widely and impact inventory planning and cash flow. Buyers from emerging markets should negotiate MOQs that align with market demand to avoid overstock or stockouts. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal inquiry sent to suppliers to obtain pricing, lead times, and terms. A detailed RFQ specifying technical requirements and quantities helps streamline supplier responses and supports transparent comparison, critical for international buyers managing multiple suppliers. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized terms defining responsibilities between buyers and sellers regarding shipment, insurance, and customs clearance (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP). Understanding Incoterms protects buyers from hidden costs and clarifies risk transfer points during international shipping. -
Lead Time
The total time from placing an order to receiving goods. Lead times affect project scheduling and cash flow management. For B2B buyers in regions with complex import procedures, factoring realistic lead times reduces delays and penalties. -
Bin Number / Bin Code
A classification code used by LED manufacturers to indicate specific performance characteristics like brightness and color consistency. Requesting bin numbers ensures uniformity across batches, critical for large-scale lighting projects requiring consistent visual output.
By mastering these technical specifications and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, negotiate better deals, and source LED strip lights that deliver reliable performance and meet market-specific requirements. This knowledge is particularly valuable when engaging suppliers across different continents with varying manufacturing standards and trade practices.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the LED Strip light Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global LED strip light market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient and versatile lighting solutions across commercial, industrial, and residential sectors. Key market drivers include rapid urbanization, smart city initiatives, and rising investments in infrastructure, particularly in emerging economies across Africa, South America, and the Middle East. In Europe, countries like France prioritize energy conservation and innovative lighting designs, fueling demand for high-performance LED strip lighting.
Emerging B2B sourcing trends reflect a shift towards customization, with buyers seeking tailored solutions that integrate smart controls, color tunability, and enhanced durability. Modular and flexible LED strips that can adapt to varied architectural and industrial applications are gaining traction. Additionally, international buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who offer comprehensive product certifications (such as CE, RoHS, and UL), ensuring compliance with regional safety and quality standards.
From a market dynamics perspective, global supply chain diversification is critical. Buyers from Africa and South America face challenges related to logistics and import tariffs, prompting a growing interest in regional manufacturing hubs or partnerships in Asia and Europe. Digital sourcing platforms and virtual product showcases are becoming vital tools to facilitate transparent supplier evaluation and streamline procurement processes. For Middle Eastern buyers, the integration of LED strip lighting into large-scale commercial projects, including hospitality and retail, continues to expand, emphasizing the need for scalable, cost-effective solutions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a decisive factor in the LED strip light supply chain. Energy efficiency is a core attribute of LED technology, but buyers must look beyond operational savings to assess the environmental footprint of manufacturing and materials. Ethical sourcing involves ensuring that raw materials, such as rare earth elements and semiconductors, are obtained responsibly, avoiding conflict minerals and minimizing ecological disruption.
International B2B buyers are increasingly demanding transparency in supplier practices, favoring manufacturers that comply with environmental standards like ISO 14001 and engage in circular economy initiatives, such as recycling programs for electronic waste. The adoption of ‘green’ certifications—including Energy Star, TUV Rheinland’s sustainable product labels, and eco-design compliance—serves as a benchmark for responsible sourcing and product lifecycle management.
For regions like Europe, sustainability regulations are stringent, compelling buyers to prioritize vendors with proven commitments to reducing carbon footprints and hazardous substances. Similarly, buyers from Africa and South America are recognizing the reputational and operational benefits of partnering with sustainable suppliers, who can also provide documentation to meet local environmental regulations and international trade requirements. Ethical supply chains not only mitigate risks but also align with growing corporate social responsibility (CSR) mandates worldwide.
Brief Evolution and Historical Context
LED strip lighting has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 2000s, transitioning from simple, low-brightness decorative elements to sophisticated, high-efficiency lighting systems. Initially, LED strips were primarily used for accent lighting with limited color options and low durability. Advances in semiconductor technology and materials science have enabled the development of brighter, more energy-efficient LEDs with extended lifespans.
The introduction of flexible circuit boards and surface-mounted device (SMD) LEDs expanded the application scope, allowing integration into architectural lighting, signage, and industrial environments. Recent innovations include smart LED strips with IoT connectivity, enabling remote control and automation, which is particularly appealing to commercial buyers looking to enhance operational efficiency and user experience.
Understanding this evolution helps B2B buyers appreciate the technological maturity and varied application potential of LED strip lights, informing smarter sourcing decisions aligned with future-ready infrastructure projects.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of LED Strip light
-
How can I effectively vet LED strip light suppliers from different regions such as Asia or Europe?
Supplier vetting is crucial to ensure product quality and reliability. Start by verifying certifications like ISO 9001, CE, RoHS, and UL relevant to your market. Request samples and conduct performance tests under your operating conditions. Review the supplier’s export history and client references, especially from your region. Utilize third-party inspection services for factory audits and quality checks. Also, assess financial stability and communication responsiveness. For African, South American, Middle Eastern, and European buyers, partnering with suppliers who understand regional compliance and shipping nuances is highly beneficial. -
What customization options are typically available for LED strip lights, and how do they affect pricing and lead times?
LED strip light manufacturers often offer customization in color temperature, IP rating (waterproofing), length, LED density, voltage, and control compatibility (e.g., DMX, Zigbee). Custom PCB designs or branding options may also be available. Custom orders generally require higher Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) and extend lead times by 2–6 weeks depending on complexity. Pricing increases with bespoke features or certification requirements. Discuss your specific application needs upfront to balance customization benefits with cost and delivery expectations. -
What are common MOQs and lead times for international LED strip light orders, and how can buyers negotiate better terms?
MOQs vary widely, typically ranging from 500 to 5,000 meters per SKU for standard models. Lead times average 4–8 weeks, influenced by order size, customization, and factory workload. Buyers from emerging markets can negotiate MOQs by consolidating orders across product variants or working with suppliers offering mixed SKU shipments. Establishing long-term partnerships and committing to repeat orders often unlocks more flexible terms. Early order placement before peak seasons and transparent communication also improve lead time predictability. -
Which quality assurance certifications and testing standards should B2B buyers prioritize when sourcing LED strip lights internationally?
Key certifications include CE (Europe), RoHS (hazardous substances restriction), UL or ETL (North America safety), and IEC standards. For waterproof LED strips, IP ratings (IP65, IP67, IP68) are essential. Buyers should also demand photometric data, lumen maintenance reports, and thermal management tests. Verifying compliance with local electrical regulations in your target market (e.g., INMETRO in Brazil, SASO in Saudi Arabia) prevents customs delays and legal issues. Insist on supplier-provided test reports or third-party lab certifications before bulk purchasing.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
What are best practices for managing international logistics and customs clearance of LED strip light shipments?
Opt for suppliers experienced with international freight forwarding and Incoterms such as FOB or CIF. Prioritize suppliers who provide complete documentation: commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and compliance certificates. Work closely with freight forwarders familiar with your region’s import regulations to avoid delays. For Africa and South America, consider port infrastructure and customs clearance efficiency when selecting shipping routes. Insurance coverage and tracking solutions mitigate risks. Early engagement with customs brokers ensures smoother clearance and cost transparency. -
How should payment terms be structured to protect both buyer and supplier interests in cross-border LED strip light transactions?
Common payment methods include Letters of Credit (LC), Telegraphic Transfers (T/T), and escrow services. LCs offer strong security but involve higher bank fees and paperwork, suitable for large orders. T/T payments typically require 30% upfront and 70% upon shipment or inspection. Negotiate milestone payments aligned with order progress to reduce risk. For new suppliers, consider third-party inspection before final payment. Ensure contracts clearly define payment conditions, penalties, and dispute resolution mechanisms to protect both parties. -
What strategies can B2B buyers employ to resolve disputes or quality issues with LED strip light suppliers internationally?
Prompt communication is key. Document all discrepancies with photos and test reports. Reference agreed-upon contract terms and quality standards. Engage suppliers in collaborative problem-solving, possibly involving third-party inspection agencies to validate claims. For unresolved disputes, mediation or arbitration under international trade laws (e.g., ICC rules) can be effective alternatives to litigation. Maintain professional relations to facilitate amicable solutions. Consider including warranty clauses and penalty terms in contracts to safeguard your interests. -
How can buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe leverage regional trade agreements or sourcing hubs to optimize costs and delivery times?
Utilizing regional trade agreements like the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), Mercosur in South America, or the EU’s trade frameworks can reduce tariffs and simplify customs. Sourcing from established regional hubs (e.g., Turkey for Europe/Middle East, UAE for the Gulf, or China’s nearby ports for South America) may shorten lead times and lower shipping costs. Collaborate with local agents or sourcing offices to navigate regional logistics and regulatory environments efficiently. Leveraging these advantages enhances competitiveness and supply chain resilience.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for LED Strip light
Strategic sourcing of LED strip lights presents a compelling opportunity for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize cost, quality, and innovation. Key takeaways include the importance of vetting suppliers rigorously, prioritizing manufacturers with strong quality control and compliance certifications, and leveraging regional expertise to navigate logistics and regulatory landscapes effectively. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local market demands and aligning sourcing strategies accordingly is essential to maximize ROI and customer satisfaction.
Key strategic considerations include:
- Building long-term partnerships with reliable manufacturers to ensure supply chain resilience.
- Emphasizing product customization and energy efficiency to meet evolving market trends.
- Utilizing digital sourcing platforms and trade networks to access competitive pricing and advanced technologies.
- Staying informed about geopolitical shifts and trade policies that may impact procurement costs and timelines.
Looking ahead, the LED strip light market is poised for continued growth driven by rising demand for smart lighting and sustainable solutions. Buyers who adopt a proactive, strategic sourcing approach will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging innovations and regional opportunities. International buyers are encouraged to engage deeply with suppliers, invest in market intelligence, and prioritize sustainability to future-proof their supply chains and meet increasing customer expectations worldwide.
