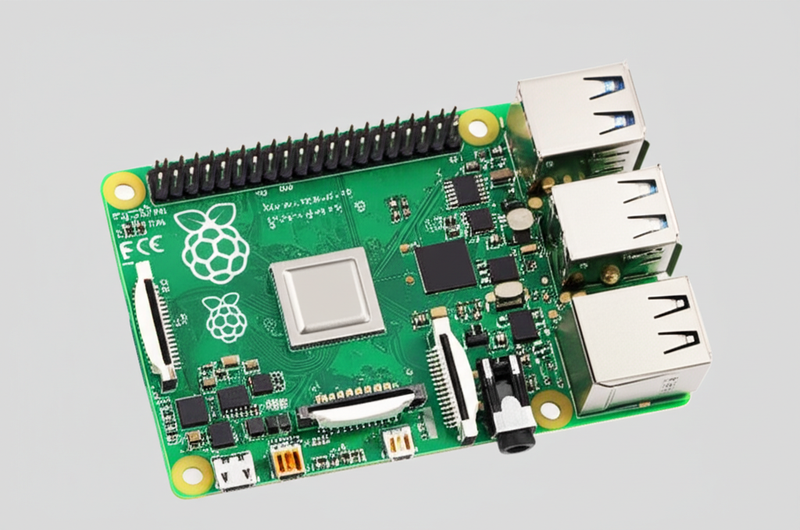
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for drive led strip with raspberry pi 4
The integration of LED strips with Raspberry Pi 4 technology is transforming industries by enabling dynamic, customizable lighting solutions that are both cost-effective and scalable. For international B2B buyers, especially those in emerging and diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including tech hubs like Vietnam and Saudi Arabia—understanding the nuances of driving LED strips with Raspberry Pi 4 is crucial to sourcing competitive, high-quality components.
This guide delivers a comprehensive roadmap covering critical aspects such as the different types of LED strips—addressable and non-addressable—their electrical and material specifications, and how the Raspberry Pi 4’s GPIO interface and software ecosystem can be leveraged to maximize performance. Buyers will also gain insights into manufacturing standards, quality control protocols, and supplier evaluation criteria, ensuring reliability and compliance in global supply chains.
Additionally, the guide offers detailed cost analysis and market trends, helping buyers navigate pricing structures and identify value-driven procurement opportunities. A dedicated FAQ section addresses common technical and logistical queries, empowering decision-makers to mitigate risks and streamline project deployment.
By consolidating technical know-how and strategic sourcing intelligence, this resource equips international B2B buyers with the tools to make informed, confident purchasing decisions—whether for industrial automation, smart building projects, or bespoke lighting applications—ultimately unlocking new growth potential across diverse global markets.
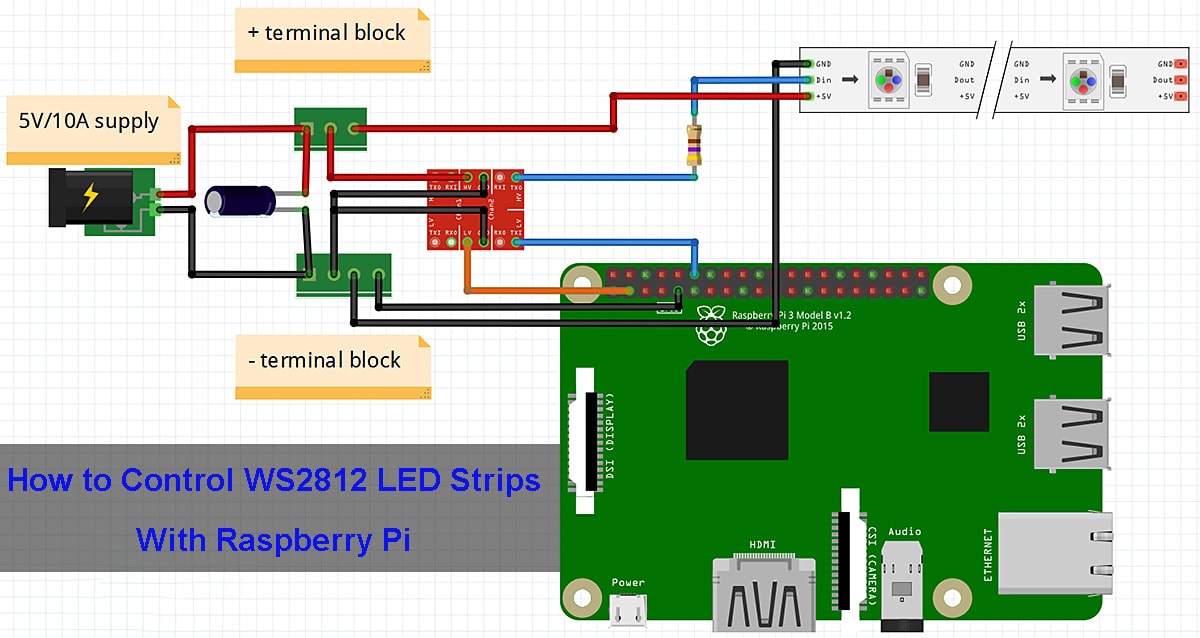
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Understanding drive led strip with raspberry pi 4 Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Single LED Control | Controls individual LEDs or simple LED circuits via GPIO pins | Prototyping, educational kits, simple indicators | Pros: Low cost, simple setup; Cons: Limited scalability, no color control |
| WS2812B (Addressable RGB) Strip | Fully addressable RGB LEDs with integrated driver ICs | Dynamic lighting, signage, decorative displays | Pros: High customization, vibrant colors; Cons: Requires power management, higher cost |
| 12V LED Strip with Step-Down | 12V LED strips requiring DC-DC step-down for Pi compatibility | Industrial lighting, large-scale installations | Pros: Longer runs possible, robust; Cons: Additional hardware needed, complexity |
| Waterproof/Flexible Variants | Flexible PCBs with optional waterproof coating | Outdoor installations, harsh environments | Pros: Durability, versatility; Cons: Higher price, may need specialized connectors |
| High-Density LED Strips | High LED node density per meter (e.g., 144 LEDs/m) | High-resolution displays, advanced visual effects | Pros: Detailed effects, professional-grade; Cons: Higher power consumption, cost |
Basic Single LED Control
This type involves controlling individual LEDs or simple LED circuits directly through Raspberry Pi 4 GPIO pins. It is ideal for basic prototyping, learning, or simple indicator applications. B2B buyers focusing on educational kits or entry-level IoT devices will find this option cost-effective and straightforward to implement. However, it lacks scalability and color control capabilities, limiting its use in complex lighting projects.
WS2812B (Addressable RGB) Strip
WS2812B strips are fully addressable RGB LED strips with integrated IC drivers allowing independent color and brightness control of each LED node. This type is highly favored in dynamic lighting, advertising displays, and decorative installations. For B2B buyers, the customization capabilities enable innovative product offerings, but attention must be paid to power supply design and data signal integrity to ensure stable operation. These strips are well-suited for markets in Europe and the Middle East where vibrant, programmable lighting solutions are in demand.
12V LED Strip with Step-Down
Some LED strips operate at 12V, necessitating additional hardware such as DC-DC step-down converters to interface safely with the 5V Raspberry Pi 4. These strips are beneficial in industrial or large-scale lighting projects where longer runs and higher power are required. B2B buyers should factor in the increased complexity and hardware costs, but gain from robust and scalable lighting solutions suitable for harsh environments often encountered in African and South American markets.
Waterproof/Flexible Variants
Flexible LED strips with waterproof coatings cater to outdoor or harsh environmental applications. These variants offer durability and adaptability, making them suitable for architectural lighting, outdoor advertising, and marine uses. B2B buyers in regions with challenging climates, such as the Middle East and parts of Africa, will appreciate the extended lifespan and reliability. However, the premium pricing and need for specialized connectors may influence procurement decisions.
High-Density LED Strips
High-density LED strips pack more LED nodes per meter (e.g., 144 LEDs/m), enabling finely detailed lighting effects and high-resolution displays. They are perfect for advanced visual installations, stage lighting, and digital signage requiring professional-grade output. B2B buyers must consider increased power consumption and higher initial costs but gain a competitive edge by offering cutting-edge, visually striking products to clients in Europe and emerging markets seeking premium lighting solutions.
Related Video: How To Use Addressable RGB WS2812B LED Strips With a Raspberry Pi Single Board Computer
Key Industrial Applications of drive led strip with raspberry pi 4
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of drive led strip with raspberry pi 4 | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing & Automation | Visual status indicators and alert systems on production lines | Real-time monitoring reduces downtime and improves operational efficiency | Robustness of LED strips, compatibility with industrial environments, power supply stability, local technical support availability |
| Retail & Advertising | Dynamic digital signage and interactive product displays | Enhances customer engagement and drives sales through customizable lighting | High color accuracy, ease of programming, energy efficiency, and scalability for different store sizes |
| Smart Building & Infrastructure | Ambient lighting control and energy-efficient illumination in smart offices and public spaces | Lower energy consumption and improved occupant comfort through adaptive lighting | Compliance with local electrical standards, integration with existing building management systems, and durability |
| Entertainment & Events | Stage lighting, mood lighting, and synchronized light shows | Creates immersive experiences and flexible lighting arrangements | Flexibility in programming, portability, power management, and compatibility with control software |
| Agriculture & Horticulture | Controlled spectrum grow lights for plant growth optimization | Increases crop yield and quality by providing tailored light cycles | Spectrum customization, weather resistance, power efficiency, and ease of integration with environmental sensors |
Manufacturing & Automation
In manufacturing plants, drive LED strips controlled by Raspberry Pi 4 serve as visual status indicators along production lines. These LED strips can signal machine states—such as operational, warning, or fault conditions—through color-coded lighting, enabling quick identification of issues and reducing downtime. For B2B buyers in regions like South America and the Middle East, sourcing LED strips with industrial-grade durability and stable power supplies is essential to withstand harsh factory conditions. Additionally, compatibility with existing automation systems and availability of local technical support are critical to ensure seamless integration and maintenance.
Retail & Advertising
Retailers and advertising agencies leverage Raspberry Pi 4-driven LED strips for dynamic digital signage and interactive product displays. These installations captivate customers with vibrant, customizable lighting effects that highlight promotions or brand messages. Buyers in Africa and Europe should prioritize sourcing LED strips with high color accuracy and energy efficiency to reduce operational costs. The ease of programming and scalability of lighting solutions are also important to accommodate diverse store layouts and evolving marketing needs, ensuring long-term value.
Smart Building & Infrastructure
In smart buildings, LED strips controlled by Raspberry Pi 4 enable adaptive ambient lighting that enhances occupant comfort and reduces energy consumption. For instance, office environments can adjust lighting intensity and color temperature based on time of day or occupancy. International buyers, especially from regions with strict electrical regulations such as Vietnam and Saudi Arabia, must ensure that LED products comply with local standards and can integrate with existing building management systems. Durability and long lifespan are also key factors to minimize maintenance in public infrastructure projects.
Entertainment & Events
Event organizers and entertainment venues utilize Raspberry Pi 4-driven LED strips for stage lighting and synchronized light shows, creating engaging and immersive experiences. The ability to program complex animations and control multiple LED strips simultaneously offers flexibility for different event scales and themes. For B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East, sourcing LED strips with robust power management and compatibility with popular lighting control software is vital. Portability and ease of setup also influence procurement decisions for frequent event installations.
Agriculture & Horticulture
Agricultural businesses are adopting LED strips powered by Raspberry Pi 4 for controlled spectrum grow lights that optimize plant growth cycles. By tailoring light intensity and wavelengths, growers can enhance crop yields and quality while reducing energy consumption compared to traditional lighting. Buyers in Africa and South America should look for LED solutions that offer spectrum customization, weather resistance for greenhouse environments, and seamless integration with environmental sensors. These features support precision agriculture and sustainable farming practices critical in these regions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for drive led strip with raspberry pi 4
Analysis of Common Materials for Drive LED Strip with Raspberry Pi 4
When selecting materials for drive LED strips integrated with Raspberry Pi 4, B2B buyers must consider electrical performance, environmental durability, and regional compliance standards. Below is a detailed analysis of four common materials used in LED strip manufacturing and their implications for international buyers.
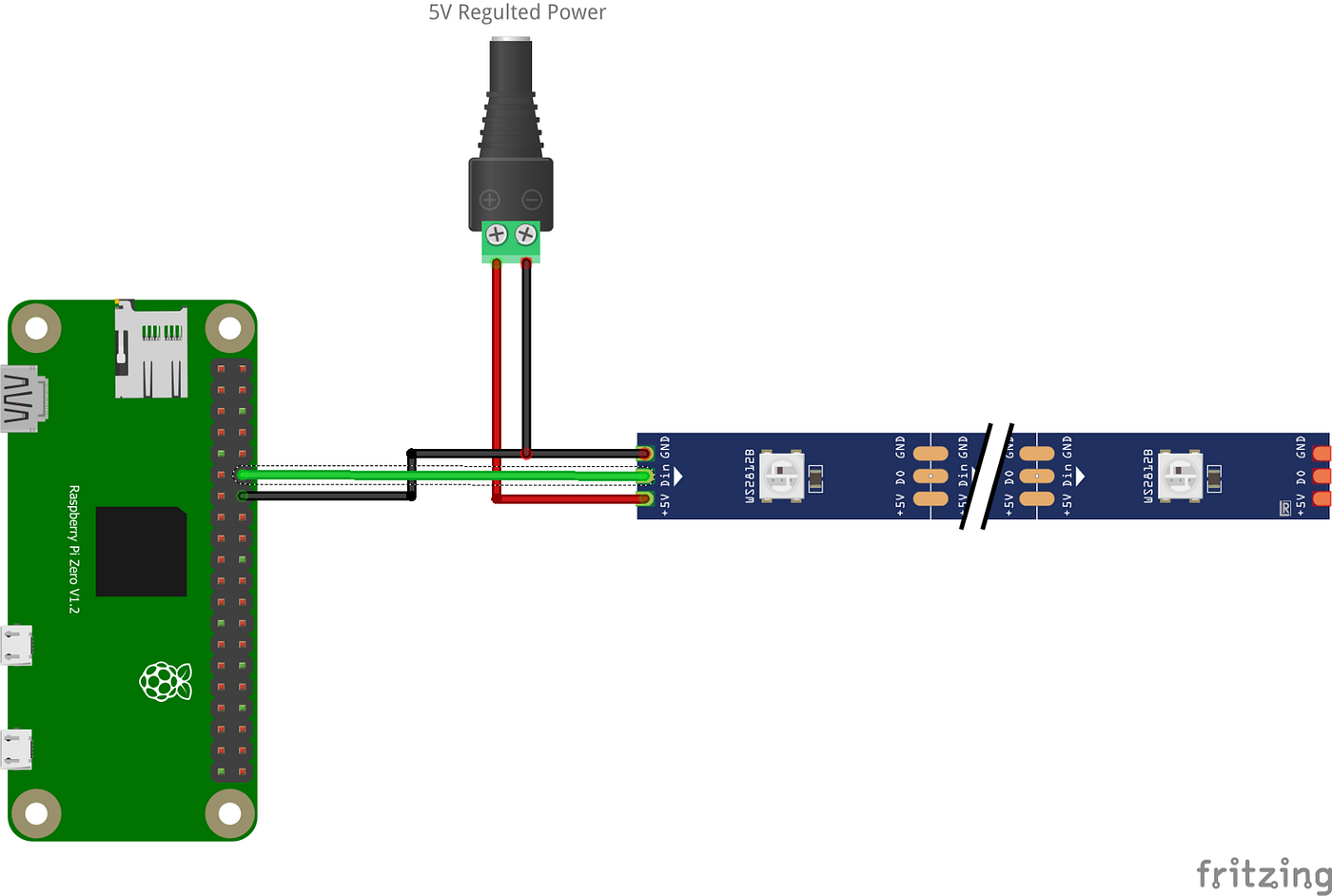
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
1. Flexible Printed Circuit Board (FPCB) – Polyimide Base
Key Properties:
Polyimide-based FPCBs offer excellent thermal stability (up to 260°C), flexibility, and good dielectric properties. They resist moisture and chemicals moderately well but are sensitive to prolonged UV exposure.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: High flexibility allows for curved installations and compact designs; good thermal resistance supports high-brightness LEDs; lightweight and thin, reducing overall product bulk.
– Cons: Higher manufacturing complexity and cost compared to rigid PCBs; moderate mechanical strength may require protective coatings; sensitive to harsh chemicals and UV degradation without additional treatment.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for indoor and semi-protected outdoor environments where flexibility is required, such as architectural lighting or wearable tech. Not recommended for harsh outdoor conditions without encapsulation.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions with high ambient temperatures (Middle East, parts of Africa) should ensure the polyimide material meets local heat resistance standards (e.g., ASTM D2307). Compliance with IPC-2223 for flexible circuits is essential. In Europe, adherence to RoHS and REACH regulations is mandatory. South American markets may require certifications aligning with IEC standards for electrical safety.
2. Rigid Printed Circuit Board (FR4 Epoxy Glass)
Key Properties:
FR4 is a widely used rigid PCB substrate with good mechanical strength, flame retardance (UL94 V-0), and stable electrical insulation. It operates reliably up to 130°C but is inflexible.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Cost-effective and easy to manufacture; robust mechanical support for components; excellent dimensional stability.
– Cons: Lack of flexibility limits design options; heavier and thicker than FPCBs; lower thermal tolerance compared to polyimide.
Impact on Application:
Best suited for fixed installations where rigidity is acceptable, such as signage or industrial control panels. Its durability supports long-term use in controlled environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
FR4 boards are globally standardized, but buyers should verify compliance with IEC 61189 and UL standards, especially for fire safety in regions like Europe and the Middle East. African and South American buyers should confirm local import regulations and certifications to avoid customs delays.
3. Silicone Encapsulation (for LED Strip Coating)
Key Properties:
Silicone provides excellent environmental protection, with high UV resistance, flexibility, and operating temperature range (-60°C to 200°C). It offers superior moisture and chemical resistance.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Enhances durability and lifespan of LED strips; protects against dust, water (IP67/IP68 ratings achievable), and mechanical stress; flexible and lightweight.
– Cons: Adds to manufacturing cost and complexity; can complicate heat dissipation if applied excessively; requires specialized equipment for consistent application.
Impact on Application:
Critical for outdoor, automotive, or industrial LED strip applications where exposure to harsh conditions is expected. Enables use in wet or dusty environments common in African and Middle Eastern markets.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure silicone coatings meet regional environmental and safety standards (e.g., REACH in Europe, GCC GSO standards in the Middle East). For African and South American markets, certifications related to IP ratings and chemical safety should be verified. Additionally, consider local climate factors to select silicone grades optimized for UV and heat resistance.
4. Aluminum PCB Substrate
Key Properties:
Aluminum PCBs offer excellent thermal conductivity (up to 2 W/mK), mechanical strength, and electrical insulation through a thin dielectric layer. They operate well in high-temperature environments.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Superior heat dissipation extends LED lifespan and performance; robust and durable; relatively low cost compared to other metal substrates.
– Cons: Heavier than FPCB and FR4; less flexible, limiting design versatility; requires careful handling to prevent short circuits.
Impact on Application:
Highly suitable for high-power LED strips where heat management is critical, such as industrial lighting or outdoor displays. The aluminum base helps maintain LED efficiency and prevents thermal degradation.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with ASTM B209 for aluminum quality and IPC-4101 for PCB materials is important. European buyers should check for RoHS compliance and thermal management certifications. In regions like the Middle East and South America, aluminum PCBs are favored for their durability in hot climates, but buyers should ensure supply chain reliability and local support for thermal design expertise.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Drive LED Strip with Raspberry Pi 4
| Material | Typical Use Case for drive led strip with raspberry pi 4 | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyimide FPCB | Flexible LED strips for curved or wearable applications | High thermal stability and flexibility | Higher cost and moderate chemical sensitivity | High |
| FR4 Rigid PCB | Fixed installations like signage and industrial control panels | Cost-effective and mechanically robust | Inflexible and lower thermal tolerance | Low |
| Silicone Encapsulation | Outdoor or harsh environment LED strips requiring protection | Excellent environmental resistance and flexibility | Adds manufacturing complexity and cost | Medium |
| Aluminum PCB Substrate | High-power LED strips needing efficient heat dissipation | Superior thermal management and durability | Heavier and less flexible | Medium |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for drive led strip with raspberry pi 4
Manufacturing a drive LED strip integrated with a Raspberry Pi 4 involves a meticulous multi-stage process that combines electronic component preparation, precision assembly, and stringent quality assurance to ensure product reliability and performance. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from emerging and established markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these manufacturing stages and quality control (QC) protocols is essential for selecting trustworthy suppliers and ensuring compliance with global standards.
Key Manufacturing Stages and Techniques
1. Material Preparation
This foundational stage involves sourcing and preparing raw materials critical for both the LED strip and the Raspberry Pi integration. Materials include:
- PCB substrates for LED strips, typically flexible or rigid printed circuit boards with copper traces.
- LED components such as WS2812B or similar addressable LEDs, resistors, capacitors, and connectors.
- Raspberry Pi 4 modules or compatible single-board computers.
- Wiring harnesses, solder, and protective coatings.
Material quality directly impacts longevity and performance. Suppliers often verify incoming components through Incoming Quality Control (IQC), checking parameters like electrical characteristics and physical integrity.
2. Forming and Fabrication
This stage transforms raw materials into components ready for assembly:
- PCB fabrication using photolithography and etching to create precise circuit patterns.
- Solder paste application via stencil printing on PCB pads.
- Pick-and-place machines position LEDs and electronic components on the PCB with high accuracy.
- Reflow soldering solidifies solder joints to ensure mechanical and electrical connections.
- For Raspberry Pi 4, pre-assembled modules are prepared and tested separately before integration.
Advanced manufacturing facilities employ automated optical inspection (AOI) post-reflow to detect soldering defects such as bridges or cold joints.
3. Assembly and Integration
Assembly involves connecting the LED strip to the Raspberry Pi 4 and any additional circuitry for power regulation and control:
- Manual or automated wire harness assembly ensures secure connections between LED strips and Raspberry Pi GPIO pins.
- Encapsulation or conformal coating may be applied for moisture and dust protection, critical for outdoor or industrial applications.
- Integration testing verifies correct GPIO pin mapping, power supply stability, and initial LED control functionality using test scripts (e.g., Python programs controlling LEDs).
4. Finishing and Packaging
Final finishing includes:
- Applying protective casings or enclosures to safeguard the Raspberry Pi and circuitry.
- Labeling with compliance marks and serial numbers.
- Packaging designed to minimize electrostatic discharge (ESD) risks and physical damage during transit.
Quality Assurance and Control Frameworks
International and Industry Standards
- ISO 9001:2015 – The global benchmark for quality management systems, ensuring consistent manufacturing quality and continual improvement.
- CE Marking – Mandatory for products sold in the European Economic Area, covering safety, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), and environmental directives.
- RoHS Compliance – Restricts hazardous substances in electronic components, essential for environmental and regulatory adherence.
- UL Certification – Especially relevant for power supplies and electrical safety in North America but increasingly recognized globally.
- API or Industry-Specific Standards – Depending on end-use (e.g., automotive, industrial automation), additional certifications may be required.
Quality Control Checkpoints
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Verifies raw materials and components before production begins to prevent defective inputs.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous inspection during manufacturing stages, including solder joint inspection, component placement accuracy, and assembly integrity.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive functional testing of the fully assembled product, including:
-
Electrical tests for continuity, short circuits, and correct voltage levels.
- Functional tests running LED control scripts on the Raspberry Pi to verify responsiveness and color accuracy.
- Environmental stress tests such as thermal cycling and humidity exposure to validate durability.
- Visual inspection for physical defects or cosmetic issues.
Testing Methods
- Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): Detects soldering and component placement defects.
- Functional Testing with Custom Software: Scripts in Python or C++ simulate typical LED control scenarios to ensure hardware-software integration.
- Burn-in Testing: Prolonged operation under load to identify early-life failures.
- EMC Testing: Ensures electromagnetic emissions and immunity meet regulatory limits, critical for CE marking.
How B2B Buyers Can Verify Supplier Quality
1. Factory Audits and Site Visits
International buyers should conduct or commission third-party audits focusing on:
- Production capability and equipment sophistication.
- Quality management system compliance with ISO 9001.
- Traceability of components and process documentation.
- Worker training and ESD handling procedures.
2. Reviewing Quality Documentation
Request and analyze:
- Certificates of conformity (CoC) for components and finished goods.
- Test reports including AOI results, functional test logs, and environmental stress test outcomes.
- Process control documents such as SPC (Statistical Process Control) charts.
3. Third-Party Inspections and Testing
Engage independent labs or inspection agencies to:
- Perform random sampling and batch testing.
- Verify compliance with international standards.
- Provide unbiased reports to facilitate import clearance and reduce risks.
QC and Certification Nuances for Diverse International Markets
Africa and South America
These markets often face challenges like variable customs regulations and infrastructure constraints. Buyers should:
- Prioritize suppliers with globally recognized certifications (ISO, CE) to ease import and distribution.
- Ensure packaging meets transit durability needs considering local climate and logistics.
- Consider suppliers offering localized technical support and documentation in relevant languages.
Middle East (e.g., Saudi Arabia)
Regulatory environments are evolving with emphasis on safety and sustainability:
- Compliance with GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council) standards may be required alongside CE and RoHS.
- Suppliers must demonstrate robust EMC and safety testing given the electrically sensitive environments.
- Certifications should be accompanied by Halal compliance documentation if applicable in specific use cases.
Europe and Vietnam
European buyers demand stringent adherence to EU directives:
- Confirm full CE marking compliance, including REACH and WEEE directives.
- Verify traceability and supplier transparency under the EU’s strict regulatory framework.
- Vietnam’s growing manufacturing sector benefits from suppliers with ISO and industry-specific certifications, ensuring exports meet global standards.
In Summary, for B2B buyers investing in drive LED strips integrated with Raspberry Pi 4, a deep understanding of the manufacturing workflow, rigorous quality assurance protocols, and regional certification requirements is critical. Engaging with suppliers who demonstrate transparent QC processes, hold internationally recognized certifications, and provide comprehensive testing documentation will mitigate risks and ensure product excellence across diverse global markets.
Related Video: LED Light Making Process | How LED Lights Made Inside Factory | Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for drive led strip with raspberry pi 4 Sourcing
Breakdown of Cost Components for Drive LED Strip with Raspberry Pi 4
When sourcing a drive LED strip integrated with a Raspberry Pi 4 for B2B applications, understanding the cost structure is essential to optimize procurement and negotiate effectively. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: This covers the LED strip itself (typically WS2812B or similar fully addressable RGB LEDs), the Raspberry Pi 4 board, resistors, connectors, wiring, and PCB materials. Material costs fluctuate based on LED node density (e.g., 30, 60, 144 LEDs/meter), Raspberry Pi model variant (2GB, 4GB RAM), and quality certifications such as RoHS or CE compliance.
-
Labor: Assembly and testing labor costs depend on the manufacturing location and complexity of integration. Manual soldering of LED strips, GPIO pin wiring, and software flashing require skilled technicians. Labor rates vary significantly across regions, with Southeast Asia generally offering competitive costs compared to Europe or the Middle East.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes factory utilities, equipment depreciation, quality control (QC) infrastructure, and indirect labor. Overhead rates are influenced by factory scale, automation level, and local operating expenses.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for custom PCB fabrication, LED strip cutting, and enclosure molding can be significant but amortized over large production runs. For highly customized solutions (e.g., waterproof LED strips, specialized connectors), tooling expenses rise.
-
Quality Control: QC involves inspection of electrical connections, functionality testing of LED control via Raspberry Pi GPIO pins, and software validation. Certified suppliers may charge a premium for documented QC processes and certifications.
-
Logistics: International shipping, customs duties, import taxes, and warehousing costs vary by destination. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, logistics can represent 10-20% of landed cost due to variable freight options and customs clearance complexities.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build in a margin of 10-30% depending on order volume, customization level, and market competition.
Key Price Influencers to Consider
-
Order Volume / Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger volumes drastically reduce per-unit costs due to economies of scale and better tooling amortization. MOQ thresholds often start around 100 units but can vary. Buyers should balance volume discounts against inventory carrying costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized firmware, LED density, waterproofing, and enclosure design increase costs. Standardized modules with minimal customization offer the best price efficiency.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: Premium-grade Raspberry Pi 4 boards (official vs. clones), high-quality LED strips, and certified components increase cost but improve reliability and reduce long-term failures.
-
Supplier Location and Reliability: Suppliers closer to the buyer’s region can lower logistics and lead times. Verified suppliers with ISO certifications and robust QC processes may charge a premium but reduce risk.
-
Incoterms: Understanding trade terms (FOB, CIF, DDP) impacts who pays for shipping, insurance, and customs duties. Choosing the right Incoterm can optimize cash flow and reduce hidden costs.
Practical Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency and Negotiation
-
Negotiate on MOQ and Payment Terms: Especially in emerging markets such as Vietnam or Saudi Arabia, suppliers may be willing to reduce MOQ or offer flexible payment terms to secure long-term partnerships.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond unit price to include warranty, after-sales support, shipping reliability, and potential downtime costs from quality issues.
-
Leverage Regional Trade Agreements: Buyers in Europe or the Middle East should explore preferential trade agreements to reduce tariffs and customs delays.
-
Request Detailed Cost Breakdown: Transparent suppliers provide insight into material, labor, and overhead costs, enabling targeted negotiations.
-
Plan for Logistics and Customs Delays: Factor in buffer time and costs for customs clearance, especially for African and South American markets where import processes can be slower.
-
Consider Bundled Procurement: Combining drive LED strips with Raspberry Pi 4 and accessories in a single order can yield better pricing and simplify supply chain management.
-
Verify Supplier Certifications: Prioritize suppliers with relevant certifications (ISO 9001, CE, RoHS) to ensure component quality and compliance with regional standards.
Indicative Pricing Disclaimer
Prices for drive LED strips integrated with Raspberry Pi 4 vary widely based on volume, customization, and supplier location. As a rough benchmark, small batch orders (under 100 units) may range from $25 to $50 per unit, while large volume orders (above 1,000 units) can see prices as low as $15 to $20 per unit. These figures are indicative and should be validated with multiple suppliers considering current market conditions and specific buyer requirements.
By carefully analyzing these cost drivers and market factors, international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can make informed sourcing decisions, negotiate favorable terms, and optimize their procurement strategy for drive LED strips with Raspberry Pi 4 integration.
Spotlight on Potential drive led strip with raspberry pi 4 Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘drive led strip with raspberry pi 4’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for drive led strip with raspberry pi 4
Critical Technical Properties for Driving LED Strips with Raspberry Pi 4
-
Operating Voltage and Current Requirements
LED strips compatible with Raspberry Pi 4 typically operate at 5V DC, matching the Pi’s power output capabilities. However, power consumption varies by LED density and length; for example, WS2812B strips can draw up to 60mA per LED at full brightness. Understanding the current draw is vital for selecting appropriate power supplies and avoiding damage to the Raspberry Pi or LED strips. International buyers should verify voltage compatibility to ensure safe integration with local power standards. -
LED Type and Addressability
The most common LED strips used with Raspberry Pi are fully addressable RGB LEDs (e.g., WS2812B). Each LED node contains an integrated driver IC allowing independent color and brightness control. This property enables sophisticated lighting effects and animations, crucial for applications such as digital signage, architectural lighting, and interactive displays. Buyers must confirm the LED strip supports the Raspberry Pi’s GPIO communication protocols (usually via a single data line). -
LED Node Density (LEDs per Meter)
LED strips come in various densities, such as 30, 60, or 144 LEDs per meter. Higher density means finer resolution and smoother lighting effects but also increases power consumption and cost. When sourcing, consider the trade-off between visual quality and budget, as well as the intended application environment (e.g., indoor vs. outdoor). -
Signal Protocol and Timing
Addressable LED strips use precise digital signal protocols (e.g., one-wire data transmission for WS2812B) with strict timing requirements. The Raspberry Pi 4’s GPIO pins can handle these protocols via software libraries, but buyers should ensure the LED strip’s protocol is supported by available Raspberry Pi drivers and firmware. This compatibility impacts development time and system reliability. -
Material and Environmental Ratings
LED strips are typically mounted on flexible PCBs with varying degrees of waterproofing (IP rating) and temperature tolerance. For outdoor or harsh environments common in parts of Africa, South America, and the Middle East, selecting strips with appropriate IP65 or higher ratings is essential to ensure durability and reduce maintenance costs. -
Connector and Wiring Standards
The physical interface between the Raspberry Pi and LED strip involves GPIO pins, power lines, and sometimes level shifters or amplifiers. Understanding connector types (e.g., JST, Dupont) and wiring conventions is important for integration and serviceability. Clear specification of wiring diagrams and pin assignments can prevent costly errors during installation.
Key Trade Terminology for International B2B Transactions
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce parts or products used in another company’s end product. For LED strips and Raspberry Pi solutions, OEMs may manufacture custom LED modules or Raspberry Pi-based controllers tailored to buyer specifications. Engaging OEMs can offer cost advantages and customization but requires careful quality control. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell. MOQs for LED strips and Raspberry Pi kits vary widely depending on manufacturer scale and customization. B2B buyers from emerging markets should negotiate MOQs to balance inventory risk and cost efficiency, especially when testing new products or launching pilot projects. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal document issued by buyers to suppliers requesting price and delivery information for specified products and quantities. Crafting precise RFQs that include technical specifications (e.g., LED type, voltage, IP rating) and compliance requirements (e.g., CE, RoHS) accelerates supplier response and reduces misunderstandings. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce defining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international shipments. Common terms include FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight). Understanding Incoterms helps buyers from different regions clarify shipping costs, risk transfer points, and customs duties. -
Lead Time
The total time from order placement to product delivery. Lead times for LED strips and Raspberry Pi accessories can be affected by manufacturing complexity, customization, and global supply chain conditions. Buyers should factor in lead times for production, shipping, and customs clearance when planning projects. -
Compliance Certifications
Certifications such as CE (Europe), FCC (USA), and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) ensure products meet regional safety and environmental standards. For international buyers, verifying these certifications is crucial to avoid regulatory issues and facilitate smooth market entry.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms empowers international B2B buyers to make informed decisions, optimize procurement, and streamline integration of Raspberry Pi-driven LED strip solutions tailored to their regional market needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the drive led strip with raspberry pi 4 Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for drive LED strips integrated with Raspberry Pi 4 platforms is expanding rapidly, driven by increasing demand for customizable, energy-efficient lighting solutions across industrial, commercial, and smart infrastructure applications. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this sector offers significant opportunities due to growing investments in automation, IoT deployments, and digital transformation initiatives.
Key market drivers include:
- Customization and programmability: The Raspberry Pi 4’s advanced processing capabilities enable complex control of LED strips, appealing to sectors requiring dynamic lighting—such as retail displays, architectural lighting, and entertainment.
- Cost-effectiveness: Compared to proprietary lighting controllers, Raspberry Pi-based LED strip solutions reduce hardware costs and facilitate rapid prototyping, which is especially attractive for emerging markets with budget constraints.
- Supply chain diversification: Buyers in Vietnam, Saudi Arabia, and other emerging hubs benefit from a wide supplier base spanning Asia, Europe, and North America, enabling flexible sourcing options and competitive pricing.
- Technological convergence: Integration with sensors, cloud platforms, and AI enhances LED strip applications, creating demand for modular, scalable solutions that are easily programmable via Python or similar languages.
Sourcing trends highlight:
- Preference for fully addressable LED strips such as WS2812B variants, which provide granular control of individual LEDs, allowing for sophisticated lighting effects.
- Increasing adoption of open-source software frameworks and community-driven development to accelerate deployment cycles.
- Shift towards suppliers offering end-to-end support, including hardware customization, firmware updates, and technical training, which is critical for buyers in developing regions.
- Growing interest in local assembly and value-added services to reduce lead times and import duties, especially in the Middle East and Africa.
B2B buyers should closely monitor geopolitical factors, such as trade tariffs and shipping logistics, which can affect component availability and costs. Establishing relationships with suppliers who maintain robust inventory and flexible fulfillment policies is essential to mitigate these risks.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is increasingly pivotal in the procurement of drive LED strips paired with Raspberry Pi 4 controllers. The environmental footprint of LED manufacturing, electronic waste, and energy consumption during operation are critical considerations for international buyers committed to responsible sourcing.
Environmental impact considerations include:
- Material selection: Opting for LED strips manufactured with RoHS-compliant components reduces hazardous substances like lead and mercury. Sourcing from suppliers who use recycled or low-impact materials further enhances sustainability credentials.
- Energy efficiency: LEDs inherently consume less power than traditional lighting; however, choosing high-quality, efficient LED nodes (e.g., WS2812B with optimized power consumption) can significantly lower operational costs and carbon emissions.
- Lifecycle management: Buyers should prioritize suppliers offering take-back programs or designing products for easier disassembly and recycling, helping to minimize e-waste in regions with limited recycling infrastructure.
Ethical sourcing practices are equally important:
- Ensuring supply chains are free from forced labor and conflict minerals aligns with international compliance standards and mitigates reputational risks.
- Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and SA8000 (Social Accountability) can serve as benchmarks when selecting manufacturers.
- Transparency in supplier audits and traceability systems supports buyer due diligence, particularly for companies operating under strict ESG mandates.
For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East, engaging suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability not only fulfills corporate social responsibility goals but also positions their offerings favorably with increasingly eco-conscious end customers.
Evolution and Historical Context
The integration of LED strips with microcontroller platforms has evolved significantly over the past decade. Initially, LED lighting solutions were limited to static color schemes controlled by basic circuitry. The introduction of addressable LED strips such as the WS2812 series revolutionized the market by enabling individual LED control, opening doors to complex animations and interactive lighting.
The Raspberry Pi 4, launched in 2019, brought a substantial upgrade in processing power, memory, and connectivity compared to its predecessors. This enabled more sophisticated programming environments and real-time control capabilities, making it a preferred choice for B2B customers aiming to deploy flexible, programmable LED lighting solutions.
Today, the convergence of affordable, high-performance single-board computers with advanced LED technologies supports a growing ecosystem of developers, manufacturers, and system integrators, fueling innovation in smart lighting across diverse global markets. This historical progression underscores the importance of selecting adaptable, future-proof components in B2B procurement strategies.
Related Video: How to control a WS2812 LED Strip with a Raspberry Pi in Python
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of drive led strip with raspberry pi 4
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers of drive LED strips compatible with Raspberry Pi 4 for international B2B sourcing?
To vet suppliers, focus on verifying their manufacturing capabilities, certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, CE, RoHS), and product quality through samples. Request references from other international clients, especially in regions like Africa, South America, or the Middle East. Evaluate their experience with Raspberry Pi-compatible products and inquire about after-sales support. Utilize third-party inspection services or factory audits to confirm compliance. Online platforms with verified supplier profiles and trade assurance can also mitigate risks in cross-border transactions. -
What customization options are typically available for LED strips driven by Raspberry Pi 4, and how can buyers negotiate them?
Customizations often include LED density per meter, strip length, waterproofing, voltage requirements (5V vs 12V), and software integration for addressable LEDs like WS2812B. Buyers should clearly specify desired GPIO compatibility, color configurations, and control protocols. Early communication about firmware or Python script support is critical. Negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) and pricing based on customization complexity. Suppliers may offer tiered customization packages—request detailed quotes and prototype samples to ensure alignment with your technical and market needs. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs), lead times, and payment terms when sourcing drive LED strips with Raspberry Pi 4 internationally?
MOQs vary widely but generally start from 100 to 500 units depending on customization. Lead times typically range from 3 to 8 weeks, influenced by order size and complexity. Payment terms for international buyers often include a 30% deposit with balance upon shipment or via letter of credit to safeguard both parties. For buyers in Africa, South America, or the Middle East, negotiating flexible payment terms or escrow services can reduce financial risk. Always confirm production schedules and shipping timelines upfront to coordinate inventory and sales planning. -
Which quality assurance processes and certifications should B2B buyers prioritize when purchasing LED strips for Raspberry Pi 4 integration?
Prioritize suppliers with robust quality management systems certified under ISO 9001. Ensure products comply with CE (Europe), RoHS (hazardous substances), and FCC (radio frequency) standards where applicable. For international shipments, certifications such as UL or ETL can also be relevant. Request batch testing reports, including electrical safety and LED lifespan. Insist on pre-shipment inspections or third-party testing, especially for large orders. Documentation supporting compliance facilitates smoother customs clearance and builds confidence in product reliability. -
What logistical considerations should international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe keep in mind when importing drive LED strips with Raspberry Pi 4 compatibility?
Consider port accessibility, customs regulations, and import duties specific to your country. Choose suppliers experienced with shipping to your region and capable of providing Incoterms like FOB, CIF, or DDP depending on your preference for risk and cost allocation. Factor in the need for proper packaging to avoid damage during transit, especially for delicate electronics. Shipping modes (air vs sea) affect lead time and cost; air freight is faster but more expensive. Engage freight forwarders familiar with handling electronics to streamline customs clearance and delivery. -
How should B2B buyers handle disputes or quality issues with suppliers after receiving drive LED strips for Raspberry Pi 4 projects?
Establish clear contract terms covering quality standards, inspection rights, and dispute resolution mechanisms before ordering. Maintain detailed records of communications, purchase orders, and product specifications. If defects or discrepancies arise, document them with photos and test reports, then promptly notify the supplier. Many suppliers offer warranty periods—leverage these to negotiate replacements or refunds. For complex disputes, consider mediation or arbitration clauses. Working with suppliers on long-term relationships encourages cooperative problem-solving rather than adversarial approaches. -
What are the key technical compatibility factors to verify when sourcing LED strips intended for use with Raspberry Pi 4?
Confirm voltage compatibility (typically 5V for Raspberry Pi 4), GPIO pin assignments, and data protocols (e.g., WS2812B uses a specific timing protocol). Check if the LED strip is fully addressable and compatible with Python libraries commonly used on Raspberry Pi, such as rpi_ws281x. Evaluate power requirements and whether an external power supply is necessary for longer strips. Ensure that the supplier provides technical documentation and sample code to facilitate integration and reduce development time. -
How can buyers from emerging markets like Vietnam or Saudi Arabia optimize procurement of drive LED strips with Raspberry Pi 4 for cost efficiency and scalability?
Leverage regional trade agreements to reduce tariffs and import costs. Consolidate orders with other buyers or across product lines to negotiate better MOQs and pricing. Seek suppliers offering modular or scalable LED strip solutions that allow incremental upgrades. Factor in total landed cost, including shipping, customs, and local taxes. Establish local partnerships or distributors to improve after-sales support and reduce logistics complexity. Finally, invest in supplier relationships through regular communication and feedback to unlock volume discounts and priority production slots.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for drive led strip with raspberry pi 4
The integration of drive LED strips with Raspberry Pi 4 platforms presents a compelling opportunity for businesses seeking innovative, customizable lighting solutions. For international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging and diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging the flexibility and programmability of Raspberry Pi-controlled LED strips can significantly enhance product offerings and operational efficiencies.
Key strategic sourcing insights include:
- Prioritizing suppliers who provide high-quality, fully addressable LED strips (e.g., WS2812B) compatible with Raspberry Pi 4 to ensure scalability and customization.
- Evaluating power supply solutions carefully to match LED density and length, optimizing both cost and performance.
- Focusing on vendors with strong technical support and software resources, enabling seamless integration and future-proofing of LED lighting projects.
- Considering regional logistics and supplier reliability to mitigate supply chain risks in international trade contexts.
Looking ahead, the demand for smart, programmable lighting systems is expected to grow, driven by IoT adoption and digital transformation across industries. B2B buyers in regions like Vietnam and Saudi Arabia should actively engage with technology partners who offer both hardware and software expertise, enabling tailored solutions that address local market needs. Embracing strategic sourcing not only reduces costs but also accelerates innovation cycles, positioning businesses to lead in the evolving LED and embedded systems landscape.